Abstract
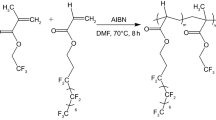
In this paper, a series of ABC-type fluorinated amphiphilic triblock copolymer composed of hydrophilic block (PEG block), hydrophobic “anchoring” block (poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) block), and nonpolar hydrophobic block (poly(2-perfluorooctylethyl methacrylate) (PFMA) block) were prepared by atom transfer radical polymerization and characterized. By manipulating the bulk composition and annealing treatment, the films with various surface compositions were prepared and then the adsorption behaviors of human plasma fibrinogen (HFg) and bacterial (Escherichia coli) adhesion on these surfaces were investigated by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The antifouling performances of the amphiphilic triblock copolymers after incorporation of fluorinated block are enhanced compared to PMMA-b-PEG and homopolymer PMMA. The surface compositional heterogeneities with special content of hydrophilic and fluorinated moieties play a significant role in antifouling properties. When the percentage of hydrophobic fluorinated moieties is 21 % and the percentage of hydrophilic ether group is 9.5 % on the surface, the copolymer surface is most unfavorable for protein adsorption. The bacterial adhesion experiment shows the similar results. These results demonstrate the desirable antifouling performance from the ABC-type fluorinated amphiphilic triblock copolymers and provide further realization of the effect of amphiphilic surface structures on the protein adsorption and bacterial adhesion behavior.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhatt S, Pulpytel J, Ceccone G, Lisboa P, Rossi F, Kumar V, Arefi-Khonari F (2011) Nanostructure protein repellant amphiphilic copolymer coatings with optimized surface energy by inductively excited low pressure plasma. Langmuir 27:14570
Huchnall A, Rangarajan S, Chikoti A (2009) In pursuit of zero: polymer brushes that resist the adsorption of proteins. Adv Mater 21:2441
Amiji M, Park K (1993) Surface modification of polymeric biomaterials with poly(ethylene oxide), albumin and heparin for reduced thrombogenicity. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed 4(3):217
Lynch AS, Robertson GT (2008) Bacterial and fungal biofilm infections. Ann Rev Med 59:415
Kumar V, Pulpytel J, Rauscher H, Mannelli I, Rossi F, Arefi-Khonsari F (2010) Fluorocarbon coatings via plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition of 1H,1H,2H,2H-perfluorodecyl acrylate-2, morphology, wettability and antifouling characterization. Plasma Process Polym 7:926
Ratner BD, Bryant SJ (2004) Biomaterials: where we have been and where we are going. Ann Rev Biomed Eng 6:41
Kingshott P, Griesser HJ (1999) Surfaces that resist bioadhesion. Curr Opin Solid State Mater Sci 4:403
Dickson JS, Koohmaraie M (1989) Cell surface charge characteristics and their relationship to bacterial attachment to meat surfaces. Appl Environ Microbiol 55:832
Kumar CG, Anand SK (1998) Significance of microbial biofilms in food industry: a review. Int J Food Microbiol 42:9
Kamino K, Inoue K, Maruyama T, Takamatsu N, Harayama S, Shizuri Y (2000) Barnacle cement proteins. Importance of disulfide bonds in their insolubility. J Biol Chem 275:27360
Senaratne W, Andruzzi L, Ober CK (2005) Self-assembled monolayers and polymer brushes in biotechnology: current applications and future perspectives. Biomacromolecules 6:2427
