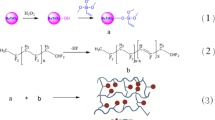
Abstract
An intercalated blend polymer nanocomposite (PNC) films based on blend (PEO–PVC), LiPF6 as salt and modified montmorillonite (MMMT) as nanoclay are prepared via solution cast method. The impact of the nanoclay on the morphology, structure, polymer–polymer, polymer–ion interactions, ionic conductivity, voltage stability window, glass transition temperature, dielectric permittivity, and ac conductivity has been explored. The structural analysis evidenced the formation of blended and intercalated polymer nanocomposites. The FTIR analysis confirmed the interaction between polymer–ion-nanoclay, and polymer intercalation is evidenced by the out-of-the-plane mode [Si–O mode] of MMMT. An increase in the fraction of free anions with clay addition is confirmed. The highest ionic conductivity of about ~ 8.2 × 10−5 S cm−1 (at RT) and 1.01 × 10−3 S cm−1 (at 100 °C) is exhibited by 5 wt% MMMT based PNC. A strong correlation is observed between the glass transition temperature, crystallinity, melting temperature (Tm), ionic conductivity, relaxation time, and dielectric strength. The dielectric data have been fitted and enhanced dielectric strength and lowering of the relaxation time (\( \tau_{{\varepsilon^{\prime} }} \;{\text{and}}\;\tau_{\text{m}} \)) with clay addition evidences the faster segmental motion of polymer chain. The intercalated PNC shows thermal stability up to ~ 300 °C, high ion transference number (~ 1), and broad voltage stability window of ~ 5 V. An absolute agreement between ion mobility (μ), diffusion coefficient (D), and ionic conductivity is observed. An ion transport mechanism has been proposed on the basis of experimental results. Therefore, the proposed PNC can be adopted as electrolyte cum separator for energy storage devices.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barbosa JC, Dias JP, Lanceros-Méndez S, Costa CM (2018) Recent advances in poly(Vinylidene fluoride) and its copolymers for lithium-ion battery separators. Membranes 8:45
Hong SY, Kim Y, Park Y et al (2013) Charge carriers in rechargeable batteries: Na ions vs. Li ions. Energy Environ Sci 6:2067–2081
Yang Q, Zhang Z, Sun XG et al (2018) Ionic liquids and derived materials for lithium and sodium batteries. Chem Soc Rev 47:2020–2064
Armand MB (1980) Intercalation electrodes. Materials for advanced batteries. Springer, Boston, pp 145–161
Arya A, Sharma AL (2019) Electrolyte for energy storage/conversion (Li+, Na+, Mg2+) devices based on PVC and their associated polymer: a comprehensive review. J Solid State Electrochem 23(4):997–1059
Arya A, Sharma AL (2017) Polymer electrolytes for lithium ion batteries: a critical study. Ionics 23:497–540
Zhang Z, Shao Y, Lotsch B et al (2018) New horizons for inorganic solid state ion conductors. Energy Environ Sci 11:1945–1976
Fenton DE, Parker JM, Wright PV (1973) Complexes of alkali metal ions with poly(ethylene oxide). Polymer 14:589
Shriver DF, Bruce PG, In Bruce PG (1995) Solid state electrochemistry. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, p 95
Zhao C, Liu L, Qi X et al (2018) Solid-state sodium batteries. Adv Energy Mater 8:173012
Arya A, Sharma AL (2017) Insights into the use of polyethylene oxide in energy storage/conversion devices: a critical review. J Phys D Appl Phys 50:443002
Etacheri V, Marom R, Elazari R et al (2011) Challenges in the development of advanced Li-ion batteries: a review. Energy Environ Sci 4:3243–3262
Vegge T, Younesi R, Johansson P et al (2015) Lithium salts for advanced lithium batteries: Li–metal, Li–O2, and Li–S. Energy Environ Sci 8:1905–1922
