Abstract
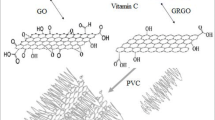
Graphene oxide/ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (GO/UHMWPE) composite was prepared by hot pressing and irradiation cross-linked by γ-ray. Vitamin-E (VE) solution was diffused into matrix and homogenize treated to study the diffusion behavior. Weight change, diffusion depth and VE index after VE diffusion were studied. The results show that after VE soaking, the weight change is, however, not obvious at low temperature (80 °C and 100 °C), while apparent at 120 °C. Furthermore, the weight change of UHMWPE is most, while least of irradiation cross-linked GO/UHMWPE. GO filling and irradiation cross-linking had no significant effect on the molecular structure of UHMWPE, the characteristic peaks of VE can be clearly seen in the FT-IR. The diffusion depth of VE in UHMWPE is the largest, which is 280 μm. On the contrary, the shallowest diffusion depth of 70 μm in composites modified by GO and irradiation. The cross-linking degree caused by irradiation and larger two-dimensional structure of GO hindering VE diffusion, more soaking time and temperature are required to provide greater activation energy to obtain desired thickness. Besides, diffusion equation also established as a function of time and temperature based on Fickian theory, which is conducive to predict the diffusion depth of VE into UHMWPE matrix composite for targeted modification. Furthermore, diffusion mechanisms of VE also illustrated.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal C (1998) Reconstructing the human body using biomaterials. JOM 50(1):31–35
Tipper JL, Galvin AL, Ingham E, Fisher J (2006) Estimation of the osteolytic potential of noncrosslinked polyethylenes and ceramic-on-ceramic total hip prostheses. J ASTM Int 6(3):1–16
Katz JN (2006) Total joint replacement in osteoarthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 20(1):145–153
Steven K, Fionna M, Kevin O, Nathan C, Edmund L, Michael H (2007) Projections of primary and revision hip and knee arthroplasty in the united states from 2005 to 2030. J Bone Joint Surg 89(4):780–785
Gomez BE, Puertolas JA, Munuera L, Konttinen YT (2008) Update on UHMWPE research from the bench to the bedside. Acta Orthop 79(6):832–840
Katta J, Jin Z, Ingham E, Fisher J (2008) Biotribology of articular cartilage e a review of the recent advances. Med Eng Phys 30(10):1349–1363
Kurtz S M (2016), The origins of UHMWPE in total hip arthroplasty. UHMWPE biomaterials handbook 33–44.
Shah JM, Fuzail M (2007) Examination of the long-lived, oxygen-induced radicals in irradiated ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene. Nucl Instrum Meth B 265(1):67–71
Wang HL, Xu L, Hu JT, Wang MH, Wu GZ (2015) Radiation induced oxidation of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) powder by gamma rays and electron beams: aclear dependence of dose rate. Radiat Phys Chem 115:88–96
Huang GD, Ni ZF, Chen GM, Li GF, Zhao YW (2016) Investigation of irradiation grapheme oxide/ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene nanocomposites by ESR and FTIR spectroscopy. Fuller Nanotub Car N 24:698–704
Huang GD, Ni ZF, Chen GM, Zhao YW (2016) The influence of irradiation and accelerated aging on the mechanical and tribological properties of the graphene oxide/ultra-highmolecular-weight polyethylene nanocomposites. Int J Polym Sci 9:1–9
Huang GD, Ni ZF, Chen GM, Pang WC, Zhao YW (2016) Effects of gamma irradiation and accelerated aging on GO/UHMWPE nanocomposites. Int J Polym Anal Charact 21:417–427
Chih A, Ansón CA, Puértolas JA (2017) Frictional and mechanical behaviour of graphene/UHMWPE composite coatings. Tribol Int 116:295–302
Pang WC, Ni ZF, Chen GM, Huang GD, Huang HD, Zhao YW (2015) Mechanical and thermal properties of grapheme oxide/ ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene nanocomposites. RSC Adv 5:63063–63072
Liu KS, Boer D, Ele L, Yao YF, Romano D, Ronca S, Rastogi S (2016) Heterogeneous distribution of entanglements in a nonequilibrium polymer melt of UHMWPE: influence on crystallization without and with Graphene Oxide. Macromolecules 49:7497–7509
