Abstract
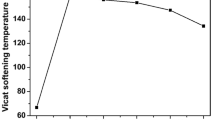
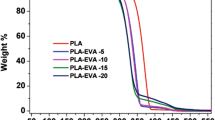
In this work, poly(lactic acid) (PLA) was melt blended with liquid natural rubber (LNR) and linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE) to fabricate a PLA–LNR–LLDPE ternary blend. The torque rheology demonstrates the melt mixing behavior of PLA–LLDPE binary and PLA–LNR–LLDPE ternary blends. Mechanical properties of ternary blend illustrate the highest toughness as compared to neat PLA and PLA–LLDPE binary blend. Fracture morphology reveals the plastic deformation behavior in the ternary blend which is illustrated in TEM micrograph. The cold crystallization temperature of the ternary blend appears at a lower temperature as compared to the binary blend. The thermal stability of PLA is improved due to blending with LLDPE and LNR. The ternary blend exhibits greater storage modulus in the glassy state as well as in the rubbery state as compared to neat PLA and binary blend. Finally, LNR performed as an effective compatibilizer between PLA and LLDPE.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zeng X, Wu B, Wu L, Hu J, Bu Z, Li B (2014) Poly(l-lactic acid)-block-poly(butylene succinate-co-butylene adipate) multiblock copolymers: from synthesis to thermo-mechanical properties. Ind Eng Chem Res 53(9):3550–3558
Moshiul Alam AKM, Shubhra QTH (2015) Surface modified thin film from silk and gelatin for sustained drug release to heal wound. J Mater Chem B 3(31):6473–6479
Moshiul Alam AKM, Beg MDH, Mina MF, Mamun AA, Bledzki AK (2014) Degradation and stability of green composites fabricated from oil palm empty fruit bunch fiber and poly lactic acid: effect of fiber length. J Compos Mater. doi:10.1177/0123456789123456
Williams CK, Hillmyer MA (2008) Polymers from renewable resources: a perspective for a special issue of polymer reviews. Polym Rev 48:1–10
Li J, Song Z, Gao L, Shan H (2016) Preparation of carbon nanotubes/polylactic acid nanocomposites using a non-covalent method. Polym Bull 73:2121–2128
Alam AKMM, Beg MDH, Mina MF, Khan MR, Prasad DRM (2012) Structures and performances of simultaneous ultrasound and alkali treated oil palm empty fruit bunch fiber reinforced poly(lactic acid) composites. Compos A 43:1921–1929
Moshiul Alam AKM, Mina MF, Beg MDH, Mamun AA, Bledzki AK, Shubhra QTH (2014) Thermo-mechanical and morphological properties of short natural fiber reinforced poly (lactic acid) biocomposite: effect of fiber treatment. Fibers Polym 15(6):1303–1309
Ishida S, Nagasaki R, Chino K, Dong T, Inoue Y (2009) Toughening of poly(l-lactide) by melt blending with rubbers. J Appl Polym Sci 113:558–566
Bitinis N, Verdejo R, Cassagnau P, Lopez-Manchado MA (2011) Structure and properties of polylactide/natural rubber blends. Mater Chem Phys 129(3):823–831
Bijarimi M, Ahmad S, Rasid R (2014) Mechanical, thermal and morphological properties of poly(lactic acid)/epoxidized natural rubber blends. J Elastomers Plast 46(4):338–354
Dahlan HM, Khairul Zaman MD, Ibrahim A (2000) Liquid natural rubber (LNR) as a compatibilizer in NR/LLDPE blends. J Appl Polym Sci 78(10):1776–1782
Dahlan HM, Khairul Zaman MD, Ibrahim A (2002) The morphology and thermal properties of liquid natural rubber (LNR)-compatibilized 60/40 NR/LLDPE blends. Polym Test 21(8):905–911
Dahlan HM, Zaman MDK, Ibrahim A (2002) Liquid natural rubber (LNR) as a compatibiliser in NR/LLDPE blends–II: the effects of electron-beam (EB) irradiation. Radiat Phys Chem 64(5–6):429–436
Lee Hyun Jae, Won Jong Sung, Lim Sung Chan, Lee Seung Goo (2016) Preparation and characterization of the PVDF/LDPE thermoplastic composite having piezoelectric property. Polym Bull 73:2639–2647
Yang K, Zhang T, Zhu C, Zhang P, Zhao S, Guo L (2016) The reinforcing mechanism study of carbon nanotube in the NR matrix. Polym Bull. doi:10.1007/s00289-016-1755-7
Fischer EW, Sterzel HJ, Wegner G (1973) Investigation of the structure of solution grown crystals of lactide copolymers by means of chemical reaction. Colloid Polym Sci 251:980–990
Brandrup J, Immergut EH (1975) Polymer handbook V-16
Moly KA, Radusch HJ, Androsh R, Bhagawan SS, Thomas S (2005) Nonisothermal crystallisation, melting behavior and wide angle X-ray scattering investigations on linear low density polyethylene (LLDPE)/ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) blends: effects of compatibilisation and dynamic crosslinking. Eur Polym J 41:1410–1419
Maity AK, Xavier SF (1999) Rheological properties of ethylene-propylene block copolymer and EPDM rubber blends using a torque rheometer. Eur Polym J 35:173–181
Cheng B, Zhou C, Yu W, Sun X (2001) Evaluation of rheological parameters of polymer melts in torque rheometers. Polym Test 20:811–818
Ahmad A, Mohd Dahlan Hj, Ibrahim A (2004) Mechanical properties of filled NR/LLDPE blends. Iran Polym J 13(3):173–178
Liu H, Song W, Chen F, Guo L, Zhang J (2011) Interaction of Microstructure and interfacial adhesion on impact performance of polylactide (PLA) ternary blends. Macromolecules 44:1513–1522
Zhang H, Huang J, Yang L, Chen R, Zou W, Lin X, Qu J (2015) Preparation, characterization and properties of PLA/TiO2 nanocomposites based on a novel vane extruder. RSC Adv. 5:4639–4647
Shubhra QTH, Alam AKMM, Quaiyyum MA (2011) Mechanical properties of polypropylene composites: a review. J Thermoplast Compos Mater 26(3):362–391
Calafel MI, Remiro PM, Cortázar MM, Calahorra ME (2010) Cold crystallization and multiple melting behavior of poly(l-lactide) in homogeneous and in multiphasic epoxy blends. Colloid Polym Sci 288:283–296
Yuryev Y, Wood-Adams PJ (2010) Rheological properties of crystallizing polylactide: detection of induction time and modeling the evolving structure and properties. Polym Sci Polym Phys 48:812–822
Visakh PM, Thomas S, Oksman K, Mathew AP (2012) Crosslinked natural rubber nanocomposites reinforced with cellulose whiskers isolated from bamboo waste: processing and mechanical/thermal properties. Compos A 43:735–741
Acknowledgements
Authors would like to acknowledge Universiti Malaysia Pahang, Malaysia for providing financial support to project RDU140331.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bijarimi, M., Ahmad, S. & Alam, A.K.M.M. Toughening effect of liquid natural rubber on the morphology and thermo-mechanical properties of the poly(lactic acid) ternary blend. Polym. Bull. 74, 3301–3317 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-016-1889-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-016-1889-7