Sharma AL, Thakur AK (2010) Improvement in voltage, thermal, mechanical stability and ion transport properties in polymer–clay nanocomposites. J Appl Polym Sci 118:2743–2753
Arya A, Sadiq M, Sharma AL (2018) Effect of variation of different nanofillers on structural, electrical, dielectric, and transport properties of blend polymer nanocomposites. Ionics 24:2295–2319
Prasanth R, Shubha N, Hng HH, Srinivasan M (2013) Effect of nano-clay on ionic conductivity and electrochemical properties of poly(vinylidene fluoride) based nanocomposite porous polymer membranes and their application as polymer electrolyte in lithium ion batteries. Eur Polym J 49:307–318
Sharma AL, Thakur AK (2010) Polymer–ion–clay interaction based model for ion conduction in intercalation-type polymer nanocomposite. Ionics 16:339–350
Arya A, Sharma AL (2018) Structural, microstructural and electrochemical properties of dispersed-type polymer nanocomposite films. J Phys D Appl Phys 51:045504
Kazim S, Ahmad S, Pfleger J et al (2012) Polyaniline–sodium montmorillonite clay nanocomposites: effect of clay concentration on thermal, structural, and electrical properties. J Mater Sci 47:420–428
Shukla N, Thakur AK (2010) Ion transport model in exfoliated and intercalated polymer–clay nanocomposites. Solid State Ion 181:921–932
Ray SS, Okamoto M (2003) Polymer/layered silicate nanocomposites: a review from preparation to processing. Prog Polym Sci 28:1539–1641
Kim S, Hwang EJ, Jung Y et al (2008) Ionic conductivity of polymeric nanocomposite electrolytes based on poly(ethylene oxide) and organo-clay materials. Colloids Surf, A 313–314:216–219
Choudhary S, Sengwa RJ (2012) Ionic conductivity of lithium perchlorate salt in polymeric electrolyte solutions and MMT nano-sheets dispersed colloids. Indian J Eng Mater Sci 19:245–252
Chen HW, Chiu CY, Chang FC (2002) Conductivity enhancement mechanism of the poly(ethylene oxide)/modified-clay/LiClO4 systems. J Polym Sci, Part B: Polym Phys 40:1342–1353
Chen HW, Lin TP, Chang FC (2002) Ionic conductivity enhancement of the plasticized PMMA/LiClO4 polymer nanocomposite electrolyte containing clay. Polymer 43:5281–5288
Feldman D (2015) Polyblend nanocomposites. J Macromol Sci Part A: Pure Appl Chem 52:648–658
Fischer H (2003) Polymer nanocomposites: from fundamental research to specific applications. Mater Sci Eng, C 23:763–772
Sai Prasanna CM, Austin Suthanthiraraj S (2019) PVC/PEMA-based blended nanocomposite gel polymer electrolytes plasticized with room temperature ionic liquid and dispersed with nano-ZrO2 for zinc ion batteries. Polym Compos. https://doi.org/10.1002/pc.25201
Sharma AL, Thakur AK (2011) Polymer matrix-clay interaction mediated mechanism of electrical transport in exfoliated and intercalated polymer nanocomposites. J Mater Sci 46:1916–1931
Araujo EM, Leite AMD, da Paz RA et al (2011) Polyamide 6 nanocomposites with inorganic particles modified with three quaternary ammonium salts. Materials 4:1956–1966
Fawaz J, Mittal V (2015) Synthesis of polymer nanocomposites: review of various techniques. Wiley, Weinheim, pp 992–1057
Fu X, Qutubuddin S (2001) Polymer–clay nanocomposites: exfoliation of organophilic montmorillonite nanolayers in polystyrene. Polymer 42:807–813
Ni’Mah YL, Cheng MY, Cheng JH et al (2015) Solid-state polymer nanocomposite electrolyte of TiO2/PEO/NaClO4 for sodium ion batteries. J Power Sources 278:375–381
Subban RHY, Arof AK (2004) Plasticiser interactions with polymer and salt in PVC-LiCF 3SO3-DMF electrolytes. Eur Polym J 40:1841–1847
Cole KC (2008) Use of infrared spectroscopy to characterize clay intercalation and exfoliation in polymer nanocomposites. Macromolecules 41:834–843