Hui J, Ren PG, Sun ZF, Ren F, Xu L, Zhang ZP, Ji X (2017) Influences of interfacial adhesion on gas barrier property of functionalized graphene oxide/ultrahigh-molecular-weight polyethylene composites with segregated structure. Compos Interface 24(8):729–741
Suner S, Gowland N, Craven R, Joffe R (2018) Ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene/graphene oxide nanocomposites: wear characterization and biological response to wear particles. J Biomed Mater Res Part B 106B:183–190
Arash G, Alfred W, Nazanin E (2016) An investigation into tribological behaviour of multi-walled carbon nanotube/graphene oxide reinforced UHMWPE in water lubricated contacts. Tribol Int 95:156–161
Li XB, Yue FL, Pang WC, Wu JL, Kong BB (2019) Mechanical and wear properties of GO-enhanced irradiated UHMWPE with good oxidation resistance. Fuller Nanotub Car N 27(5):459–467
Chen YF, Qi YY, Tai ZX, Yan XB, Zhu FL, Xue QJ (2012) Preparation, mechanical properties and biocompatibility of graphene oxide/ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene composites. Eur Polym J 48:1026–1033
Suñer S, Joffe R, Tipper JL, Emami N (2015) Ultra high molecular weight polyethylene/graphene oxide nanocomposites: thermal, mechanical and wettability characterization. Compos Part B-Eng 78:185–191
Parth M, Aust N, Lederer K (2002) Studies on the effect of electron beam radiation on the molecular structure of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene under the influence of alpha-tocopherol with respect to its application in medical implants. J Mater Sci 213:917–921
Oral E, Greenbaum ES, Malhi AS, Harris WH, Muratoglu OK (2005) Characterization of irradiated blends of alpha-tocopherol and UHMWPE. Biomaterials 26:6657–6663
Oral E, Godleski C, Malhi AS, Muratoglu OK (2008) The effects of high dose irradiation on the cross-linking of vitamin E-blended ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene. Biomaterials 29:3557–3560
Oral E, Wannomae KK, Rowell SL, Muratoglu OK (2007) Diffusion of vitamin E in ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene. Biomaterials 28:5225–5237
Mats S, Olle M, Torbjörn A, Henrik B, Ghazi C, André S, Olof S (2015) Vitamin-E diffused highly cross-linked polyethylene liner ompared to standard liners in total hip arthroplasty. a randomized, controlled trial. Int Orthop 39:3643–3648
Oral E, Christensen SD, Malhi AS, Wannomae KK, Muratoglu OK (2006) Wear resistance and mechanical properties of highly cross-linked, ultrahigh-molecular weight polyethylene doped With vitamin E. J Arthroplasty 21(4):580–591
Wolf C, Maninger J, Lederer K, Fruehwirth-Smounig H, Gamse T, Marr R (2006) Stabilisation of crosslinked ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMW-PE)-acetabular components with α-tocopherol. J Mater Sci Mater Med 17:1323–1331
Malik SM, Tariq Y, Muhammad SJ, Benjamin MW, Manzoor A, Masroor I (2013) EPR study of c-Irradiated UHMWPE doped with vitamin E: assessment of thermal effects on the organic radicals during vitamin E diffusion. Appl Magn Reson 44:531–542
Duan WP, Wu MP, Han JT (2020) Research into the thermal stability and mechanical properties of vitamin E diffusion modified irradiation cross-linked graphene oxide/ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene composites. RSC Adv 10:4175–4188
Hummers SH, Offeman RE (1958) Preparation of graphitic oxide. J Am Chem Soc 80:1339
Lu PP, Wu MP, Ni ZF, Huang GD (2020) Oxidative degradation behavior of irradiated GO/UHMWPE nanocomposites immersed in simulated body fluid. Polym Bull 23:1–12
Pang WC, Wu JZ, Zhang QF, Li GF (2017) Graphene oxide enhanced, radiation cross-linked, vitamin E stabilized oxidation resistant UHMWPE with high hardness and tensile properties. RSC Adv 87:55536–55546
Acknowledgement
This study is supported by the National Defense Science and Technology Innovation Zone Project, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, J., Duan, W., Xia, Q. et al. Diffusion behavior of vitamin-E in irradiation cross-linked GO/UHMWPE composites. Polym. Bull. 79, 3649–3664 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-021-03652-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-021-03652-7