Abstract
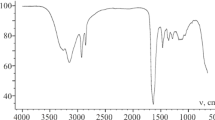
N-vinyl imidazole (NVI) was grafted onto gelatin using potassium persulphate (KPS) as thermal initiator in aqueous medium. The effects of various parameters such as different KPS and NVI concentrations, the time and reaction temperature on the grafting process have been investigated. The optimum conditions were found to get the highest grafting efficiency as follow [KPS] = 6 × 10−3 mol L−1, [NVI] = 1.5 mol L−1 at reaction temperature 60 °C for 90 min. The grafted gelatin copolymers were characterized using different techniques namely Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) and 1H NMR spectroscopy, scanning electron microscope, X-ray diffraction (XRD) and thermal analysis. The antibacterial activity of gelatin and its grafted copolymers was evaluated. The highest percent of grafting (G% = 215%) showed strong improvement in activity of gelatin against gram-negative bacteria used Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumonia. In case of Klebsiella pneumonia, grafted gelatin copolymer showed the same inhibition zone of gentamicin (standard antibiotic).











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Soleimani F, Sadeghi M, Shahsavari H (2012) Graft copolymerization of Gelatin-g-poly (Acrylic acid-co-Acrylamide) and calculation of grafting parameters. Ind J Sci Tech 5(2):2041–2046
Ninan G, Zynudheen AA, Joshy CG, Yousuf KS (2013) Physical, chemical and functional properties of gelatin extracted from the skin of rohu, Labeorohita and yellow fin tuna, Thunnus albacores. Indian J Fish 60(2):123–128
Araghi M, Moslehi Z, Nafchi AM, Mostahsan A, Salamat N, Garmakhany AD (2015) Cold water fish gelatin modification by a natural phenolic cross-linker (ferulic acid and caffeic acid). J Wiley Periodicals Inc 3(5):370–375
Nursel P, Olgum G (2002) Synthesis and characterization of poly(N- vinylimidazole) hydrogels crosslinked by gamma irradiation. Polym Int 51:1404–1410
Ren Y, Zhao X, Liang X, Ma PX, Guo B (2017) Injectable hydrogel based on quaternized chitosan, gelatin and dopamine as localized drug delivery system to treat Parkinson’s disease. Int J Biol Macromol 105(1):1079–1087
Wu Y, Wang L, Guo B, Ma PX (2017) Interwoven aligned conductive nanofiber yarn/hydrogel composite scaffolds for engineered 3D cardiac anisotropy. ACS Nano 11(6):5646–5659
Zhao X, Guo B, Wu H, Liang Y, Ma PX (2018) Injectable antibacterial conductive nanocomposite cryogels with rapid shape recovery for noncompressible hemorrhage and wound healing. Nat Commun 9:2784–2797
Zhao X, Wu H, Guo B, Dong R, Qiu Y, Ma PX (2017) Antibacterial anti-oxidant electroactive injectable hydrogel as self-healing wound dressing with hemostasis and adhesiveness for cutaneous wound healing. Biomaterials 122:34–47
Zhao X, Li P, Guo B, Ma PX (2015) Antibacterial and conductive injectable hydrogels based on quaternized chitosan-graft-polyaniline/oxidized dextran for tissue engineering. Acta Biomater 26:236–248
Qu J, Zhao X, Liang Y, Zhang T, Ma PX, Guo B (2018) Antibacterial adhesive injectable hydrogels with rapid self-healing, extensibility and compressibility as wound dressing for joints skin wound healing. Biomaterials 183:185–199
Halil U, Can I, Oya SA (2003) Graft copolymerization of N-vinylimidazole on poly(ethyleneterephthalate) fibers in a swelling solvent using Azobisisobutyronitrile as initiator. Turk J Chem 27:4003–4015
Shirzadeh Z, Foladi S, Didehban Kh (2015) Swelling characterization of nanocomposite hydrogels of poly(acrylamide-N-vinylimidazole). JACR 9(2):33–36
Strat M, Vasiliu S, Strat G, Luca C, Grecu I, Gurlui S, Stratulat SI (2006) Spectral and thermogravimetric analysis of some poly(carboxybetaine)s polymers. J Optoelectron Adv M 8(1):181–184
Kim JY, Ha CS, Jo NJ (2002) Synthesis and Properties of biodegradable chitin-graftpoly(l-lactide) copolymers. Polym Int 51:1123–1128
Sabaa MW, Mohamed NA, Mohamed RR, Khalil NM, Abd El Latif SM (2010) Synthesis, characterization and antimicrobial activity of poly (N-vinyl imidazole) grafted carboxymethyl chitosan. Carbohydr Polym 79(4):998–1005
Young S, Wong M, Tabata Y, Mikos AG (2005) Gelatin as a delivery vehicle for the controlled release of bioactive molecules. J Control Release 109:256–274