Park D, Weinman CJ, Finlay JA, Fletcher BR, Paik MY, Sundaram HS, Dimitriou MD, Sohn KE, Callow ME, Callow JA, Handlin DL, Willis CL, Fischer DA, Kramer EJ, Ober CK (2010) Amphiphilic surface active triblock copolymers with mixed hydrophobic and hydrophilic side chains for tuned marine fouling-release properties. Langmuir 26:9772
Unsworth LD, Sheardown H, Brash JL (2005) Protein resistance of surfaces prepared by sorption of end-thiolated poly(ethylene glycol) to gold: effect of surface chain density. Langmuir 21:1036
Li L, Chen S, Zheng J, Ratner BD, Jiang S (2005) Protein adsorption on oligo(ethylene glycol)-terminated alkanethiolate self-assembled monolayers: the molecular basis for nonfouling behavior. J Phys Chem B 109:2934
Luk Y-Y, Kato M, Mrksich M (2000) Self-assembled monolayers of alkanethiolates presenting mannitol groups are inert to protein adsorption and cell attachment. Langmuir 16:9604
GuoWJ Tang XD, Xu J, Wang X, Chen Y, Yu FQ, Pei MS (2011) Synthesis, characterization, and property of amphiphilic fluorinated abc-type triblock copolymers. J Polym Sci Part A Polym Chem 49:1528
Cho Y, Sundaram HS, Weinman CJ, Paik MY, Dimitriou MD, Finaly JA, Callow ME, Callow JA, Kramer EJ, Ober CK (2011) Triblock copolymers with grafted fluorine-free, amphiphilic, non-ionic side chains for antifouling and fouling-release applications. Macromolecules 44:4783
Zhao WF, He C, Wang HY, Su BH, Sun SD, Zhao CS (2011) Improved antifouling property of polyethersulfone hollow fiber membranes using additive of poly(ethylene glycol) methyl ether-b-poly(styrene) copolymers. Ind Eng Chem Res 50:3295
Georgievski OP, Verreault D, Diesner MO, Proks V, Heissler S, Rypάček F, Koelsch P (2012) Nonfouling poly(ethylene oxide) layers end-tethered to polydopamine. Langmuir 28:14273
Ogaki R, Andersen OZ, Jensen GV, Kolind K, Kraft DCE, Pedersen JS, Foss M (2012) Temperature-induced ultradense PEG polyelectrolyte surface grafting provides effective long-term bioresistance against mammalian cells, serum, and whole blood. Biomacromolecules 13:3668
Misra A, Jarrett WL, Urban MW (2009) New poly(methyl methacrylate)/n-butyl acrylate/pentafluorostyrene/poly(ethylene glycol) (p-MMA/nBA/PFS/PEG) colloidal dispersions: synthesis, film formation, and protein adsorption. Macromolecules 42:7299
Yarbrough JC, Rolland JP, DeSimone JM, Callow ME, Finlay JA, Call JA (2006) Contact angle analysis, surface dynamics, and biofouling characteristics of cross-linkable, random perfluoropolyether-based graft terpolymers. Macromolecules 39:2521
Hu Z, Chen L, Betts D, Pandya A, Hillmyer MA, DeSimone JM (2008) Optically transparent, amphiphilic networks based on blends of perfluoropolyethers and poly(ethylene glycol). J Am Chem Soc 130:14244
Gao J, Hu YY, Ni HG, Wang L, Yang YH, Wang XP (2013) Protein-resistance performance enhanced by formation of highly-ordered perfluorinated alkyls on fluorinated polymer surfaces. J Colloid Interface Sci 393:361
Kanno M, Kawakami H, Nagaoka S, Kubota S (2002) Biocompatibility of fluorinated polyimide. J Biomed Mater Res 60:53
Kawakami H, Kanno M, Nagaoka S, Kubota S (2003) Competitive plasma protein adsorption onto fluorinated polyimide surfaces. J Biomed Mater Res 67A:1393
Finlay JA, Krishman S, Callow ME, Callow JA, Dong R, Asgill N, Wong K, Kramer EJ, Ober CK (2008) Settlement of Ulva zoospores on patterned fluorinated and PEGylated monolayer surfaces. Langmuir 24:503
Martinelli E, Agostini S, Galli G, Chiellini E, Glisenti A, Pettitt ME, Callow ME, Callow JA, Graf K, Bartels FW (2008) Nanostructured films of amphiphilic fluorinated block copolymers for fouling release application. Langmuir 24:13138