Sengwa RJ, Dhatarwal P, Choudhary S (2018) Study of time-ageing effect on the ionic conduction and structural dynamics in solid polymer electrolytes by dielectric relaxation spectroscopy. Solid State Ion 324:247–259
Ibrahim S, Yassin MM, Ahmad R, Johan MR (2011) Effects of various LiPF6 salt concentrations on PEO-based solid polymer electrolytes. Ionics 17:399–405
Anilkumar KM, Jinisha B, Manoj M, Jayalekshmi S (2017) Poly(ethylene oxide) (PEO)—Poly(vinyl pyrrolidone) (PVP) blend polymer based solid electrolyte membranes for developing solid state magnesium ion cells. Eur Polym J 89:249–262
Das A, Thakur AK, Kumar K (2013) Exploring low temperature Li+ ion conducting plastic battery electrolyte. Ionics 19:1811–1823
Arya A, Sharma AL (2018) Effect of salt concentration on dielectric properties of Li-ion conducting blend polymer electrolytes. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 29:17903–17920
Han SD, Yun SH, Borodin O, Seo D, Sommer DM, Young RD, Henderson WA (2015) Solvate structures and computational/spectroscopic characterization of LiPF6 electrolytes. J Phys Chem C 119:8492–8500
Ducasse L, Dussauze M, Grondin J, Lassègues JC, Naudin C, Servant L (2003) Spectroscopic study of poly(ethylene oxide)6: LiX complexes (X = PF6, AsF6, SbF6, ClO4. Phys Chem Chem Phys 5:567–574
Chen HW, Chang FC (2001) The novel polymer electrolyte nanocomposite composed of poly(ethylene oxide), lithium triflate and mineral clay. Polymer 42:9763–9769
Jonscher AK (1983) Dielectric relaxation in solids. Chelsea Dielectric, London
Scrosati B, Croce F, Persi L (2002) Impedance spectroscopy study of PEO-based nanocomposite polymer electrolytes. J Electrochem Soc 147:1718–1721
Pritam Arya A, Sharma AL (2019) Dielectric relaxations and transport properties parameter analysis of novel blended solid polymer electrolyte for sodium ion rechargeable batteries. J Mater Sci 54:7131–7155
Ghadami A, Taheri Qazvini N, Nikfarjam N (2014) Ionic conductivity in gelatin-based hybrid solid electrolytes: the non-trivial role of nanoclay. J Mater Sci Technol 30:1096–1102
Hackett E, Manias E, Giannelis EP (2000) Computer simulation studies of PEO/layer silicate nanocomposites. Chem Mater 12:2161–2167
Giannelis EP (1996) Polymer layered silicate nanocomposites. Adv Mater 8:29–35
Dam T, Karan NK, Thomas R, Pradhan DK, Katiyar RS (2015) Observation of ionic transport and ion-coordinated segmental motions in composite (polymer–salt–clay) solid polymer electrolyte. Ionics 21:401–410
Reddy Polu A, Kumar R (2012) Impedance spectroscopy and FTIR studies of PEG—based polymer electrolytes. E-J Chem 8:347–353
Mohamad AA, Mohamed NS, Yahya MZA et al (2003) Ionic conductivity studies of poly(vinyl alcohol) alkaline solid polymer electrolyte and its use in nickel-zinc cells. Solid State Ion 156:171–177
Arya A, Sharma AL (2018) Optimization of salt concentration and explanation of two peak percolation in blend solid polymer nanocomposite films. J Solid State Electrochem 22:2725–2745
Chrissopoulou K, Andrikopoulos KS, Fotiadou S et al (2011) Crystallinity and chain conformation in PEO/layered silicate nanocomposites. Macromolecules 44:9710–9722
Jinisha B, Anilkumar KM, Manoj M, Pradeep VS, Jayalekshmi S (2017) Development of a novel type of solid polymer electrolyte for solid state lithium battery applications based on lithium enriched poly (ethylene oxide)(PEO)/poly (vinyl pyrrolidone)(PVP) blend polymer. Electrochim Acta 235:210–222
Fan L, Dang Z, Nan CW, Li M (2002) Thermal, electrical and mechanical properties of plasticized polymer electrolytes based on PEO/P (VDF-HFP) blends. Electrochim Acta 48:205–209
Arof AK, Amirudin S, Yusof SZ, Noor IM (2014) A method based on impedance spectroscopy to determine transport properties of polymer electrolytes. Phys Chem Chem Phys 16:1856–1867
