Abstract
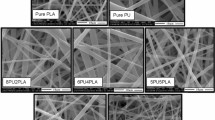
In this study, a series of novel superhydrophobic polyimide–siloxane electrospun mats was prepared using an electrospinning process. Segmented polyimide–siloxane copolymers were prepared using 4,4′-oxydianiline (ODA) and 3,3′,4,4′-benzophenone tetracarboxylic dianhydride (BTDA) as hard segments and aminopropyl terminated polydimethylsiloxane (APPS) and BTDA as soft segment. The polyimide–siloxane copolymers were synthesized by varying the APPS loading (10 and 20 mol%) and also the molecular weight of APPS (1000 and 2500 g/mol), respectively. Electrospinning of the polyamic acids was followed by thermal imidization to construct the electrospun polyimide–siloxane mats. The electrospun mats were characterized by FTIR, scanning electron microcopy (SEM), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), differential scanning calorimeter (DSC) and contact angle measurement. According to SEM results, the polyimide–siloxane electrospun mats have nano-roughness morphology. Bead on string type surface morphology that has been generated by electrospinning yields stable superhydrophobicity with a contact angle of 167°.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ma M, Mao Y, Gupta M, Gleason KK, Rutledge GC (2005) Superhydrophobic fabrics produced by electrospinning and chemical vapor deposition. Macromol 38:9742–9748
Asmatulu R, Ceylan M, Nuraje N (2011) Study of superhydrophobic electrospun nanocomposite fibers for energy systems. Langmuir 27:504–507
Nuraje N, Khan WS, Ceylan M, Lie Y, Asmatulu R (2013) Superhydrophobic electrospun nanofibers. J Mater Chem 1:1929–1946
Parker AR, Lawrence CR (2001) Water capture from desert fogs by a Namibian Beetle. Nature 414:33–34
Gao X, Jiang L (2004) Water-repellent legs of water striders. Nature 432:36
Byuna D, Hong J, Saputra Ko JH, Lee YJ, Park HC, Byund BK, Lukes JR (2009) Wetting characteristics of insect wing surfaces. J Biomech Eng 6:63–70
Erbil HY, Demirel AL, Avci Y, Mert O (2003) Transformation of a simple plastic into a super-hydrophobic surface. Science 299:1377–1380
Shirtcliffe NJ, McHale G, Newton MI, Chabrol G, Perry CC (2004) Dual-scale roughness produces un-usually water-repellent surfaces. Adv Mater 16:1929–1932
Latthe SS, Imai H, Ganesan V, Rao AV (2009) Super-hydrophobic silica films by sol-gel co-precursor method. Appl Surf Sci 256(1):217–222
Zhao XD, Xu GQ, Liu XY (2012) Superhydrophobic surfaces: beyond lotus effect. In: Liu XY (ed) Bioinspiration: from nano to micro scales, biological and medical physics, biomedical engineering. Springer, New York, pp 331–378
Khan WS, Asmatulu R, Ceylan M, Jabbarnia A (2013) Recent progress on conventional and non-conventional electrospinning processes. Fiber Polym 14:235–1247
Goponenko AV, Hou H, Dzenis YA (2011) Avoiding fusion of electrospun 3,3,4,4-biphenyltetracarboxylic dianhydride-4,4- oxydianiline copolymer nanofibers during conversion to polyimide. Polym 52:3776–3782
Cheng S, Shen D, Zhu X, Tian X, Zhou D, Fan LJ (2009) Preparation of nonwoven polyimide/silica hybrid nanofiberous fabrics by combining electrospinning and controlled in situ sol–gel techniques. Eur Polym J 45:2767–2778
Sas I, Gorga RE, Joines JA, Thoney KA (2012) Literature review on superhydrophobic self-cleaning surfaces produced by electrospinning. J Polym Sci Part B: Polym Phys 50:824–845
Agarwal S, Greiner A, Wendorff JH (2013) Functional materials by electrospinning of polymers. Prog Polym Sci 38:963–971
Chen H, Snyder JD, Elabd YA (2008) Electrospinning and solution properties of nafion and poly(acrylic acid). Macromol 41:125–128
Cengiz U, Avci MZ, Erbil HY, Saraç AS (2012) Superhydrophobic terpolymer nanofibers containing perfluoroethyl alkyl methacrylate by electrospinning. Appl Surf Sci 258:5815–5821
Weng CJ, Jhuo YS, Chang CH, Feng CF, Peng CW, Dai CF, Yeh JM, Wei Y (2011) A smart surface prepared using the switchable superhydrophobicity of neat
Oktay B, Baştürk E, Apohan NK, Kahraman MV (2013) Highly porous starch/poly(ethylene-alt-maleic anhydride) composite nanofiber mesh. Polym Compo. 34:1321–1324