Zhao ZL, Ni HG, Han ZY, Jiang TF, Xu YJ, Lu XL, Ye P (2013) Effect of surface compositional heterogeneities and microphase segregation of fluorinated amphiphilic copolymers on antifouling performance. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5:7808
Gudipati CS, Finaly JA, Callow JA, Callow ME, Wooley KL (2005) The antifouling and fouling-release performance of hyperbranched fluoropolymer (HBFP)–poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) composite coatings evaluated by adsorption of biomacromolecules and the green fouling alga ulva. Langmuir 21:3044
Dimitriou MD, Zhou Z, Yoo H-S, Killops KL, Finlay JA, Cone G, Sundaram HS, Lynd NA, Barteau KP, Campos LM, Fischer DA, Callow ME, Callow JA, Ober CK, Hawker CJ, Kramer EJ (2011) A general approach to controlling the surface composition of poly(ethylene oxide)-based block copolymers for antifouling coatings. Langmuir 27:13762
Sudaram HS, Cho Y, Dimitriou MD, Finlay JA, Cone G, Williams S, Handlin D, Gatto J, Callow ME, Callow JA, Kramer EJ, Ober CK (2011) Fluorinated amphiphilic polymers and their blends for fouling-release applications: the benefits of a triblock copolymer surface. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 3:3366
Chen WJ, Su YL, Peng JM, Zhao XT, Jiang ZY, Dong YN, Zhang Y, Liang YG, Liu JZ (2011) Efficient wastewater treatment by membranes through constructing tunable antifouling membrane surfaces. Environ Sci Technol 45:6545
Wang YP, Finlay JA, Desimone JM (2011) Amphiphilic co-networks with moisture-induced surface segregation for high-performance nonfouling coatings. Langmuir 27:10365
Jankova K, Chen X, Kops J, Batsberg W (1998) Synthesis of amphiphilic PS-b-PEG-b-PS by atom transfer radical polymerization. Macromolecules 31:538
Owens DK, Wendt RC (1969) Estimation of the surface free energy of polymers. J Appl Polym Sci 13:1741
Chen Y, Thayumanavan S (2009) Amphiphilicity in homopolymer surfaces reduces nonspecific protein adsorption. Langmuir 25:13795
Li M, Neoh KG, Xu LQ, Wang R, Kang ET, Lau T, Olszyna DP, Chiong E (2012) Surface modification of silicone for biomedical applications requiring long-term antibacterial, antifouling, and hemocompatible properties. Langmuir 28:16408
Li K, Wu PP, Han ZW (2002) Preparation and surface properties of fluorine-containing diblock copolymers. Polymer 43:4079
Ni HG, Wang XF, Zhang W, Wang XP, Shen ZQ (2007) Stable hydrophobic surfaces created by self-assembly of poly(methyl methacrylate) end-capped with 2-perfluorooctylethyl methacrylate units. Surf Sci 601:3632
Gitsov I, Frechet JMJ (1996) Stimuli-responsive hybrid macromolecules: novel amphiphilic star copolymers with dendritic groups at the periphery. J Am Chem Soc 118:3785
Ni HG, Li XH, Hu YY, Zuo B, Zhao ZL, Yang JP, Yuan DX, Ye XY, Wang XP (2012) Surface structure of spin-coated fluorinated polymers films dominated by corresponding film-formation solution/air interface structure. J Phys Chem C 116:24151
Tingey KG, Andrade JD (1991) Probing surface microheterogeneity of poly(ether urethanes) in an aqueous environment. Langmuir 7:2471
Kwok DY, Neumann AW (1999) Contact angle measurement and contact angle interpretation. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 81:167
Baxamusa SH, Gleason KK (2009) Random copolymer films with molecular-scale compositional heterogeneities that interfere with protein adsorption. Adv Funct Mater 19:3489
Yao F, Xu LQ, Fu GD, Lin BP (2010) Sliding-graft interpenetrating polymer networks from simultaneous “click chemistry” and atom transfer radical polymerization. Macromolecules 43:9761
