Abstract
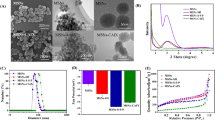
Nano core–shell drug carriers with high stability, low toxicity, and targeted drug delivery are significance for the delivery of anti-tumor drugs. In this study, Albumin from bovine serum (BSA), serving as a capping agent, was conjugated to MSNs via a cleavable disulfide bond to generate a redox-responsive nanocarrier (MSNs@BSA). Subsequently, cRGD peptide, as a targeting ligand, was modified on the particle surface by a protein cross-linker to obtain nanoparticles with tumor cell-targeting properties (RGD-MSNs@BSA). The construction of RGD-MSNs@BSA was confirmed by DLS analysis, scanning electron microscope (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), electron dispersive spectroscopy (EDS), X-Ray Diffraction (XRD), and Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR), respectively. It was displayed that the model anticancer drug doxorubicin (DOX) was efficiently and stably encapsulated in RGD-MSNs@BSA in the absence of glutathione (GSH), and an outbreak of DOX was observed when the particles were exposed to a GSH-containing environment. It demonstrated that disulfide-linked BSA capping can increase the drug loading stability, while enduing it redox sensitivity. Flow cytometry and fluorescence microscope tests displayed that cellular uptake of RGD-MSNs@BSA was much higher than that of particles without cRGD and free DOX. These results indicated that RGD-MSNs@BSA can increase drug tumor-targeting and drug cellular uptake.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Maity AR, Stepensky D (2016) Limited efficiency of drug delivery to specific intracellular organelles using subcellularly “targeted” drug delivery systems. Mol Pharm 13(1):1–7
Zhao H, Feng H, Liu D, Liu J, Ji N, Chen F, Luo X, Zhou Y, Dan H, Zeng X, Li J, Sun C, Meng J, Ju X, Zhou M, Yang H, Li L, Liang X, Chu L, Jiang L, He Y, Chen Q (2015) Self-assembling monomeric nucleoside molecular nanoparticles loaded with 5-FU enhancing therapeutic efficacy against oral cancer. ACS Nano 9(10):9638–9651
Buehler DC, Marsden MD, Shen S, Toso DB, Wu X, Loo JA, Zhou ZH, Kickhoefer VA, Wender PA, Zack JA, Rome LH (2014) Bioengineered vaults: self-assembling protein shell-lipophilic core nanoparticles for drug delivery. ACS Nano 8(8):7723–7732
Peng L, Liu S, Feng A, Yuan J (2017) Polymeric nanocarriers based on cyclodextrins for drug delivery: host-guest interaction as stimuli responsive linker. Mol Pharm 14(8):2475–2486
Lu J, Liong M, Li Z, Zink JI, Tamanoi F (2010) Biocompatibility, biodistribution, and drug-delivery efficiency of mesoporous silica nanoparticles for cancer therapy in animals. Small 6(16):1794–1805
Pan J, Wu R, Dai X, Yin Y, Pan G, Meng M, Shi W, Yan Y (2015) A hierarchical porous bowl-like PLA@MSNs-COOH composite for ph-dominated long-term controlled release of doxorubicin and integrated nanoparticle for potential second treatment. Biomacromol 16(4):1131–1145
Cheng W, Nie J, Xu L, Liang C, Peng Y, Liu G, Wang T, Mei L, Huang L, Zeng X (2017) pH-sensitive delivery vehicle based on folic acid-conjugated polydopamine-modified mesoporous silica nanoparticles for targeted cancer therapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9(22):18462
Liu YL, Wu YH, Tsai WB, Tsai CC, Chen WS, Wu CS (2011) Core–shell silica@chitosan nanoparticles and hollow chitosan nanospheres using silica nanoparticles as templates: preparation and ultrasound bubble application. Carbohyd Polym 84(2):770–774
Giménez C, ITC De, Gorbe M, Aznar E, Sancenón F, Murguía JR, Martínez-Máñez R, Marcos MD, Amorós P (2015) Gated mesoporous silica nanoparticles for the controlled delivery of drugs in cancer cells. Langmuir Acs J Surf Colloids 31(12): 3753
Zhang B, Luo Z, Liu J, Ding X, Li J, Cai K (2014) Cytochrome c end-capped mesoporous silica nanoparticles as redox-responsive drug delivery vehicles for liver tumor-targeted triplex therapy in vitro and in vivo. J Control Release 192(7):192–201
Cheng Y, Zhang AQ, Hu JJ, He F, Zeng X, Zhang XZ (2017) Multifunctional peptide-amphiphile end-capped mesoporous silica nanoparticles for tumor targeting drug delivery. Acs Appl Mater Interfaces 9(3):2093–2103
Hu C, Huang P, Zheng Z, Yang Z, Wang X (2017) A facile strategy to prepare an enzyme-responsive mussel mimetic coating for drug delivery based on mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Langmuir 33(22):5511–5518
Yang Y, Lin Y, Di D, Zhang X, Wang D, Zhao Q, Wang S (2017) Gold nanoparticle-gated mesoporous silica as redox-triggered drug delivery for chemo-photothermal synergistic therapy. J Colloid Interface Sci 508:323–331
Park K, Park SS, Yun YH, Ha CS (2017) Mesoporous silica nanoparticles functionalized with a redox-responsive biopolymer. J Porous Mater 24(5):1–11
Sun JT, Piao JG, Wang LH, Javed M, Hong CY, Pan CY (2013) One-pot synthesis of redox-responsive polymers-coated mesoporous silica nanoparticles and their controlled drug release. Macromol Rapid Commun 34(17):1387–1394
