Abstract
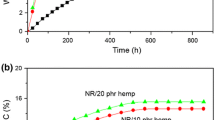
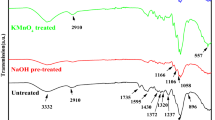
The obtaining and characterization of polymer composites based on natural rubber and hemp, in which the elastomer crosslinking has been achieved with benzoyl peroxide, are presented. The mechanical characteristics, gel fraction, crosslink density, water uptake swelling parameters and FTIR of the composites based on natural rubber and hemp fiber vulcanized by dibenzoyl peroxide have been investigated as a function of the hemp content. The hardness, modulus at 100 % elongation, tearing strength, tensile strength and elongation at break have been improving with the increasing of fiber content in composites materials due to the better interaction of fiber in natural rubber composites. These results indicate that hemp has a reinforcing effect on natural rubber. Gel fraction value is over 95 % for all blends and varies irregularly depending on the amount of hemp in the composites. The crosslinking density (ν) of samples increases as the amount of hemp in blends increases, because hemp act as a filler in natural rubber blends and leads to reinforcement of the blends. The water uptake and swelling parameters also increases with the increasing of the amount of fiber content, because of the hemp hydrophilic characteristics.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hussain AI, Abdel-Kader AH, Ibrahim AA (2010) Effect of modified linen fiber waste on physico-mechanical properties of polar and non-polar rubber. Nat Sci 8(7):82–93
Karus M, Vogt D (2004) European hemp industry: cultivation, processing and product lines. Euphytica 140:7–12
Osabohien E, Egboh SHO (2008) Utilization of bowstring hemp fiber as a filler in natural rubber compounds. J Appl Polym Sci 107(1):210–214
Van Duin M (2002) Chemistry of EPDM cross-linking. Kautsch Gummi Kunstst 55(4):150–156
Hertz DL Jr (1984) Elastomerics. Theory and practice of vulcanization. A Publication of Communication Channels Inc, USA
Stelescu MD, Georgescu M, Manaila E (2010) Aspects regarding crosslinking of a natural rubber blend. In: Proceedings of the 3rd international conference advanced materials and systems ICAMS 2010, 16–18 September, Bucharest, Romania, 313–318
Manaila E, Stelescu MD, Craciun G (2011) Characteristics of natural rubber blends vulcanized with electron beam and microwave. Leather Footwear J 11(1):43–52
Mathew NM (2001) Natural rubber. In: White JR, De SK (eds) Rubber technologist’s handbook. Rapra Technology Limited, Shropshire, UK, p 38
Dluzneski PR (2001) Peroxide vulcanization of elastomers. Rubber Chem Technol 74:451–492
Stelescu MD, Manaila E, Zuga N (2011) The use of polyfunctional monomers in the radical cure of chlorinated polyethylene. Polym J 43(9):792–800
Stelescu MD, Manaila E, Craciun G, Zuga N (2012) Crosslinking and grafting ethylene vinyl acetate copolymer with accelerated electrons in the presence of polyfunctional monomers. Polym Bull 68(1):263–285
Quirk RP (1988) Overview of curing and crosslinking of elastomers. Prog Rubber Plast Technol 4(1):31–45
Ogunniyi DS (1999) Peroxide vulcanisation of rubber. Prog Rubber Plast Technol 15(2):95–112
Van Duin M, Dees M, Dikland H (2008) Advantages of EPDM rubber products with a third monomer Part I—improved peroxide curing efficiency in window gasket applications. Kautsch Gummi Kunstst 49:233–243
Kalia S, Kumar A, Kaith BS (2011) Sunn hemp cellulose graft copolymers polyhydroxybutyrate composites: morphological and mechanical studies. Adv Mater Lett 2(1):17–25
Stelescu MD, Manaila E, Craciun G, Dumitrascu M (2014) New green polymeric composites based on hemp and natural rubber processed by electron beam irradiation. Sci World J 2014:684047-1–684047-13
Manaila E, Craciun G, Stelescu MD, Ighigeanu D, Ficai M (2014) Radiation vulcanization of natural rubber with polyfunctional monomers. Polym Bull 71(1):57–82
Paul A, Joseph K, Thomas S (1997) Effect of surface treatments on the electrical properties of low-density polyethylene composites reinforced with short sisal fibers. Compos Sci Technol 57(1):67–79
Joseph K, Thomas S, Pavithran C (1996) Effect of chemical treatment on the tensile properties of short sisal fibre-reinforced polyethylene composites. Polymer 37(23):5139–5149
Kumar R, Obrai S, Sharma A (2011) Chemical modifications of natural fiber for composite material. Pelagia Research Library, Der Chemica Sinica 2(4):219–228
Bledzki AK, Gassan J (1999) J Composites reinforced with cellulose based fibres. Prog Polym Sci 24(2):221–274
