Abstract
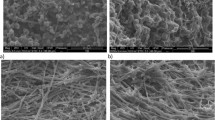
Microfibrillar composites from high-density polyethylene (HDPE-75 wt%) and polyamide-6 (PA6-25 wt%) were made through a reactive extrusion at the processing temperature of PA6 in combination with hot stretching to form microfibrillar composites, and injection molding at the melt temperature of HDPE to form final composites. The scanning electron microscope observations demonstrated the formation of the PA6 microfibers during extrusion. Incorporation of PA6 microfibers led to an improvement in both flexural and tensile properties as compared to the neat HDPE. Use of ethylene–glycidyl methacrylate copolymers (E-GMA) in the composites gave the highest tensile modulus, while ethylene, butyl acrylate and maleic anhydride terpolymer (E-BA-MA) led to the highest tensile strength and elongation. The maleic anhydride grafted polyethylene (MAPE) was the most efficient among three coupling agents in improving impact strength. With the addition of 5 wt% E-GMA, E-BA-MA and MAPE, the HDPE/PA6 composites exhibited an improvement of 87, 116, and 387 %, respectively, compared to the uncoupled controls. The PA6 microfibers exhibited a regular orientation along the stretching direction in the presence of 2.5 wt% coupling agents; increasing the loading level of coupling agents caused a reduction in the diameter of PA6 microfibers. FT-IR analyses showed the reactions between PA6 and the coupling agents used.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Scaffaro R, Mistretta MC, La Mantia FP, Gleria M, Bertani R, Samperi F, Puglisi C (2006) On the preparation and characterization of polyethylene/polyamide blends by melt processing in the presence of an ethylene/acrylic acid copolymer and of new phosphazene compounds. Macromol Chem Phys 207:1986–1997
Chandramouli K, Jabarin S (1995) Morphology and property relationships in ternary blends of polyethylene/polyamide-6/compatibilizing agents. Adv Polym Technol 14:35–46
Palabiyik M, Bahadur S (2000) Mechanical and tribological properties of polyamide-6 and high density polyethylene polyblends with and without compatibilizer. Wear 246:149–158
Yeh JT, Huang SS, Chen HY (2005) White spirit permeation resistance of polyethylene, polyethylene/modified polyamide, and polyethylene/blends of modified polyamide and ethylene vinyl alcohol bottles. Polym Eng Sci 45:25–32
Dencheva N, Oliveira MJ, Carneiro OS, Nunes TG, Denchev ZZ (2008) Preparation and properties of novel in situ composite materials based on polyethylene-polyamide oriented blends. Trans Tech Publ 515–519
Reyes-Lozano CA, Gudiño PO, González-Núñez R, Rodrigue D (2011) Preparation and characterization of HDPE/PA6 foam blends. J Cell Plast 47:153–172
Pan L, Inoue T, Hayami H, Nishikawa S (2002) Reactive blending of polyamide with polyethylene: pull-out of in situ-formed graft copolymers and its application for high-temperature materials. Polymer 43:337–343
Huang HX, Liao CM (2003) HDPE/PA6 blends: parison formation behaviour in extrusion blow molding. Polym Test 22:509–513
Li J, Yu X, Guo S (2007) Development of morphology and properties of injection-molded bars of HDPE/PA6 blends along flow direction. J Polym Sci Part B Polym Phys 45:184–195
Lin C, Sun H, Wang S, Huang J, Li J, Guo S (2010) In-process ultrasonic measurements of orientation and disorientation relaxation of high-density polyethylene/polyamide-6 composites with compatibilizer. J Appl Polym Sci 116:320–327
Dencheva N, Oliveira MJ, Carneiro OS, Pouzada AS, Denchev Z (2010) Preparation, structural development, and mechanical properties of microfibrillar composite materials based on polyethylene/polyamide 6 oriented blends. J Appl Polym Sci 115:2918–2932
Fellahi S, Favis B, Fisa B (1996) Morphological stability in injection-moulded high-density polyethylene/polyamide-6 blends. Polymer 37:2615–2626
Agrawal P, Rodrigues AWB, Araújo EM, Mélo TJA (2010) Influence of reactive compatibilizers on the rheometrical and mechanical properties of PA6/LDPE and PA6/HDPE blends. J Mater Sci 45:496–502
Filippone G, Dintcheva NT, Acierno D, La Mantia F (2008) The role of organoclay in promoting co-continuous morphology in high-density poly (ethylene)/poly (amide) 6 blends. Polymer 49:1312–1322
Evstatiev M, Fakirov S (1992) Microfibrillar reinforcement of polymer blends. Polymer 33:877–880
Fakirov S, Evstatiev M, Schultz J (1993) Microfibrillar reinforced composite from drawn poly (ethylene terephthalate)/nylon-6 blend. Polymer 34:4669–4679
Fakirov S, Evstatiev M (1994) Microfibrillar reinforced composites—new materials from polymer blends. Adv Mater 6:395–398
Evstatiev M, Nicolov N, Fakirov S (1996) Morphology of microfibrillar reinforced composites PET/PA 6 blend. Polymer 37:4455–4463
Monticciolo A, Cassagnau P, Michel A (1998) Fibrillar morphology development of PE/PBT blends: rheology and solvent permeability. Polym Eng Sci 38:1882–1889
Evstatiev M, Fakirov S, Krasteva B, Friedrich K, Covas J, Cunha A (2002) Recycling of poly (ethylene terephthalate) as polymer–polymer composites. Polym Eng Sci 42:826–835