Jongjareonrak A, Benjakul S, Visessanguan W, Prodpran T, Tanaka M (2006) Characterization of edible films from skin gelatin of brown stripe red snapper and big eye snapper. Food Hydrocolloids 20:492–501
Huss FRM, Junker JPE, Johnson H, Kratz G (2007) Macroporous gelatine spheres as culture substrate, transplantation vehicle, and biodegradable scaffold for guided regeneration of soft tissues. In vivo study in nude mice. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 60:543–555
Vandervoort J, Ludwig A (2004) Preparation and evaluation of drug-loaded gelatin nanoparticles for topical ophthalmic use. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 57:251–261
Tabata Y, Hijikata S, Ikada Y (1994) Enhanced vascularization and tissue granulation by basic fibroblast growth factor impregnated in gelatin hydrogels. J Control Release 31:189–199
Liu TY, Hu SH, Liu KH, Liu DM, Chen SY (2006) Preparation and characterization of smart magnetic hydrogels and its use for drug release. J Magn Magn Mater 304:397–399
Liu J, Meisner D, Kwong E, Wu XY, Johnston MR (2007) A novel trans-lymphatic drug delivery system: implantable gelatin sponge impregnated with PLGA–paclitaxel microspheres. Biomaterials 28:3236–3244
Fukae R, Maekawa A, Sangen O (2005) Gel-spinning and drawing of gelatin. Polymer 46:11193–11204
Huang ZM, Zhang YZ, Ramakrishna S, Lim CT (2004) Electrospinning and mechanical characterization of gelatin nanofibers. Polymer 45:5361–5368
Zhang Y, Ouyang H, Lim CT, Ramakrishna S, Huang ZM (2005) Electrospinning of gelatin fibers and gelatin/PCL composite fibrous scaffolds. J Biomed Mater Res Appl Biomater 72B:156–165
Ki CS, Baek DH, Gang KD, Lee KH, Um IC, Park YH (2005) Characterization of gelatin nanofiber prepared from gelatin–formic acid solution. Polymer 46:5094–5102
Li M, Mondrinos MJ, Gandhi MR, Ko FK, Weiss AS, Lelkes PI (2005) Electrospun protein fibers as matrices for tissue engineering. Biomaterials 26:5999–6008
Nurse P, Zakir M, Olgun G (2004) Synthesis and characterization of poly(N-vinyl imidazole-co-acrylonitrile) and determination of monomer reactivity ratios. Macromol Chem Phys 205:1088–1095
Kizhnyaev VN, Petrova TL, Pokatilov FA, Zhitov RG, Edel’shtein OA (2014) Synthesis of network poly(N-vinyl imidazole) and properties of the related hydrogels. Polym Sci Ser B 56(2):645–649
Shiner N, Butun S, Ozay O, Dibek B (2012) Utilization of smart hydrogel-metal composites as catalysis media. J Colloid Interface Sci 373(1):122–128
Li M, Guo Y, Wei Y, MacDiarmid AG, Lelkes PI (2006) Electrospinning polyaniline contained gelatin nanofibers for tissue engineering applications. Biomaterials 27:2705–2715
Choktaweesap N, Arayanarakul K, Aht-ong D, Meechaisue C, Supaphol P (2007) Electrospun gelatin fibers: effect of solvent system on morphology and fiber diameters. Polym J 39:622–631
Songchotikunpan P, Tattiyakul J, Supaphol P (2008) Extraction and electrospinning of gelatin from fish skin. Int J Biol Macromol 42:247–255
Soliman SMA, Mohamed ME, Sabaa MW (2018) Synthesis, characterization and application of gelatin-g-polyacrylonitrile and its nanoparticles. Polym Bull 75:1403–1416
Guo D, Zhuo YZ, Lai AN, Zhang QG, Zhu AM, Liu QL (2016) Interpenetrating anion exchange membranes using poly(1-vinylimidazole) as bifunctional crosslinker for fuel cells. J Membr Sci 518:295–304
Mohsen SMY, Hamzah HA, Imad Al-Deen MM, Baharudin R (2016) Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Klebsiella pneumoniae and Escherichia coli with Extended-Spectrum β-lactamase associated Genes in Hospital Tengku Ampuan Afzan, Kuantan. Pahang. Malays. J Med Sci 23(2):14–20
Carlet J, Jarlier V, Harbarth S, Voss A, Goossens H, Pittet D (2012) Ready for a world without antibiotics? The pensières antibiotic resistance call to action. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control 1(11):1–13
Kang C, Song J (2013) Antimicrobial resistance in Asia: current epidemiology and clinical implications. Infect Chemother 45(1):22–31
Rani N, Sharma A, Singh R (2013) Imidazoles as promising scaffolds for antibacterial activity: a review. Mini Rev Med Chem 13(12):1812–1835
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sabaa, M.W., Mohamed, M.E., Abdellatif, M.M. et al. Antibacterial effect of novel grafted gelatin on gram-negative bacteria. Polym. Bull. 77, 427–440 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-019-02752-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-019-02752-9