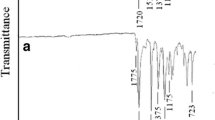
Abstract
High-performance alicyclic-containing polyimides for advanced applications, derived from 5-(2,5-dioxotetrahydrofurfuryl)-3-methyl-3-cyclohexene-1,2-dicarboxylic acid anhydride or bicyclo[2.2.2]oct-7-ene-2,3,5,6-tetracarboxylic dianhydride and two flexible aromatic diamines, were synthesized by a classical two-step polycondensation reaction and analyzed by rheological method. The results were discussed according to the chemical structure of polyimides and their different properties, such as flexibility, hydrophobicity and surface morphology. It has been showed that the obtained parameters, controlled by the interactions occurring in the polyimide systems, can be correlated with the adhesion/cohesion of blood components and plasma proteins. Thus, the results of the work of spreading proteins on the hydrophobic polyimide surfaces indicated that albumin is not absorbed preferentially, while fibrinogen is characterized by a higher degree of adhesion on the surfaces, and also that selective adsorption of plasma proteins modifies blood compatibility. In addition, these results and the ascertained antimicrobial activity of the studied polyimides contribute to the development of new applications in the bio-technical field.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ando S (2004) Optical properties of fluorinated polyimides and their applications to optical components and waveguide circuits. J Photopolym Sci Technol 17:219–232
Maier G (2001) Low dielectric constant polymers for microelectronics. Prog Polym Sci 26:3–65
Gonzalo B, Vilas JL, Breczewski T, Perez-Jubindo MA, De La Fuente MR, Rodriguez M, Leon LM (2009) Synthesis, characterization, and thermal properties of piezoelectric polyimides. J Polym Sci Part A Polym Chem 47:722–730
Wang S, Zhou HW, Dang GD, Chen C (2009) Synthesis and characterization of thermally stable, high-modulus polyimides containing benzimidazole moieties. J Polym Sci Part A Polym Chem 47:2024–2031
Zhang QX, Naito K, Tanaka Y, Kagawa Y (2008) Grafting polyimides from nanodiamonds. Macromolecules 41:536–538
Chang CM, Chang CC (2008) Preparation and characterization of polyimide–nanogold nanocomposites from 3-mercaptopropyl-trimethoxysilane encapsulated gold nanoparticles. Polym Degrad Stabil 93:109–116
Hougham G, Tesoro G, Viehbeck A, Chapple-Sokolg JD (1994) Polarization effects of fluorine on the relative permittivity in polyimides. Macromolecules 27:5964–5971
Myung BY, Kim JS, Kim JJ, Yoon TH (2003) Synthesis and characterization of novel polyimides with 2,2-bis[4(4-aminophenoxy)phenyl]phthalein-3′,5′-bis(trifluoromethyl)anilide. J Polym Sci Part A Polym Chem 41:3361–3374
Yang CP, Hsiao SH, Wu KL (2003) Organosoluble and light-colored fluorinated polyimides derived from 2,3-bis(4-amino-2-trifluoromethylphenoxy)naphthalene and aromatic dianhydrides. Polymer 44:7067–7078
Yang CP, Su YY, Hsiao FZ (2004) Synthesis and properties of organosoluble polyimides based on 1,1-bis[4-(4-amino-2-trifluoromethylphenoxy)phenyl]cyclohexane. Polymer 45:7529–7538
Eichstadt AE, Ward TC, Bagwell MD, Farr IV, Dunson DL, McGrath JE (2002) Synthesis and characterization of amorphous partially aliphatic polyimide copolymers based on bisphenol-A dianhydride. Macromolecules 35:7561–7568
Chou CH, Reddy DS, Shu CF (2002) Synthesis and characterization of spirobifluorene-based polyimides. J Polym Sci Part A Polym Chem 40:3615–3621
Chung IS, Kim SY (2000) Soluble polyimides from unsymmetrical diamine with trifluoromethyl pendent group. Macromolecules 33:3190–3193
Hwang HJ, Li CH, Wang CS (2006) Dielectric and thermal properties of dicyclopentadiene containing bismaleimide and cyanate ester. Part IV. Polymer 47:1291–1299
Chern YT, Shiue HC (1997) Low dielectric constants of soluble polyimides derived from the novel 4,9-bis[4-(4-aminophenoxy)phenyl]diamantine. Macromolecules 30:5766–5772
Kreuz JA, Hsiao BS, Renner CA, Goff DL (1995) Crystalline homopolyimides and copolyimides derived from 3,3′,4,4′-biphenyltetracarboxylic dianhydride/1,3-bis(4-aminophenoxy)benzene/1,12-dodecanediamine. 1. Materials, preparation, and characterization. Macromolecules 28:6926–6930
Hulubei C, Popovici D (2011) Novel polyimides containing alicyclic units. Synthesis and characterization. Rev Roum Chim 56:209–215
Popovici D, Hulubei C, Cozan V, Lisa G, Bruma M (2012) Polyimides containing cycloaliphatic segments for low dielectric material. High Perform Polym 24:194–199
Cosutchi AI, Hulubei C, Stoica I, Ioan S (2010) Morphological and structural–rheological relationship in epiclon-based polyimide/hydroxypropylcellulose blend systems. J Polym Res 17:541–550
Cosutchi AI, Nica SL, Hulubei C, Homocianu M, Ioan S (2012) Effects of the aliphatic/aromatic structure on the miscibility, thermal, optical, and rheological properties of some polyimide blends. Polym Eng Sci 52:1429–1439
Nica SL, Hulubei C, Stoica I, Ioanid GE, Ioan S (2013) Surface properties and blood compatibility of some aliphatic/aromatic polyimide blends. Polym Eng Sci 53:263–272