Elman JF, Gerenser LJ, Goppert-Berarducci KE, Pochan JM (1990) Kinetics of the gas-phase halogenation of a polyethylene surface as studied with X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Macromolecules 23:3922
Scopelliti PE, Antonio Borgonovo A, Indrieri M, Giorgetti L, Bongiorno G, Carbone R, Podestà A, Milani P (2010) The effect of surface nanometre-scale morphology on protein adsorption. PLoS One 5:11862
Schricker SR, Palacio MLB, Bhushan B (2012) Designing nanostructured block copolymer surfaces to control protein adhesion. Phil Trans R Soc A 370:2348
Kristalyn CB, Lu XL, Weinman CJ, Ober CK, Kramer EJ, Chen Z (2010) Surface structures of an amphiphilic tri-block copolymer in air and in water probed using sum frequency generation vibrational spectroscopy. Langmuir 26:11337
Ward MD, Buttry DA (1990) In situ interfacial mass detection with piezoelectric transducers. Science 249:1000
Höök F, Kasemo B, Nylander T, Fant C, Sott K, Elwing H (2001) Variations in coupled water, viscoelastic properties, and film thickness of a Mefp-1 protein film during adsorption and cross-linking: a quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation monitoring, ellipsometry, and surface plasmon resonance study. Anal Chem 73:5796
Sigal GB, Mrksich M, Whitesides GM (1998) Effect of surface wettability on the adsorption of proteins and detergents. J Am Chem Soc 120:3464
Green RJ, Frazier RA, Shakesheff KM, Davies MC, Roberts CJ, Tendler SJB (2000) Surface plasmon resonance analysis of dynamic biological interactions with biomaterials. Biomaterials 21:1823
Muir BW, Tarasova A, Gengenbach TR, Menzies DJ, Meagher L, Rovere F, Fairbrother A, McLean KM, Hartley PG (2008) Characterization of low-fouling ethylene glycol containing plasma polymer films. Langmuir 24:3828
Ray S, Shard AG (2011) Quantitative analysis of adsorbed proteins by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Anal Chem 83:8659
Wagner MS, McArthur SL, Shen M, Horbett TA, Castner DG (2002) Limits of detection for time of flight secondary ion mass spectrometry (ToF-SIMS) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS): detection of low amounts of adsorbed protein. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed 13:407
Baier RE (1984–1985) Adhesion in the biological environment. Biomater Med DeVices Artif Organs 12:133
Schrader ME (1982) On adhesion of biological substances to low energy solid surfaces. J Colloid Interface Sci 88:296
Dexter SC (1979) Influence of substratum critical surface tension on bacterial adhesion—in situ studies. J Colloid Interface Sci 70:346
Coelho MAN, Vieira EP, Motschmann H, Möhwald H, Thünemann AF (2003) Human serum albumin on fluorinated surfaces. Langmuir 19:7544
Cheng G, Xue H, Li GZ, Jiang SY (2010) Integrated antimicrobial and nonfouling hydrogels to inhibit the growth of planktonic bacterial cells and keep the surface clean. Langmuir 26:10425
Acknowledgments
The work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC, Nos. 51003097, 51173169, and 51473148), Science Foundation of Zhejiang Top Academic Discipline of Applied Chemistry and Eco-Dyeing and Finishing and Engineering Research Center for Eco-Dyeing and Finishing of Textiles of Zhejiang Sci-Tech University, and China Scholarship Council.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, P., Jiang, T., Ni, H. et al. Synthesis, characterization and antifouling performance of ABC-type fluorinated amphiphilic triblock copolymer. Polym. Bull. 73, 1405–1426 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-015-1554-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-015-1554-6