Abstract
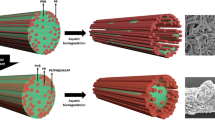
Polypropylene (PP) is one of the most widely used polymers in the world, mainly due to its versatility, good properties and low cost. However, as it does not easily degrade in the natural environment, several research projects have been developed in order to increase its biodegradability. The use of pro-degrading additives has been explored, as they promote the polymer degradation process. However, few studies have evaluated the degradation of these materials in natural aqueous environments such as rivers and lakes, which contain large amounts of PP residues. Thus, the present work aims to evaluate the influence of different additives on the degradation process of PP in natural freshwater. Samples from degradation tests were evaluated for 6 months, and their structural, morphological and thermal properties (crystallinity, etc.) were monitored. From the obtained results, it was observed that the additives influenced the degradation of PP. In addition, the enzymatic additive had more promising results since it caused more significant changes in the properties analysed, especially in relation to the morphology and structural characteristics analyses (and consequently the carbonyl index), indicating a greater influence on the degradation process. Thus, the materials studied in this work are an alternative in the field of plastic packaging, reducing the effects caused by plastic waste on the environment.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acik G, Altinkok C (2019) Polypropylene micro fibers via solution electrospinning under ambient conditions. J Appl Polym Sci 48199:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.48199
Macko T, Brull R, Zhu Y (2010) A review on the development of liquid chromatography systems for polyolefins. J Sep Sci 33:3446–3454. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201000516
Leja K, Lewandowicz G (2010) Polymer biodegradation and biodegradable polymers – a review. Pol J Environ Stud 19:255–266
De Faria AU, Martins-Franchetti SM (2010) Biodegradação de filmes de polipropileno (PP), poli(3-hidroxibutirato) (PHB) e blenda de PP/PHB por microrganismos das águas do rio atibaia. Polimeros 20:141–147. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0104-14282010005000024
Acik G (2020) Synthesis, properties and enzymatic biodegradation behavior of fluorinated poly (ε-caprolactone) s. Express Polym Lett 14:272–280
Orhan Y, Büyükgüngör H (2000) Enhancement of biodegradability of disposable polyethylene in controlled biological soil. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 45:49–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0964-8305(00)00048-2
PlasticsEurope (2017) Plastics—the facts 2017. An analysis of European plastics production, demand and waste data. https://www.plasticseurope.org/application/files/5715/1717/4180/Plastics_the_facts_2017_FINAL_for_website_one_page.pdf. Accessed 28 Feb 2019
Jambeck JR, Geyer R, Wilcox C, Siegler TR, Perryman M, Andrady A, Narayan R, Law KL (2015) Plastic waste inputs from land into the ocean. Science 347:768–771. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1260352
Coe JM, Rogers D (2012) Marine debris: sources, impacts, and solutions. Springer, Berlin
Imhof HK, Schmid J, Niessner R, Ivleva NP, Laforsch C (2012) A novel, highly efficient method for the separation and quantification of plastic particles in sediments of aquatic environments. Limnol Oceanogr Methods 10:524–537. https://doi.org/10.4319/lom.2012.10.524
Gregory, MR, Andrady AL (2003) Plastics in the marine environment. In: Plastics and the environment. Wiley, New Jersey, pp 379–402
Krueger MC, Harms H, Schlosser D (2015) Prospects for microbiological solutions to environmental pollution with plastics. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99:8857–8874. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6879-4
Pires JP, Miranda GM, de Souza GL, Fraga F, da Silva Ramos A, de Araújo GE, Ligabue RA, Azevedo CMN, Lourega RV, de Lima JEA (2019) Investigation of degradation of polypropylene in soil using an enzymatic additive. Iran Polym J (English Ed) 28:1045–1055. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13726-019-00766-8
Liu X, Gao C, Sangwan P, Yu L (2014) Accelerating the degradation of polyolefins through additives and blending. J Appl Polym Sci 131:9001–9015. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.40750
Fontanella S, Bonhomme S, Brusson JM, Pitteri S, Guy Samuel, Pichon G, Lacoste J, Fromageat D, Lemaire J, Delort AM (2013) Comparison of biodegradability of various polypropylene films containing pro-oxidant additives based on Mn, Mn/Fe or Co. Polym Degrad Stab 98:875–884. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2013.01.002
Thomas NL, Clarke J, McLauchlin AR, Patrick SG (2012) Oxo-degradable plastics: degradation, environmental impact and recycling. Proc Inst Civ Eng Waste Resour Manag 165:133–140. https://doi.org/10.1680/warm.11.00014
Chiellini E, Corti A, D’Antone S (2007) Oxo-biodegradable full carbon backbone polymers - biodegradation behaviour of thermally oxidized polyethylene in an aqueous medium. Polym Degrad Stab 92:1378–1383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2007.03.007
Montagna LS, De Camargo Madalena, Forte M, Marlene R, Santana C (2013) Induced degradation of polypropylene with an organic pro-degradant additive. J Mater Sci Eng A 3:123–131
Villamizar CA, Morillas AV (2018) Degradation of conventional and oxodegradable high density polyethylene in tropical aqueous and outdoor environments. Rev Int Contam Ambient 34:137–141. https://doi.org/10.20937/RICA.2018.34.01.12
Mohamad N, Zainol NS, Rahim FF, Moulod HEA, Rahim TA, Shamsuri SR, Azam MA, Yaakub MY, Abdollah MFB, Manaf MEA (2013) Mechanical and morphological properties of polypropylene/epoxidized natural rubber blends at various mixing ratio. Procedia Eng 68:439–445. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2013.12.204
Veethahavya KS, Rajath BS, Noobia S, Kumar BM (2016) Biodegradation of low density polyethylene in aqueous media. Procedia Environ Sci 35:709–713. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proenv.2016.07.072