Matthews JA, Wnek GE, Simpson DG, Bowlin GL (2002) Electrospinning of collagen nanofibers. Biomacromol 3:232–238
Zhao X, Wang C, Ji J, Sun Z (2013) The controllable surface morphology of polyimide (pi) electrospun fibers. J Macromol Sci Part B Phys 52:364–372
Çakmakçı E, Güngör A (2013) Preparation and characterization of flame retardant and proton conducting boron phosphate/polyimide composites. Polym Degrada Stabil 98:927–933
Kizilkaya C, Karataş S, Apohan NK, Güngör A (2012) Synthesis and characterization of novel polyimide/sio2 nanocomposite materials containing phenylphosphine oxide via sol-gel technique. J Appl Polym Sci 115:3256–3264
Chen Y, Iroh JO (1999) Synthesis and characterization of polyimide/silica hybrid composites. Chem Mater 11:1218–1222
Ahmad Z, Mark JE (2001) Polyimide–ceramic hybrid composites by the sol–gel route. Chem Mater 13:3320–3330
Zhu M, Zuo W, Yu H, Yang W, Chen Y (2006) Superhydrophobic surface directly created by electrospinning based on hydrophilic material. J Mater Sci 41:3793–3797
Son WK, Youk JH, Lee TS, Park WH (2004) The effects of solution properties on electrospinning of ultrafine poly(ethylene oxide) fibers. Polymer 45:2959–2966
Carroll CP, Joo YL (2008) Axisymmetric instabilities of electrically driven viscoelastic jets. J Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech 153:130–148
Marra KG, Chapman TM, Orban JM (1996) Determination of low critical surface tensions of novel fluorinated poly(amide urethane) block copolymers. 3 Siloxane-containing side chains. Macromol 29:7553–7558
Rimdusit S, Benjapan W, Assabumrungrat S, Takeichi T, Yokota R (2007) Surface segregation of siloxane containing component in polysiloxane-block-polyimide and s-BPDA/ODA polyimide blends. Polym Eng Sci 47:489–498
Wohl CJ, Atkins BM, Belcher MA, Connell JW (2012) Synthesis, characterization, topographical modification, and surface properties of copoly(imide siloxane)s. High Perform Polym 24:40–49
Novak I, Sysel P, Popelka A, Spirkova M, Sedlıa J, Hodak I, Kleınova A, Matyasovsky J (2011) Adhesion and surface energy of polyimide-based copolymer. Forest Wood Technol 75:142–147
Quere D (2002) Surface chemistry: Fakir droplets. Nat Mater 1:14–15
Singh A, Steely L, Allcock HR (2005) Poly[bis(2,2,2-trifluoroethoxy)phosphazene Superhydrophobic Nanofibers. Langmuir 21:11604–11607
Pei X, Chen G, Fang X (2013) Synthesis and properties of poly(imide siloxane) block copolymers with different block. J Appl Polym Sci 129:3718–3727
Ribeiro CR, Freeman BD, Kalika DS, Kalakkunnath S (2013) Pervaporative separation of aromatic/aliphatic mixtures with poly(siloxane-co-imide) and poly(ether-co-imide) membranes. Ind Eng Chem Res 52:8906–8916
Ghosh A, Banerjee S, Wang DY, Komber H, Voit B (2012) Synthesis, characterization, and properties of new siloxane grafted copolyimides. J Appl Polym Sci 123:2959–2967
Yamada Y, Furukawa N (1997) Preparation and characterization of siloxane-imide block copolymers based on 3,3′,4,4′benzophenonetetracarboxylic dianhydride. Polym Journal 29:923–930
Arnold CA, Summers JD, Chen YP, Bott RH, Chen D, McGrath JE (1989) Structure-property behaviour of soluble polyimide-polydimethylsiloxane segmented copolymers. Polymer 30:986–995
Wohl CJ, Atkins BM, Belcher MA, Connell JW Copoly(imide siloxane) abhesive materials with varied siloxane oligomer length. National Aeronautics and Space Administration Conference proceedings
Feng D, Wilkes GL, Crivello JV (1989) Structure-property behavior of free radical synthesized polydimethylsiloxane-polystyrene multiblock polymers: 1. Effect of the siloxane block length. Polymer 30:1800–1813
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Marmara University, Commission of Scientific Research Project under grant Project FEN-E-090113-0006.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oktay, B., Toker, R.D. & Kayaman-Apohan, N. Superhydrophobic behavior of polyimide–siloxane mats produced by electrospinning. Polym. Bull. 72, 2831–2842 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-015-1438-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-015-1438-9