Ioan S, Hulubei C, Popovici D, Musteata VE (2012) Origin of dielectric response and conductivity of some alicyclic polyimides. Polym Eng Sci. doi:10.1002/pen.23409
Cosutchi AI, Hulubei C, Stoica I, Ioan S (2011) A new approach for patterning epiclon-based polyimide precursor films using a lyotropic liquid crystal template. J Polym Res 18:2389–2402
Hamciuc E, Lungu R, Hulubei C, Bruma M (2006) New poly(imide-ether-amide)s based on epiclon. J Macromol Sci Part A Pure Appl Chem 43:247–258
Ioanid EG (2008) Ro Patent 122:166
van Oss CJ, Good RJ, Chaudhury MK (1988) Additive and nonadditive surface tension components and the interpretation of contact angles. Langmuir 4:884–891
Rankl M, Laib S, Seeger S (2003) Surface tension properties of surface-coatings for application in biodiagnostics determined by contact angle measurements. Colloid Surf B Biointerface 30:177–186
Vijayanand K, Deepak K, Pattanayak DK, Rama Mohan TR, Banerjee R (2005) Interpenetrating blood–biomaterial interactions from surface free energy and work of adhesion. Trends Biomater Artif Organs 18:73–83
Kwok SCH, Wang J, Chu PK (2005) Surface energy, wettability, and blood compatibility phosphorus doped diamond-like carbon films. Diamond Relat Mater 14:78–85
Agathopoulos S, Nikolopoulos P (1995) Wettability and interfacial interactions in bioceramic-body-liquid systems. J Biomed Mater Res Part A 29:421–429
van Oss CJ (1990) Surface properties of fibrinogen and fibrin. J Protein Chem 9:487–491
van Oss CJ (2003) Long-range and short-range mechanisms of hydrophobic attraction and hydrophilic repulsion in specific and aspecific interactions. J Mol Recognit 16:177–190
Wang KL, Liou WT, Liaw DJ, Huang ST (2008) High glass transition and thermal stability of new pyridine-containing polyimides: effect of protonation on fluorescence. Polymer 49:1538–1546
Wang H, Ugomori T, Tanaka K, Kita H, Okamoto KI, Suma Y (2000) Sorption and pervaporation properties of sulfonyl-containing polyimide membrane to aromatic/non-aromatic hydrocarbon mixtures. J Polym Sci Part B Polym Phys 38:2954–2964
Gupta K, Yaseen M (1997) Viscosity–temperature relationship of dilute solution of poly(vinyl chloride) in cyclohexanone and in its blends with xylene. J Appl Polym Sci 65:2749–2760
Bas C, Tamagna C, Pascal T, Alberola D (2003) On the dynamic mechanical behavior of polyimides based on aromatic and alicyclic dianhydrides. Polym Eng Sci 43:344–355
Sader JE, Chon JWM, Mulvaney P (1999) Calibration of rectangular atomic force microscope cantilevers. Rev Sci Instrum 70:3967–3969
Sader E, Pacifico J, Green CP, Mulvaney P (2005) General scaling law for stiffness measurement of small bodies with applications to the atomic force microscope. J Appl Phys 97:124903–124909
Noy A, Vezenov DV, Lieber CM (1997) Chemical force microscopy. Annu Rev Mater Sci 27:381–421
Labarre D (2001) Improving blood-compatibility of polymeric surfaces. Trends Biomater Artif Organs 15:1–3
Anderson JM (2001) Biological responses to materials. Annu Rev Mater Res 31:81–110
Ioan S, Filimon A (2012) Biocompatibility and antimicrobial activity of some quaternized polysulfones. In: Bobbarala V (ed) Antimicrobial agents, Book 2, Chap 13. InTech, Rijeka, pp 249–274
Albu RM, Avram E, Stoica I, Ioanid EG, Popovici D, Ioan S (2011) Surface properties and compatibility with blood of new quaternized polysulfones. J Biomater Nanobiotechol 2:114–123
Kawakami H, Takahashi H, Nagaoka S, Nakayama Y (2001) Albumin adsorption to surface of annealed fluorinated polyimide. Polym Adv Technol 12:244–252
Nagaoka S, Ashiba K, Kawakami H (2002) Interaction between biocomponents and surface modified fluorinated polyimide. Mater Sci Eng C 20:181–185
Reitsma S, Slaaf DW, Vink H, van Zandvoort MAMJ, oude Egbrink MGA (2007) The endothelial glycocalyx: composition, functions, and visualization. Pflugers Arch Eur J Physiol 454:345–359
Richardson RR Jr, Miller JA, Reichert WM (1993) Polyimides as biomaterials: preliminary biocompatibility testing. Biomaterials 14:627–635
HajjHassan M, Chodavarapu V, Musallam S (2008) NeuroMEMS: neural probe microtechnologies. Sensors 8:6704–6726
Ong Y-L, Razatos A, Georgiou G, Sharma MM (1999) Adhesion forces between E. coli bacteria and biomaterial surfaces. Langmuir 15:2719–2725
Hren J, Polanc S, Kočevar M (2008) The synthesis and transformations of fused bicyclo[2.2.2]octenes. ARKIVOC (Part (i): Special Issue ‘Reviews and Accounts), pp 209–231
Acknowledgments
The Romanian National Authority for Scientific Research (CNCS, UEFISCDI; Project PN-II-ID-PCE-2011-3-0937, No. 302/5.10.2011; 2013 phase) is contract grant sponsor.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ioan, S., Filimon, A., Hulubei, C. et al. Origin of rheological behavior and surface/interfacial properties of some semi-alicyclic polyimides for biomedical applications. Polym. Bull. 70, 2873–2893 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-013-0994-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-013-0994-0