Barbeş L, Rădulescu C, Stihi C (2014) ATR-FTIR spectrometry characterisation of polymeric materials. Rom Rep Phys 66:765–777. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2013.185
Miyazaki K, Arai T, Shibata K, Terano M, Nakatani H (2012) Study on biodegradation mechanism of novel oxo-biodegradable polypropylenes in an aqueous medium. Polym Degrad Stab 97:2177–2184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2012.08.010
Tavares LB, Rocha RG, Rosa DS (2017) An organic bioactive pro-oxidant behavior in thermal degradation kinetics of polypropylene films. Iran Polym J (English Ed) 26:273–280. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13726-017-0517-1
Auta HS, Emenike CU, Jayanthi B, Fauziah SH (2018) Growth kinetics and biodeterioration of polypropylene microplastics by Bacillus sp. and Rhodococcus sp. isolated from mangrove sediment. Mar Pollut Bull 127:15–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.11.036
Peixoto J, Silva LP, Krüger RH (2017) Brazilian Cerrado soil reveals an untapped microbial potential for unpretreated polyethylene biodegradation. J Hazard Mater 324:634–644. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.11.037
Gulmine JV, Janissek PR, Heise HM, Akcelrud L (2003) Degradation profile of polyethylene after artificial accelerated weathering. Polym Degrad Stab 79:385–397. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-3910(02)00338-5
Skariyachan S, Patil AA, Shankar A, Shankar A, Manjunath M, Bachappanavar N, Kiran S (2018) Enhanced polymer degradation of polyethylene and polypropylene by novel thermophilic consortia of Brevibacillus sps. and Aneurinibacillus sp. screened from waste management landfills and sewage treatment plants. Polym Degrad Stab 149:52–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2018.01.018
Das MP, Kumar S (2015) An approach to low-density polyethylene biodegradation by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. 3 Biotech 5:81–86. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-014-0205-1
Chiellini E, Corti A, Swift G (2003) Biodegradation of thermally-oxidized, fragmented low-density polyethylenes. Polym Degrad Stab 81:341–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-3910(03)00105-8
Matsunaga M, Whitney PJ (2000) Surface changes brought about by corona discharge treatment of polyethylene film and the effect on subsequent microbial colonisation. Polym Degrad Stab 70:325–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-3910(00)00105-1
Husarova L, Machovsky M, Gerych P, Houser J, Koutny M (2010) Aerobic biodegradation of calcium carbonate filled polyethylene film containing pro-oxidant additives. Polym Degrad Stab 95:1794–1799. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2010.05.009
Sivan A (2011) New perspectives in plastic biodegradation. Curr Opin Biotechnol 22:422–426. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2011.01.013
Gu JD (2003) Microbiological deterioration and degradation of synthetic polymeric materials: recent research advances. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 52:69–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0964-8305(02)00177-4
Arkatkar A, Arutchelvi J, Sudhakar M, Bhaduri S, Uppara PV, Doble M (2009) Approaches to enhance the biodegradation of polyolefins. Open Environ Eng J 2:68–80. https://doi.org/10.2174/1874829500902010068
Chawla S, Ghosh AK, Ahmad S, Avasthi DK (2006) Swift heavy ion induced structural and chemical changes in BOPP film. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res Sect B Beam Interact Mater Atoms 244:248–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nimb.2005.11.159
Cadenato A, Ramis X, Salla JM, Moracho JM, Contat-Rodrigo L, Vallés-Lluch A, Ribes-Greus A (2006) Calorimetric studies of PP/Mater-Bi blends aged in soil. J Appl Polym Sci 100:3446–3453. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.22084
Longo C, Savaris M, Zeni M, Brandalise RN, Grisa AMC (2011) Degradation study of polypropylene (PP) and bioriented polypropylene (BOPP) in the environment. Mater Res 14:442–448. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1516-14392011005000080
Sheik S, Chandrashekar KR, Swaroop K, Somashekarappa HM (2015) Biodegradation of gamma irradiated low density polyethylene and polypropylene by endophytic fungi. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 105:21–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2015.08.006
Roy PK, Surekha P, Rajagopal C, Chatterjee V, Choudhary V (2007) Studies on the photo-oxidative degradation of LDPE films in the presence of oxidised polyethylene. Polym Degrad Stab 92:1151–1160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2007.01.010
Ramos M, Jiménez A, Peltzer M, Garrigós MC (2012) Characterization and antimicrobial activity studies of polypropylene films with carvacrol and thymol for active packaging. J Food Eng 109:513–519. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2011.10.031
Persico P, Ambrogi V, Carfagna C, Cerruti P, Ferrocino I, Mauriello G (2009) Nanocomposite polymer films containing carvacrol for antimicrobial active packaging. Polym Eng Sci 49:1447–1455. https://doi.org/10.1002/pen.21191
Valle MLM, Guimarães MJOC (2004) Degradação de Poliolefinas Utilizando Catalisadores Zeolíticos. Polimeros 14:17–21. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0104-14282004000100009
Montagna LS, Catto AL, Forte MMC, Chiellini E, Corti A, Morelli A, Santana RMC (2015) Comparative assessment of degradation in aqueous medium of polypropylene films doped with transition metal free (experimental) and transition metal containing (commercial) pro-oxidant/pro-degradant additives after exposure to controlled UV radiation. Polym Degrad Stab 120:186–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2015.06.019
Acknowledgements
The present work was done with the support of Coordination of Improvement of Higher Level Personnel—Brazil (CAPES)—Finance Code 001, and Brasilata Company.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pires, J.P., Ramos, A.S., Miranda, G.M. et al. Natural freshwater degradation of polypropylene blends with additives of a distinct nature. Polym. Bull. 78, 2025–2042 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-020-03200-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-020-03200-9