Yu L, Chen Y, Lin H, Du W, Chen H, Shi J (2018) Ultrasmall mesoporous organosilica nanoparticles: morphology modulations and redox-responsive biodegradability for tumor-specific drug delivery. Biomaterials 161:292–305
Thirupathi KRS, Prakash T, Gnanamani A (2017) Redox responsive albumin autogenic nanoparticles for the delivery of cancer drugs. Colloids Surf B 152:393
Lin JT, Du JK, Yang YQ, Li L, Zhang DW, Liang CL, Wang J, Mei J, Wang GH (2017) pH and redox dual stimulate-responsive nanocarriers based on hyaluronic acid coated mesoporous silica for targeted drug delivery. Mater Sci Eng C 81:478
Iyer AK, Khaled G, Fang J, Maeda H (2006) Exploiting the enhanced permeability and retention effect for tumor targeting. Drug Discov Today 11(17):812–818
Choi DS, Jin HE, Yoo SY, Lee SW (2014) Cyclic RGD peptide incorporation on phage major coat proteins for improved internalization by HeLa cells. Bioconjug Chem 25(2):216
Sun YX, Zeng X, Meng QF, Zhang XZ, Cheng SX, Zhuo RX (2008) The influence of RGD addition on the gene transfer characteristics of disulfide-containing polyethyleneimine/DNA complexes. Biomaterials 29(32):4356–4365
Estelrich J, Busquets MA, Morán MDC (2017) Effect of PEGylation on ligand-targeted magnetoliposomes: a missed goal. ACS Omega 2(10):6544–6555
Xu F, Liu J, Tian J, Gao L, Cheng X, Pan Y, Sun Z, Li X (2016) Supramolecular self-assemblies with nanoscale RGD clusters promote cell growth and intracellular drug delivery. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8(44):29906
Hao N, Liu H, Li L, Chen D, Li L, Tang F (2012) In vitro degradation behavior of silica nanoparticles under physiological conditions. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 12(8):6346
Kosmulski M (2002) The pH-dependent surface charging and the points of zero charge. J Colloid Interface Sci 253(1):77–87
Winiewska M, Szewczuk-Karpisz K, Sternik D (2015) Adsorption and thermal properties of the bovine serum albumin–silicon dioxide system. J Therm Anal Calorim 120(2):1355–1364
Sah BK, Das K, Kundu S (2019) pH-dependent structure, pattern and hysteresis behaviour of lipid (DMPA)-protein (BSA) monolayer complex. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 579:123663
Wang B, Zhou Y, Li L, Wang Y (2018) Preparation of amidoxime-functionalized mesoporous silica nanospheres (ami-MSN) from coal fly ash for the removal of U(VI). Sci Total Environ 626:219–227
Barman SC, Hossain MF, Yoon H, Park JY (2018) Trimetallic Pd@Au@Pt nanocomposites platform on –COOH terminated reduced graphene oxide for highly sensitive CEA and PSA biomarkers detection. Biosens Bioelectron 100:16–22
Yu J, Wang G, Wang X, Xu Y, Chen S, Wang X, Jiang L (2018) Improving the freeze-thaw stability of soy protein emulsions via combing limited hydrolysis and Maillard-induced glycation. LWT 91:63–69
Das G, Nicastri A, Coluccio ML, Gentile F, Candeloro P, Cojoc G, Liberale C, De AF, Di FE (2010) FT-IR, Raman, RRS measurements and DFT calculation for doxorubicin. Microsc Res Tech 73(10):991–995
Yaghoubi A, Ramazani A (2020) Anticancer DOX delivery system based on CNTs: functionalization, targeting and novel technologies. J Control Release 327:198–224
Dai L, Liu M, Long W, Hu X, Ouyang H, Feng Y, Deng F, Wen Y, Zhang X, Wei Y (2021) Synthesis of water dispersible and biocompatible nanodiamond composite via photocatalytic surface grafting of zwitterionic polymers for intracellular delivery of DOX. Mater Today Commun 103010
Such GK, Yan Y, Johnston A, Gunawan ST, Caruso F (2015) Interfacing materials science and biology for drug carrier design. Adv Mater 27(14):2278–2297
Lili Y, Ruihua M, Li L, Fei L, Li S (2016) Intracellular Doxorubicin delivery of a core cross-linked, redox-responsive polymeric micelles. Int J Pharm 498(1–2):195–204
Yi Y, Kim HJ, Mi P, Zheng M, Takemoto H, Toh K, Kim BS, Hayashi K, Naito M, Matsumoto Y (2016) Targeted systemic delivery of siRNA to cervical cancer model using cyclic RGD-installed unimer polyion complex-assembled gold nanoparticles. J Control Release 244(Pt B):247
Wu D, Zhang Y, Xu X, Guo T, Xie D, Zhu R, Chen S, Ramakrishna S, He L (2018) RGD/TAT-functionalized chitosan-graft-PEI-PEG gene nanovector for sustained delivery of NT-3 for potential application in neural regeneration. Acta Biomater 72:266–277
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the Key Research and Development Program of Shaanxi (No. 2021ZDLSF03-05), Scientific and Technological Innovation Team of Xi’an Medical College (2021DT07), Xi’an Medical University Young Outstanding Talents Supporting Fund (05041905), Shaanxi Higher Education Research Project (XGH19042), Xi’an Science and Technology Plan Project (2020KJRC0135), and Xi’an Weiyang District Science and Technology Plan Project (201930).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, L., Yao, L., Yang, K. et al. cRGD-modified core–shell mesoporous silica@BSA nanoparticles for drug delivery. Polym. Bull. 79, 10555–10571 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-021-03999-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-021-03999-x