Bandara TMWJ, Dissanayake MAKL, Albinsson I, Mellander BE (2011) Mobile charge carrier concentration and mobility of a polymer electrolyte containing PEO and Pr4N + I− using electrical and dielectric measurements. Solid State Ion 189:63–68
Salehiyan R, Yussuf AA, Hanani NF, Hassan A, Akbari A (2015) Polylactic acid/polycaprolactone nanocomposite: influence of montmorillonite and impact modifier on mechanical, thermal, and morphological properties. J Elastomers Plast 47:69–87
Kanimozhi G, Vinoth S, Harish K, Srinadhu ES, Satyanarayana N (2018) Conductivity and dielectric permittivity studies of KI- based Nanocomposite (PEO/PMMA/KI/I2/ZnO nanorods) polymer solid electrolytes. Polym Compos 40(7):2919–2928
Ravi M, Pavani y, Kiran Kumar K, Bhavani S, Sharma AK, Narasimha Rao VVR (2011) Studies on electrical and dielectric properties of PVP:KBr O4 complexed polymer electrolyte films. Mater Chem Phys 131:442–448
Jiang X, Zhao X, Peng G, Liu W, Liu K, Zhan Z (2017) Investigation on crystalline structure and dielectric relaxation behaviors of hot pressed poly (vinylidene fluoride) film. Curr Appl Phys 17:15–23
Karmakar A, Ghosh A (2012) Dielectric permittivity and electric modulus of polyethylene oxide (PEO)–LiClO4 composite electrolytes. Curr Appl Phys 12:539–543
Wei YZ, Sridhar S (1993) A new graphical representation for dielectric data. J Chem Phys 99:3119–3124
Arya A, Sharma AL (2018) Structural, electrical properties and dielectric relaxations in Na+-ion-conducting solid polymer electrolyte. J Phys: Condens Matter 30:165402
Choudhary S (2017) Dielectric dispersion and relaxations in (PVA–PEO)–ZnO polymer nanocomposites. Phys B 522:48–56
Abutalib MM (2019) Effect of zinc oxide nanorods on the structural, thermal, dielectric and electrical properties of polyvinyl alcohol/carboxymethyle cellulose composites. Phys B 557:108–116
Arya A, Sharma AL (2019) Tailoring of the structural, morphological, electrochemical, and dielectric properties of solid polymer electrolyte. Ionics 25:1617–1632
Casar G, Li X, Malic B, Zhang QM, Bobnar V (2015) Impact of structural changes on dielectric and thermal properties of vinylidene fluoride–trifluoroethylene-based terpolymer/copolymer blends. Phys B 461:5–9
Arya A, Sharma AL (2018) Temperature and salt-dependent dielectric properties of blend solid polymer electrolyte complexed with LiBOB. Macromol Res 27(4):334–345
García-Bernabé A, Rivera A, Granados A, Luis SV, Compañ V (2016) Ionic transport on composite polymers containing covalently attached and absorbed ionic liquid fragments. Electrochim Acta 213:887–897
Das S, Ghosh A (2017) Charge carrier relaxation in different plasticized PEO/PVDF-HFP blend solid polymer electrolytes. J Phys Chem B 121:5422–5432
Arya A, Saykar NG, Sharma AL (2019) Impact of Shape (nanofiller vs. nanorod) of TiO2 nanoparticle on free standing solid polymeric separator for energy storage/conversion devices. J Appl Polym Sci 136:47361
Arya A, Sadiq M, Sharma AL (2018) Structural, electrical and ion transport properties of free-standing blended solid polymeric thin films. Polym Bull. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-018-2645-y
Acknowledgements
One of the authors (AA) is thankful to the Central University of Punjab for fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arya, A., Sharma, A.L. Investigation on enhancement of electrical, dielectric and ion transport properties of nanoclay-based blend polymer nanocomposites. Polym. Bull. 77, 2965–2999 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-019-02893-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-019-02893-x