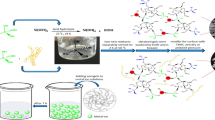
Abstract
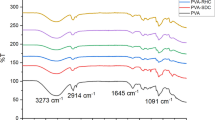
Three bio-based aerogels were prepared using a cross-linked blend of gelatin and different ratios of poly(amidoamine) hyperbranched polymer (PAMAM) via freeze-drying technique. These aerogels are assigned as cGel/PAM 1, cGel/PAM 2, and cGel/PAM 3. Aerogel of cross-linked gelatin cGel was prepared for comparison. The fabricated aerogels were characterized using FT-IR and determination of their nitrogen content. The macro-porous structures and the surface areas were investigated using the scanning electron microscope, Brunauer, Emmett and Teller (BET), and Barrett, Joyner, and Halenda (BJH) equations. The adsorption efficiencies of heavy metal ions Cr(VI) and Cd(II) were assessed in terms of the contact time and dose-effect. The adsorption results of the heavy metal ions were fitted using Freundlich and Langmuir models. The adsorption isotherm data of cGel/PAM 3 aerogel are well fitted using Langmuir model (R2 = 0.99 and 0.981) and adsorption capacity (qmax) 125.0 and 142.0 mg/g for Cr(VI) and Cd(II) ions, respectively. Freundlich model (R2 = 0.989 and 0.986 for Cr(VI) and Cd(II) ions, respectively) has been fitted with the adsorption results. The well-fitting of the Freundlich adsorption isotherm demonstrates the favorable adsorption using this promising aerogel that contains active sites with different energies. The aerogel cGel/PAM 3 was showed the highest adsorption efficiency of 98% using a 1 g/L dose within 60 min.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nada AA, Abdellatif FHH, Soliman AAF, Shen J, Hudson SM, Abou-Zeid NY (2019) Fabrication and bioevaluation of a medicated electrospun mat based on azido-cellulose acetate via click chemistry. Cellulose 26(18):9721–9736
Ahmed HM, Abdellatif MM, Ibrahim S, Abdellatif FHH (2019) Mini-emulsified Copolymer/Silica nanocomposite as effective binder and self-cleaning for textiles coating. Prog Org Coat 129:52–58
Masaki Y (2016) Characteristics of industrial wastewater discharged from industrialized provinces and specific industrial sectors in china based on the official statistical reports. J Novel Carbon Resour Sci Green Asia Strategy 3(2):59–67
Abdellatif MM, Ibrahim S, Nomura K (2020) Efficient and eco-friendly low-molecular-weight gelators based on L-phenylalanine as promising remediation tool for oil pollution. J King Saud Univ Sci 32(1):946–951
Ibrahim S, Abdellatif MM (2019) Multilayer flexible packaging materials: relationship between structure and functional properties. Egypt J Chem 62(10):1963–1969
Sarkar B (2002) Heavy metals in the environment, 1st edn. CRC Press
Abdellatif FHH, Babin J, Arnal-Herault C, David L, Jonquieres A (2018) Grafting cellulose acetate with ionic liquids for biofuel purification membranes: influence of the anion. Carbohydr Polym 196:176–186
Abdellatif FHH, Babin J, Arnal-Herault C, Nouvel C, Six JL, Jonquieres A (2017) Bio-based membranes for ethyl tert-butyl ether (ETBE) bio-fuel purification by pervaporation. J Membr Sci 524:449–459
Rajasulochana P, Preethy V (2016) Comparison on efficiency of various techniques in treatment of waste and sewage water—a comprehensive review. Resour Effic Technol 2(4):175–184
Fu F, Wang Q (2011) Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewaters: a review. J Environ Manag 92(3):407–418
Kinuthia GK, Ngure V, Beti D et al (2020) Levels of heavy metals in wastewater and soil samples from open drainage channels in Nairobi, Kenya: community health implication. Sci Rep 10:8434
Abdellatif FHH, Abdellatif MM (2020) Bio-based i-carrageenan aerogels as efficient adsorbents for heavy metal ions and acid dye from aqueous solution. Cellulose 27(1):441–453
Abdellatif MM, Soliman SMA, El-Sayed NH, Abdellatif FHH (2020) Iota-carrageenan based magnetic aerogels as an efficient adsorbent for heavy metals from aqueous solutions. J Porous Mater 27(1):277–284
