Abstract
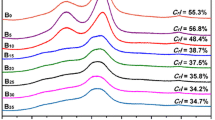
The composition of bamboo shoot shell is similar to hemp fiber, and whose traditional degumming process is expensive and easy to cause serious environmental pollution. Herein, acid pretreatment combined with alkali-oxygen bath degumming process was used to obtain bamboo shoot shell fibers. The effects of the dosages of sodium hydroxide and hydrogen peroxide, soaking temperature and time on degumming were discussed. The optimized process parameters of alkali-oxygen bath degumming were obtained by orthogonal experiment as follows: sodium hydroxide 24 g/L, hydrogen peroxide 40 mL/L, scouring temperature 95 °C and alkali boiling time 150 min. The degumming rate was 72.14%. The degummed fibers were separated from each other in a single fiber state, compared to that the control samples were closely arranged by lots of fibers with rough surface caused by the presence of many non-cellulose components. The crystallinity increased from the control (43.53%) to final fiber (64.35%). The prepared bamboo shoot shell fiber is rich in cellulose (73.19%), which would provide some references for the future application and development of bamboo shoot shell fiber potentially and widely used in many aspects.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Salah B, Djamila H, Samira D et al (2020) Preparation and characterization of novel microstructure cellulosic sawdust material: application as potential adsorbent for wastewater treatment. Cellulose 27:8169–8180
Zheng L, Du Y, Zhang J (2001) Degumming of ramie fibers by alkalophilic bacteria and their polysaccharide-degrading enzymes. Biores Technol 78:89–94
Ye L, Zhang J, Zhao J, Tu S (2014) Liquefaction of bamboo shoot shell for the production of polyols. Biores Technol 153:147–153
Li R, Xu W, Fang L et al (2017) Non-standard test method for glue line shear strength. Wood Res 62:825–830
Lojewska J, Miskowiec P, Lojewski T et al (2005) Cellulose oxidative and hydrolytic degradation: in situ FTIR approach. Polym Degrad Stab 88:512–520
Liu H, He P, He L et al (2018) Structure characterization and hypoglycemic activity of an arabinogalactan from Phyllostachys heterocycla bamboo shoot shell. Carbohydr Polym 201:189–200
Gong W, Ran Z, Ye F, Zhao G (2017) Lignin from bamboo shoot shells as an activator and novel immobilizing support for α-amylase. Food Chem 228:455–462
Ye L, Zhang J, Zhao J et al (2015) Properties of biochar obtained from pyrolysis of bamboo shoot shell. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 114:172–178
He S, Wang X, Zhang Y et al (2016) Isolation and prebiotic activity of water-soluble polysaccharides fractions from the bamboo shoots (Phyllostachys praecox). Carbohydr Polym 151:295–304
Fan F, Zhu M, Fang K, Xie J et al (2021) Comparative study on enhanced pectinase and alkali-oxygen degummings of sisal fibers. Cellulose 28:8375–8386
Guan Y (2003) Study on a new degumming and bleaching process of hemp with one bath and one step process of alkali-oxygen. Master dessertation of Qingdao University, p 8–20.
Coseri S, Biliuta G, Simionescu BC et al (2013) Oxidized cellulose—survey of the most recent achievements. Carbohydr Polym 93:207–215
Deng L, Geng M, Zhu D et al (2012) Effect of chemical and biological degumming on the adsorption of heavy metal by cellulose xan thogenates prepared from Eichhornia crassipes. Biores Technol 107:41–45
Zhou J, Li Z, Yu C (2017) Property of ramie fiber degummed with Fenton reagent. Fiber Polym 18:1891–1897
Jiang W, Song Y, Liu S et al (2018) A green degumming process of ramie. Ind Crops Prod 120:131–134
Yang Y, Zhu M, Fan F et al (2021) Extraction of bamboo shoot shell fibers by the ultrasound assisted alkali oxygen bath method. Cell Chem Technol 5–6:675–680
Cui Y, Jia M, Liu L et al (2017) Research on the character and degumming process of different parts of ramie fiber. Text Res J 83:2013
Li ZL, Yu CW (2015) The effect of oxidation-reduction potential on the degumming of ramie fibers with hydrogen peroxide. J Tex I 106(11):1251–1261
French AD, Cintrón MS (2013) Cellulose polymorphy, crystallite size, and the segal crystallinity index. Cellulose 20:583–588
Achaby ME, Miri NE, Hannache H et al (2018) Cellulose nanocrystals from miscanthus fibers: insights into rheological, physicochemical properties and polymer reinforcing ability. Cellulose 25:6603–6619
Kian LK, Saba N, Jawaid M et al (2020) Properties and characteristics of nanocrystalline cellulose isolated from olive fiber. Carbohydr Polym 241:116423
Reddy JP, Rhim JW (2018) Extraction and characterization of cellulose microfibers from agricultural wastes of onion and garlic. J Nat Fibers 15:465–473
John MJ, Rajesh DA (2008) Recent developments in chemical modification and characterization of natural fiber-reinforced composites. Polym Compos 29:187–207
Janewit W, Nakorn W, Suneerat P (2008) Product yields and characteristics of rice husk, rice straw and corncob during fast pyrolysis in a drop-tube/fixed-bed reactor. Songklanakarin J Sci Technol 30:393–404
Pelissari FM, Sobral PJA, Menegalli FC (2013) Isolation and characterization of cellulose nanofibers from banana peels. Cellulose 21:417–432
Martins MA, Teixeira EM, Corra AC et al (2011) Extraction and characterization of cellulose whiskers from commercial cotton fibers. J Mater Sci 46:7858–7864
French AD (2014) Idealized powder diffraction patterns for cellulose polymorphs. Cellulose 21(2):885–896
Ibrahim MM, Zawawy WK, Juttke Y et al (2013) Cellulose and microcrystalline cellulose from rice straw and banana plant waste: preparation and characterization. Cellulose 20:2403–2416
Manimaran P, Pitchayya Pillai G, Vignesh V (2020) Characterization of natural cellulosic fibers from nendran banana peduncle plants. Int J Biol Macromol 162:1807–1815
Kabir MM, Wang H, Lau KT, Cardona F (2013) Effects of chemical treatments on hemp fibre structure. Appl Surf Sci 276:13–23
Celebi H, Kurt A (2015) Effects of processing on the properties of chitosan/cellulose nanocrystal films. Carbohydr Polym 133:284–293
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China Youth Fund (51503162); General Project of Hubei Provincial Natural Science Foundation (2016cfb459); National Innovation Training Program for College Students (201910495014); Technical Innovation Program of Hubei Province (2019aaa005); Innovation Training Program for University Students of Hubei Province (s201910495063).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no financial and personal relationships with other people or organizations that can inappropriately influence our work, there is no professional or other personal interest of any nature or kind in any product, service and/or company that could be construed as influencing the position presented in, or the review of the manuscript entitled. This manuscript did not contain any animal studies or human participants’ involvement in the study, which also complies with ethical approval and ethical standards.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Y., Fan, F., Xie, J. et al. Isolation and characterization of cellulosic fibers from bamboo shoot shell. Polym. Bull. 80, 1817–1829 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-022-04158-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-022-04158-6