Espert A (2003) Natural fibres/polypropylene composites from residual and recycled materials: surface modification of cellulose fibers, properties and environmental degradation. Thesis KTH Fiber—och polymerteknologi, pp 1–5
Lopez-Manchado MA, Herrero B, Arroyo M (2003) Preparation and characterization of organoclay nanocomposites based on natural rubber. Polym Int 52(7):1070–1077
Chenal JM, Chazeau L, Guy L, Bomal Y, Gauthier C (2007) Molecular weight between physical entanglements in natural rubber: a critical parameter during strain-induced crystallization. Polymer 48(4):1042–1046
Kraus G (1963) Swelling of filler-reinforced vulcanizates. J Appl Polym Sci 7(3):861–871
Mathew L, Ulahannan J, Joseph R (2006) Effect of curing temperature, fibre loading and bonding agent on the equilibrium swelling of isora-natural rubber composites. Compos Interface 13(4–6):391–401
Jacob M, Thomas S, Varughese KT (2004) Mechanical properties of sisal/oil palm hybrid fiber reinforced natural rubber composites. Compos Sci Technol 64(7–8):955–965
Geethamma VG, Thomas S (2004) Transport of organic solvents through coir-fiber-reinforced natural rubber composites: a method for evaluating interfacial interaction. J Adhes Sci Technol 18(8):951–966
Dong Z, Liu M, Jia D, Zhou Y (2013) Synthesis of natural rubber-g-maleic anhydride and its use as a compatibilizer in natural rubber/short nylon fiber composites. Chin J Polym Sci 31(8):1127–1138
Mathew L, Joseph KU, Joseph R (2006) Swelling behaviour of isora/natural rubber composites in oils used in Automobiles. Bull Mater Sci 29(1):91–99
Ismail H, Edyham MR, Wirjosentono B (2002) Bamboo fibre filled natural rubber composites: the effects of filler loading and bonding agent. Polym Test 21(2):139–144
Yang HS, Kim HJ, Son J, Park HJ, Lee BJ, Hwang TS (2004) Rice-husk flour filled polypropylene composites; mechanical and morphological study. Compos Struct 63:305–312
Arroyo M, Lopez-Manchado MA, Herrero B (2003) Organo-montmorillonite as substitute of carbon black in natural rubber compounds. Polymer 44(8):2447–2453
Thomas S, Chan CH, Pothen LA, Joy J, Maria JH (2014) Natural rubber materials: composites and nanocomposites, Chapt. 5. In: Samsuri A (ed) Strength and durability of natural rubber and chemically modified natural rubber. The Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge, pp 172–173
Dhakal HN, Zhang ZY, Richardson MOW (2007) Effect of water absorption on the mechanical properties of hemp fibre reinforced unsaturated polyester composites. Compos Sci Technol 67(7–8):1674–1683
Ismail H, Edyham MR, Wirjosentono B (2001) Dynamic properties and swelling behaviour of bamboo filled natural rubber composites : the effect of bonding agent. Iran Polym J 10(6):377–383
Thomas S, Pothan LA (2009) Natural fibre reinforced polymer composites: from macro to nanoscale, Chapt. 10. In: John MJ, Anandjiwala RD, Thomas S (eds) Lignocellulosic fiber reinforced rubber composites. Old City Publishing, Inc, Philadelphia, pp 255–258
Ciolacu D, Ciolacu F, Popa VI (2011) Amorphous cellulose—structure and characterization. Cellulose Chem Technol 45(1–2):13–21
Bodirlau R, Teaca CA (2009) Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and thermal analysis of lignocellulose fillers treated with organic anhydrides. Rom J Phys 54(1–2):93–104
Pang AL, Ismail H (2013) Tensile properties, water uptake and thermal properties of polypropylene/waste pulverized tire/kenaf (PP/WPT/KNF) composites. Bio Resour 8(1):806–817
Litvinov VM, De PP (2002) Spectroscopy of rubbers and rubbery materials, Chapt. 5. In: Infrared spectroscopy of rubbery materials. Rapra Technology Limited, Shropshire, pp 57, 84, 226
Ali AMM, Subban RHY, Bahron H, Winie T, Latif F, Yahya MZA (2008) Grafted natural rubber based polymer electrolytes: ATR-FTIR and conductivity studies. Ionics 14(6):491–500
Liang CY, Marchessault RH (1959) Infrared spectra of crystalline polysaccharides. I. Hydrogen bonds in native celluloses. J Polym Sci 37(132):385–395
Eng AH, Tanaka Y, Gan SN (1992) FTIR studies on amino groups in purified Hevea rubber. J Nat Rubber Res 7:152–155
Chaikumpollert O, Yamamoto Y, Suchiva K, Kawahara S (2012) Protein-free natural rubber. Colloid Polym Sci 290:331–338
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Manaila, E., Stelescu, M.D., Craciun, G. et al. Effects of benzoyl peroxide on some properties of composites based on hemp and natural rubber. Polym. Bull. 71, 2001–2022 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-014-1168-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-014-1168-4