Pesneau I, Kadi AA, Bousmina M, Cassagnau P, Michel A (2002) From polymer blends to in situ polymer/polymer composites: morphology control and mechanical properties. Polym Eng Sci 42:1990–2004
Li ZM, Yang W, Xie BH, Shen KZ, Huang R, Yang MB (2004) Morphology and tensile strength prediction of in situ microfibrillar poly (ethylene terephthalate)/polyethylene blends fabricated via slit-die extrusion-hot stretching-quenching. Macromol Mater Eng 289:349–354
Jiang CH, Zhong GJ, Li ZM (2007) Recyclability of in situ microfibrillar poly(ethylene terephthalate)/high-density polyethylene blends. Macromol Mater Eng 292:362–372
Xu HS, Li ZM, Wang SJ, Yang MB (2007) Rheological behavior of PET/HDPE in situ microfibrillar blends: influence of microfibrils’ flexibility. J Polym Sci Part B Polym Phys 45:1205–1216
Jayanarayanan K, Thomas S, Joseph K (2008) Mechanical and thermal properties of microfibrillar polymer–polymer composites. J Polym Mater 25:381–386
Evstatiev M, Angelov I, Friedrich K (2010) Structure and properties of microfibrillar-reinforced composites based on thermoplastic PET/LDPE blends after manufacturing by means of pultrusion. Polym Eng Sci 50:402–410
Jayanarayanan K, Thomas S, Joseph K (2011) In situ microfibrillar blends and composites of polypropylene and poly (ethylene terephthalate): morphology and thermal properties. J Polym Res 18:1–11
Jayanarayanan K, Thomas S, Joseph K (2012) Effect of blend ratio on the mechanical and sorption behaviour of polymer–polymer microfibrillar composites from low-density polyethylene and polyethylene terephthalate. J Reinf Plast Comp 31:549–562
Denchev Z, Dencheva N, Funari SS, Motovilin M, Schubert T, Stribeck N (2010) Nanostructure and mechanical properties studied during dynamical straining of microfibrillar reinforced HDPE/PA blends. J Polym Sci Part B Polym Phys 48:237–250
Liu H, Wu Q, Zhang Q (2009) Preparation and properties of banana fiber-reinforced composites based on high density polyethylene (HDPE)/Nylon-6 blends. Bioresour Technol 100:6088–6097
Liu H, Yao F, Xu Y, Wu Q (2010) A novel wood flour-filled composite based on microfibrillar high-density polyethylene (HDPE)/Nylon-6 blends. Bioresour Technol 101:3295–3297
Yao F, Wu Q (2010) Coextruded polyethylene and wood-flour composite: effect of shell thickness, wood loading, and core quality. J Appl Polym Sci 118:3594–3601
Kim B-J, Yao F, Han G, Wang Q, Wu Q (2013) Mechanical and physical properties of core-shell structured wood plastic composites: effect of shells with hybrid mineral and wood fillers. Compos Part B Eng 45:1040–1048
Sirisinha K, Meksawat D (2005) Preparation and properties of metallocene ethylene copolymer crosslinked by vinyltrimethoxysilane. Polym Int 54:1014–1020
Fornes TD, Paul DR (2003) Crystallization behavior of nylon 6 nanocomposites. Polymer 44:3945–3961
Balasuriya PW, Ye L, Mai YW (2001) Mechanical properties of wood flake-polyethylene composites. Part I: effects of processing methods and matrix melt flow behaviour. Compos Part A Appl S 32:619–629
Wilkinson A, Clemens ML, Harding VM (2004) The effects of SEBS-g-maleic anhydride reaction on the morphology and properties of polypropylene/PA6/SEBS ternary blends. Polymer 45:5239–5249
Huang Y, Jiang S, Wu L, Hua Y (2004) Characterization of LLDPE/nano-SiO <sub> 2 </sub> composites by solid-state dynamic mechanical spectroscopy. Polym Test 23:9–15
Tajvidi M, Falk RH, Hermanson JC (2006) Effect of natural fibers on thermal and mechanical properties of natural fiber polypropylene composites studied by dynamic mechanical analysis. J Appl Polym Sci 101:4341–4349
Liu H, Wu Q, Han G, Yao F, Kojima Y, Suzuki S (2008) Compatibilizing and toughening bamboo flour-filled HDPE composites: mechanical properties and morphologies. Compos Part A Appl S 39:1891–1900
Koulouri EG, Georgaki AX, Kallitsis JK (1997) Reactive compatibilization of aliphatic polyimides with functionalized polyethylenes. Polymer 38:4185–4192
Qu C, Su R, Zhang Q, Du R, Fu Q (2008) Effect of ethylene-acrylate-(maleic anhydride) terpolymer on mechanical properties and morphology of poly(ethylene terephthalate)/polyamide-6 blends. Polym Int 57:139–148
Acknowledgments
This study is financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project No. 31010103905), Louisiana Board of Regents (Contract Number: LEQSF-EPS (2011)-OPT-IN-04), Chinese National Science and Technology Support Program (No. 2012BAD32B04), Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University of Ministry of Education of China (No. NCET-11-0608), and Korea Forest Research Institute (LSU AgCenter Project).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, T., Wang, Q., Xie, Y. et al. Effects of use of coupling agents on the properties of microfibrillar composite based on high-density polyethylene and polyamide-6. Polym. Bull. 71, 685–703 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-013-1086-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-013-1086-x