Abstract
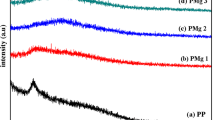
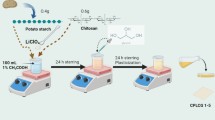
Large-scale energy storage systems with low cost and high performance are needed to allow transition from fossil fuels to renewable energy systems. Solid-state sodium-ion battery is considered as the new generation to replace the commercial lithium-ion battery, due to the abundant sodium resources, cheaper and safer. In this work, new solid polymer electrolyte (SPE) based on corn starch was prepared with a different percentage of sodium bisulfite (NaHSO3) salt via solution casting technique. The SPE was found in an amorphous state and confirmed by using the XRD analyses. The electrical properties of prepared SPE film have been analyzed through electrical impedance spectroscopy and battery analyzer. The highest ionic conductivity is 2.22 × 10–4 Scm−1 at room temperature for a sample containing 15 wt.% NaHSO3 and being used in primary sodium battery fabrication. The cell produced an open circuit voltage of 1.55 V at ambient temperature and discharge characteristics were studied. It is believed that the excellent contribution from the as-prepared electrolyte presents a high potential to be a new innovation in fabrication of energy storage applications.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li Y, Yang J, Song J (2017) Design structure model and renewable energy technology for rechargeable battery towards greener and more sustainable electric vehicle. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 74:19–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.02.021
Muruganantham B, Gnanadass R, Padhy NP (2017) Challenges with renewable energy sources and storage in practical distribution systems. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 73:125–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.01.089
Rayung M, Aung MM, Azhar SC, Abdullah LC, Su’ait MS, Ahmad A, Jamil S (2020) Bio-based polymer electrolytes for electrochemical devices: insight into the ionic conductivity performance. Materials (Basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13040838
Singh R, Bhattacharya B, Gupta M, Rahul Khan ZH, Tomar SK, Singh PK (2017) Electrical and structural properties of ionic liquid doped polymer gel electrolyte for dual energy storage devices. Int J Hydrogen Energy 42(21):14602–14607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2017.04.126
Liu J, Ahmed S, Khanam Z, Wang T, Song S (2020) Ionic liquid-incorporated Zn-Ion conducting polymer electrolyte membranes. Polymers (Basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12081755
Rathnayake RMLL, Perera KS, Vidanapathirana KP (2020) Past, present and future of ionic liquid based polymer electrolytes. AIMS Energy 8(2):231–251. https://doi.org/10.3934/energy.2020.2.231
Hassan MF, Zainuddin SK, Kamarudin KH, Sheng CK, Abdullah MA (2018) Ion-conducting polymer electrolyte films based on poly (sodium 4-styrenesulfonate) complexed with ammonium nitrate: studies based on morphology, structural and electrical spectroscopy. Malaysian J Analytic Sci. https://doi.org/10.17576/mjas-2018-2202-08
Ni’mah YL, Taufik MF, Maezah A, Kurniawan F (2018) Increasing the ionic conductivity of solid state polymer electrolyte using fly ash as a filler. Malaysian J Fundament Appl Sci 14(4):443–447
Aziz SB, Marf AS, Dannoun EMA, Brza MA, Abdullah RM (2020) The study of the degree of crystallinity, electrical equivalent circuit, and dielectric properties of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA)-based biopolymer electrolytes. Polymers. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12102184
Yerin S, Yun-Chae J, Myung-Soo P, Dong-Won K (2020) Solid polymer electrolyte supported by porous polymer membrane for all-solid-state lithium batteries. J Membr Sci 603:117995. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2020.117995
Verma ML, Sahu HD (2017) Study on ionic conductivity and dielectric properties of PEO-based solid nanocomposite polymer electrolytes. Ionics 23(9):2339–2350. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-017-2063-4
Misenan MSM, Khiar ASA (2018) Conductivity, dielectric and modulus studies of Methylcellulose-NH4TF polymer electrolyte. Eurasian J Biol Chem Sci 1(2):59–62
Awang FF, Kamarudin KH, Hassan MF (2020) Employing an electrochemical impedance spectroscopy technique to estimate the ion transport parameters in corn starch based solid polymer electrolyte. Int J Adv Res Eng Innov 2(3):78–88
Hassan MF, Awang FF, Azimi NSN, Sheng CK (2020) Starch/MgSO4 solid polymer electrolyte for zinc carbon batteries and its application in a simple circuit. J Sustain Sci Manag 15(8):1–8
Lian X, Cheng K, Wang D, Zhu W, Wang X (2018) Analysis of crystals of retrograded starch with sharp X-ray diffraction peaks made by recrystallization of amylose and amylopectin. Int J Food Prop 20(sup3):S3224–S3236. https://doi.org/10.1080/10942912.2017.1362433
Shukur, M. F. (2015). Characterization of ion conducting solid bio_polymer electrolytes based on starch-chitosan blend and application in electrochemical devices. University of Malaya, Malaysia, Dissertation
Tiwari T, Srivastava N, Srivastava PC (2013) Ion dynamics study of potato starch + sodium salts electrolyte system. Int J Electrochem 2013:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/670914
Kumar M, Tiwari T, Srivastava N (2012) Electrical transport behaviour of bio-polymer electrolyte system: potato starch+ammonium iodide. Carbohyd Polym 88(1):54–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.11.059