Ibrahim NA, Eid BM, Abdellatif FHH (2018) Advanced materials and technologies for antimicrobial finishing of cellulosic textiles. In: Handbook of renewable materials for coloration and finishing. Wiley, pp 303–356
Abdellatif FHH, Babin J, Arnal-Herault C, Jonquieres A (2015) Grafting of cellulose and cellulose derivatives by cuaac click chemistry. In: Cellulose-based graft copolymers: structure and chemistry. CRC Press, pp 568–597
Godiya CB, Cheng X, Li D, Chen Z, Lu X (2019) Carboxymethyl cellulose/polyacrylamide composite hydrogel for cascaded treatment/reuse of heavy metal ions in wastewater. J Hazard Mater 364:28–38
Liu Z, Wang H, Liu C, Jiang Y, Yu G, Mu X, Wang X (2012) Magnetic cellulose-chitosan hydrogels prepared from ionic liquids as reusable adsorbent for removal of heavy metal ions. Chem Commun 48(59):7350–7352
Pourjavadi A, Amini-Fazl MS, Barzegar S (2008) Optimization of synthesis conditions of a novel carrageenan-based superabsorbent hydrogel by Taguchi method and investigation of its metal ions adsorption. J Appl Polym Sci 107(5):2970–2976
Xia L, Huang Z, Zhong L, Xie F, Tang CY, Tsui CP (2018) Bagasse cellulose grafted with an amino-terminated hyperbranched polymer for the removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution. Polymers 10(8):931
Budtova T, Aguilera DA, Beluns S et al (2020) Biorefinery approach for aerogels. Polymers 12(12):2779
Bo S, Ren W, Lei C, Xie Y, Cai Y, Wang S, Gao J, Ni Q, Yao J (2018) Flexible and porous cellulose aerogels/zeolitic imidazolate framework (ZIF-8) hybrids for adsorption removal of Cr(IV) from water. J Solid State Chem 262:135–141
Li J, Zuo K, Wu W, Xu Z, Yi Y, Jing Y, Dai H, Fang G (2018) Shape memory aerogels from nanocellulose and polyethyleneimine as a novel adsorbent for removal of Cu(II) and Pb(II). Carbohydr Polym 196:376–384
Guo D, An Q, Xiao Z, Zhai S, Yang D (2018) Efficient removal of Pb(II), Cr(VI) and organic dyes by polydopamine modified chitosan aerogels. Carbohydr Polym 202:306–314
Lei C, Gao J, Ren W, Xie Y, Abdalkarim S, Wang S, Ni Q, Yao J (2019) Fabrication of metal-organic frameworks@cellulose aerogels composite materials for removal of heavy metal ions in water. Carbohydr Polym 205:35–41
Ebisike K, Okoronkwo A, Alaneme K (2019) Adsorption of Cd (II) on chitosan-silica hybrid aerogel from aqueous solution. Environ Technol Innov 14:100337
Guo D, An Q, Xiao Z, Zhai S, Shi Z (2017) Polyethylenimine-functionalized cellulose aerogel beads for efficient dynamic removal of chromium(VI) from aqueous solution. RSC Adv 7(85):54039–54052
Sabaa MW, Mohamed ME, Abdellatif MM, Soliman SMA (2020) Antibacterial effect of novel grafted gelatin on gram-negative bacteria. Polym Bull 77(1):427–440
Jiao C, Li T, Wang J, Wang H, Zhang X, Han X, Du Z, Shang Y, Chen Y (2020) Efficient removal of dyes from aqueous solution by a porous sodium alginate/gelatin/graphene oxide triple-network composite aerogel. J Polym Environ 28(5):1492–1502
Hui B, Zhang Y, Ye L (2015) Structure of PVA/gelatin hydrogel beads and adsorption mechanism for advanced Pb(II) removal. J Ind Eng Chem 21:868–876
Wang J, Zhao D, Shang K, Wang YT, Ye DD, Kang AH, Liao W, Wang YT (2016) Ultrasoft gelatin aerogels for oil contaminant removal. J Mater Chem A 4(24):9381–9389
Cui L, Xiong Z, Guo Y, Liu Y, Jincha Z, Zhang C, Zhu P (2015) Fabrication of interpenetrating polymer network chitosan/gelatin porous materials and study on dye adsorption properties. Carbohydr Polym 132:330–337
Dil NN, Sadeghi M (2018) Free radical synthesis of nanosilver/gelatin-poly (acrylic acid) nanocomposite hydrogels employed for antibacterial activity and removal of Cu(II) metal ions. J Hazard Mater 351:38–53
Ibrahim S, Voit B (2009) Synthesis and characterization of well-defined block copolymers by combing controlled radical and cationic polymerization. Macromol Symp 275–276(1):59–66
Ahmad K, Nazir MA, Qureshi AK et al (2020) Engineering of Zirconium based metal-organic frameworks (Zr-MOFs) as efficient adsorbents. Mater Sci Eng B 262:114766
Shah HUR, Ahmad K, Naseem HA et al (2021) Water stable graphene oxide metal-organic frameworks composite (ZIF-67@GO) for efficient removal of malachite green from water. Food Chem Toxicol 154:112312
