Abstract
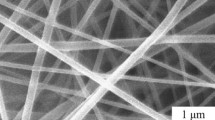
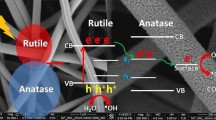
Solution blow spinning (SBS) is a recent technology to produce polymer micro- and nanofibers, including nanocomposites loaded with a wide range of nanoparticles. Because of its novelty, various studies about the properties of the produced materials are necessary, especially those related to material stability. In the present study, poly(lactic acid) (PLA)/titanium dioxide anatase (TiO2) nanocomposite fibers, with different TiO2 percentages, were produced by the SBS method. The spun nanocomposite fibers were characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), X-ray diffraction, thermogravimetric analysis and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). Moreover, the photocatalytic degradation of Rhodamine B (RhB) dye and PLA degradation by UV-C lamps were investigated. SEM and TEM micrographs show that the SBS method produced PLA/TiO2 nanofibers with uniform morphology and without beads. The DSC analyses and X-ray diffraction patterns show that incorporation of TiO2 nanoparticles could influence the PLA nanocomposite crystallinity. PLA photocatalytic degradation experiments demonstrate that the weight loss of the polymer increases with an increase in TiO2 content. The present results indicate that the SBS method can be used to produce biodegradable nanocomposite fibers with good properties and potential applications.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Man C, Zhang C, Liu Y, Wang W, Ren W, Jiang L, Reisdorffer F, Nguyen TP, Dan Y (2012) Poly (lactic acid)/titanium dioxide composites: preparation and performance under ultraviolet irradiation. Polym Degrad Stabil 97:856–862
Buzarovska A, Grozdanov A (2012) Biodegradable poly(l-lactic acid)/TiO2 nanocomposites: thermal properties and degradation. J Appl Polym Sci 123:2187–2193
Chen C, Pan C, Song M, Wu C, Guo D, Wang X, Chen B, Gu Z (2007) Poly(lactic acid) PLA based nanocomposites—a novel way of drug-releasing. Biomed Mater 2:L1–L4
Oliveira JE, Moraes EA, Marconcini JM, Mattoso LHC, Glenn GM, Medeiros ES (2013) Properties of poly(lactic acid) and poly(ethylene oxide) solvent polymer mixtures and nanofibers made by solution blow spinning. J Appl Polym Sci 129:3672–3681
Costa RGF, Oliveira JE, Paula GF, Picciani PHS, Medeiros ES, Ribeiro C, Mattoso LHC (2012) Eletrofiação de polímeros em solução: parte I: fundamentação teórica. Polímeros 22:170–177
Costa RGF, Oliveira JE, Paula GF, Picciani PHS, Medeiros ES, Ribeiro C, Mattoso LHC (2012) Eletrofiação de polímeros em solução: parte II: aplicações e perspectivas. Polímeros 22:178–185
Oliveira JE, Moraes EA, Costa RGF, Afonso AS, Mattoso LHC, Orts WJ, Medeiros ES (2011) Nano and submicrometric fibers of poly(d, l-lactide) obtained by solution blow spinning: process and solution variables. J Appl Polym Sci 122:3396–3405
Oliveira JE, Medeiros ES, Cardozo L, Voll F, Madureira EH, Mattoso LHC, Assis OBG (2013) Development of poly(lactic acid) nanostructured membranes for the controlled delivery of progesterone to livestock animals. Mater Sci Eng C 33:844–849
Medeiros ES, Glenn GM, Klamczynski AP, Orts WJ, Mattoso LHC (2009) Solution blow spinning: a new method to produce micro- and nanofibers from polymer solutions. J Appl Polym Sci 113:2322–2330
Costa RGF, Ribeiro C, Mattoso LHC (2010) Preparation and characterization of PVA-Ag nanocomposite fibers with antibacterial activities. Sci Adv Mat 2:157–162
Cargnello M, Gordon TR, Murray CB (2014) Solution-phase synthesis of titanium dioxide nanoparticles and nanocrystals. Chem Rev 114:9319–9345
Costa RGF, Ribeiro C, Mattoso LHC (2010) Morphological and photocatalytic properties of PVA/TiO2 nanocomposite fibers produced by electrospinning. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 10:5144–5152
Costa RGF, Ribeiro C, Mattoso LHC (2013) Study of the effect of rutile/anatase TiO2 nanoparticles synthesized by hydrothermal route in electrospun PVA/TiO2 nanocomposites. J Appl Polym Sci 127:4463–4469
Machado AV, Amorim S, Botelho G, Neves IC, Fonseca AM (2013) Nanocomposites of poly(epsilon-caprolactone) doped with titanium specie. J Mater Sci 48:3578–3585
Gupta KK, Kundan A, Mishra PK, Srivastava P, Mohanty S, Singh NK, Mishra A, Maiti P (2012) Polycaprolactone composites with TiO2 for potential nanobiomaterials: tunable properties using different phases. Phys Chem Chem Phys 14:12844–12853
Prahsarn C, Klinsukhon W, Roungpaisan N (2011) Electrospinning of PAN/DMF/H2O containing TiO2 and photocatalytic activity of their webs. Mater Lett 65:2498–2501
Zhang J, Ji Q, Shen X, Xia Y, Tan L, Wang F, Kong Q (2012) Flame retardancy and non-isothermal crystallization behaviour of PET/TiO2 nanocomposites. Polym Polym Compos 20:399–405
Buzarovska A (2013) PLA nanocomposites with functionalized TiO2 nanoparticles. Polym Plast Technol Eng 52:280–286
Farhoodi M, Dadashi S, Mousavi SMA, Rahmat SG, Djomeh ZA, Oromiehie A, Hemmati F (2012) Influence of TiO2 nanoparticle filler on the properties of PET and PLA nancomposites. Polymer (Korea) 36:745–755
Song M, Pan C, Chen C, Li J, Wang X, Gu Z (2008) The application of new nanocomposites: enhancement effect of polylactide nanofibers/nano-TiO2 blends on biorecognition of anticancer drug daunorubicin. Appl Surf Sci 255:610–612
Oliveira JE, Zucolotto V, Mattoso LHC, Medeiros ES (2011) Multi-wall carbon nanotube/poly(lactic acid) nanocomposite fibrous membranes prepared by Solution Blow Spinning. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 11:1–9
Medeiros ES, Glenn GM, Klamczynski AP, Orts WJ, Mattoso LHC (2009) Solution blow spinning, U.S. Patent No. 61/249
Software ImageJ. http://rsbweb.nih.gov/ij/index.html. Accessed 2 Dec 2014
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for financial support from CAPES, CNPq (Process No. 301173/2013-3) and FAPESP.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Costa, R.G.F., Brichi, G.S., Ribeiro, C. et al. Nanocomposite fibers of poly(lactic acid)/titanium dioxide prepared by solution blow spinning. Polym. Bull. 73, 2973–2985 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-016-1635-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-016-1635-1