Ramesh S, Shanti R, Morris E, Durairaj R (2013) Utilisation of corn starch in production of ‘green’ polymer electrolytes. Mater Res Innov 15(2):13–18. https://doi.org/10.1179/143307511x13031890747291
Hwang JY, Myung ST, Sun YK (2017) Sodium-ion batteries: present and future. Royal Society of chemistry 46:3485–3856. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6cs00776g
Ozcan S, Guler A, Cetinkaya T, Guler MO, Akbulut H (2017) Freestanding graphene/MnO2 cathodes for Li-ion batteries. Beilstein J Nanotechnol 8:1932–1938. https://doi.org/10.3762/bjnano.8.193
Lu Y, Li L, Zhang Q, Niu Z, Chen J (2018) Electrolyte and interface engineering for solid-state sodium batteries. Joule 2(9):1747–1770. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joule.2018.07.028
Brutti S, Navarra MA, Maresca G, Panero S, Manzi J, Simonetti E, Appetecchi GB (2019) Ionic liquid electrolytes for room temperature sodium battery systems. Electrochim Acta 306:317–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2019.03.139
Abraham KM (2020) How comparable are sodium-ion batteries to lithium-ion counterparts? ACS Energy Lett 5(11):3544–3547. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsenergylett.0c02181
Qiao L, Judez X, Rojo T, Armand M, Zhang H (2020) Review—polymer electrolytes for sodium batteries. J Electrochem Soc. https://doi.org/10.1149/1945-7111/ab7aa0
Maragani N, Vijayakumar K, Krishnajyothi N (2017) Ac conductivity and thermal studies of pan-nafdoped gel polymer electrolytes for solid state battery applications. Rasayan J Chem 10:665–672. https://doi.org/10.7324/rjc.2017.1021697
Mejenom AA, Hafiza MN, Isa MIN (2018) X-ray diffraction and infrared spectroscopic analysis of solid biopolymer electrolytes based on dual blend carboxymethyl cellulose-chitosan doped with ammonium bromide. ASM Sci J Special Issue 1:37–46
Li X, Yang L, Shao D, Luo K, Liu L, Wu Z, Wang X (2019) Preparation and application of poly(ethylene oxide)-based all solid-state electrolyte with a walnut-like SiO2 as nano-fillers. J Appl Polym Sci. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.48810
Awang FF, Kamarudin KH, Hassan MF (2021) Effect of sodium bisulfite on corn starch solid polymer electrolyte. Malaysian J Analytic Sci 25(2):224–233
Perumal P, Christopher Selvin P, Selvasekarapandian S, Abhilash KP (2019) Bio-host pectin complexed with dilithium borate based solid electrolytes for polymer batteries. Mater Res Express. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab4724
Azli AA, Manan NSA, Aziz SB, Kadir MFZ (2020) Structural, impedance and electrochemical double-layer capacitor characteristics of improved number density of charge carrier electrolytes employing potato starch blend polymers. Ionics 26(11):5773–5804. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-020-03688-1
Kumar KK, Ravi M, Pavani Y, Bhavani S, Sharma AK, Narasimha Rao VVR (2014) Investigations on PEO/PVP/NaBr complexed polymer blend electrolytes for electrochemical cell applications. J Membr Sci 454:200–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2013.12.022
Shahrudin S, Ahmad AH (2016) Corn starch based biopolymer electrolyte doped with Na3PO4. Science Letters 10(2):26–30
Hassan MF, Noruddin N (2018) The effect of lithium perchlorate on poly (sodium 4-styrenesulfonate): studies based on morphology, structural and electrical conductivity. Mater Phys Mech 36:8–17. https://doi.org/10.18720/MPM.3612018_2
Amran NNA, Manan NSA, Kadir MFZ (2016) The effect of LiCF3SO3 on the complexation with potato starch-chitosan blend polymer electrolytes. Ionics 22(9):1647–1658. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-016-1684-3
Hassan MF, Azimi NSN (2019) Conductivity and transport properties of starch/glycerin-MgSO4 solid polymer electrolytes. Int J Adv Appl Sci 6(5):38–43. https://doi.org/10.21833/ijaas.2019.05.007
Awang FF, Hassan MF, Chan KS, Kamarudin KH (2021) Ion transport study in corn starch-nahso3 based polymer electrolytes. Scientif Res J 18(2):17–36. https://doi.org/10.24191/srj.v18i2.11985
Dave G, Kanchan DK (2018) Dielectric relaxation and modulus studies of PEO-PAM blend based sodium salt electrolyte system. Indian J Pure Appl Phys 56:978–988
Bhide A, Hariharan K (2006) A new polymer electrolyte system (PEO)n:NaPO3. J Power Sourc 159(2):1450–1457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2005.11.096
Anantha P, Hariharan K (2005) Physical and ionic transport studies on poly(ethylene oxide)?NaNO polymer electrolyte system. Solid State Ionics 176(1–2):155–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssi.2004.07.006
Shukur MF, Kadir MFZ (2015) Hydrogen ion conducting starch-chitosan blend based electrolyte for application in electrochemical devices. Electrochim Acta 158:152–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2015.01.167
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to say thank you to the Ministry of Higher Education for the financial support via grant FRGS/1/2019/STG02/UMT/02/1, Vot No. (59586) and Faculty of Science and Marine Environment, University Malaysia Terengganu for the technical support for this research work to be completed.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Awang, F.F., Hassan, M.F. & Kamarudin, K.H. Investigation of structural and electrical properties of a biopolymer materials with its potential application in solid-state batteries. Polym. Bull. 80, 1463–1476 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-022-04124-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-022-04124-2