Ahmad K, Shah HUR, Parveen S et al (2021) Metal Organic Framework (KIUB-MOF-1) as efficient adsorbent for cationic and anionic dyes from brackish water. J Mol Struct 1242:130898
Khan NA, Najam T, Shah SSA et al (2020) Development of Mn-PBA on GO sheets for adsorptive removal of ciprofloxacin from water: kinetics, isothermal, thermodynamic and mechanistic studies. Mater Chem Phys 245:122737
Ahmad K, Shah HUR, Ashfaq M et al (2021) Effect of metal atom in zeolitic imidazolate frameworks (ZIF-8 & 67) for removal of Pb2+ & Hg2+ from water. Food Chem Toxicol 149:112008
Ahmad K, Shah HUR, Naseem HA et al (2021) Synthesis and characterization of water stable polymeric metallo organic composite (PMOC) for the removal of arsenic and lead from brackish water. Toxin Rev. https://doi.org/10.1080/15569543.2021.1919902
Ayub A, Irfan A, Raza ZA et al (2021) Development of poly(1-vinylimidazole)-chitosan composite sorbent under microwave irradiation for enhanced uptake of Cd(II) ions from aqueous media. Polym Bull. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-020-03523-7
Adams CI, Spaulding GH (1955) Determination of organic nitrogen by Kjeldahl method without distillation. Anal Chem 27(6):1003–1004
Liang C et al (2018) ZIF-67 derived hollow cobalt sulfide as superior adsorbent for effective adsorption removal of ciprofloxacin antibiotics. Chem Eng J 344:95–104
Khan NA, Najam T, Shah SSA et al (2020) Development of Mn-PBA on GO sheets for adsorptive removal of ciprofloxacin from water: kinetics, isothermal, thermodynamic and mechanistic studies. Mater Chem Phys 245:122737
Lata S, Singh PK, Samadder SR (2015) Regeneration of adsorbents and recovery of heavy metals: a review. Int J Environ Sci Technol 12:1461–1478
Tseng JY, Chang CY, Chang CF et al (2009) Kinetics and equilibrium of desorption removal of copper from magnetic polymer adsorbent. J Hazard Mater 171:370–377
Yingnakhon W, Srikulkit K (2013) A simple quaternization method of hyperbranched polyamidoamine polymer and antimicrobial activity evaluation of cationic hyperbranched polyamidoamine polymer. Asian J Chem 25(7):4009–4012
Nagura M, Yokota H, Ikeura M, Gotoh Y, Ohkoshi Y (2002) Structures and physical properties of cross-linked gelatin fibers. Polym J 34(10):761–766
Cui Z, Beach ES, Anastas PT (2011) Modification of chitosan films with environmentally benign reagents for increased water resistance. Green Chem Lett Rev 4(1):35–40
Yang Y, Wang L, Li S (1996) Formaldehyde-free zein fiber-preparation and investigation. J Appl Polym Sci 59(3):433–441
Uranga J, Nguyen BT, Si TT, Guerrero P, de la Caba K (2020) The effect of cross-linking with citric acid on the properties of agar/fish gelatin films. Polymers 12(2):291
Gregg SJ, Wing KSW, Salzberg HW (1967) Adsorption surface area and porosity. J Electrochem Soc 114:279C
Tan YH, Davis JA, Fujikawa K et al (2012) Surface area and pore size characteristics of nanoporous gold subjected to thermal, mechanical, or surface modification studied using gas adsorption isotherms, cyclic voltammetry, thermogravimetric analysis, and scanning electron microscopy. J Mater Chem 22(14):6733–6745
Brunauer S, Emmett PH, Teller E (1938) Adsorption of gases in multimolecular layers. J Am Chem Soc 60(2):309–319
Saha R, Nandi R, Saha B (2011) Sources and toxicity of hexavalent chromium. J Coord Chem 64(10):1782–1806
Costa M, Klein CB (2006) Toxicity and carcinogenicity of chromium compounds in humans. Crit Rev Toxicol 36(2):155–163
Joseph P (2009) Mechanisms of cadmium carcinogenesis. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 238(3):272–279
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdellatif, M.M., Abdellatif, F.H.H. & Ibrahim, S. The utilization of cross-linked gelatin/PAMAM aerogels as heavy metal ions bio-adsorbents from aqueous solutions. Polym. Bull. 79, 10931–10948 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-021-04019-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-021-04019-8