Abstract
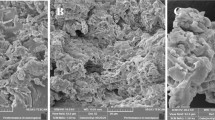
The adsorption of metal ions Cu2+ and Ni2+ from contaminated simulated water was studied using new starch/acryl amide-based hydrogels in the presence of lignin or peat to create an interpenetrating polymer network (IPN). The chemical structure of the materials was studied using infrared spectroscopy and their morphology was observed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The behavior of hydrogels in water and the water transport mechanisms were characterized using Fick’s law. Metal ion sorption was analyzed using inductively coupled plasma spectrometry. Hydrogels showed maximum water absorption values at about 100 h and all of them showed a Fickean water transport mechanism. On one hand, SEM confirmed that the new material is in fact an IPN and, on the other, that the internal porosity shown is responsible for the water absorption. On the other hand, the hydrophobic nature of the dispersed phase and its concentration in the hydrogel formulation seem to influence this process, which could also influence or facilitate the diffusion/sorption of metal ions. Peat-containing hydrogels showed a slightly lower absorption capacity of these ions than lignin-containing formulations. These hydrogels have a high potential to obtain metal ion-collector membranes.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jirgensons B (1970) Organic colloids. Elsevier, New York
Kickelbick G (2003) Concepts for the incorporation of inorganic building blocks into organic polymers on a nanoscale. Prog Polym Sci 28:83–114
Bhattacharya A, Misra BN (2004) Grafting: a versatile means to modify polymers: techniques, factors and applications. Prog Polym Sci 29:767–814
Mahmoud MN, Ahmed Hegazy El-S (2004) Preparation and applications of ion exchange membranes by radiation-induced graft copolymerization of polar monomers onto non-polar films. Prog Polym Sci 29:499–561
Paulino AT, Campese GM, Favaro SL, Guilherme MR, Tambourgi EB, Muniz EC (2007) Water absorption profile of PAAm-co-PNIPAAm/chitosan hydrogel with sandwich-like morphology. e-Polymers 122:1–14
Brown PA, Gill SA, Allen SJ (2000) Metal removal from wastewater using peat. Water Res 34:3907–3916
Guo X, Zhang S, Sahn XQ (2007) Adsorption of metal ions on lignin. J Hazard Mater 151:134–142
Mohan D, Pittman CU, Steele PH (2006) Single, binary and multi-component adsorption of copper and cadmium from aqueous solutions on Kraft lignin—a biosorbent. J Colloid Interface Sci 297:489–504
Qin F, Wen B, Shan XQ, Xie YN, Liu T, Zhang SZ, Khan SU (2006) Mechanisms of competitive adsorption of Pb, Cu, and Cd on peat. Environ Pollut 144:669
Essawy HA, Ibrahim HS (2004) Synthesis and characterization of poly(vinylpyrrolidone-co-methylacrylate) hydrogel for removal and recovery of heavy metal ions from wastewater. React Funct Polym 61:421–432
Andrzejewska E (2001) Photopolymerization kinetics of multifunctional monomers. Prog Polym Sci 26:605–665
Pallab R, Aliasgar Sh (2009) Multiparticulate formulation approach to pulsatile drug delivery: current perspectives. J Control Release 134:74–80
Garcia DM, Escobar JL, Noa Y, Bada N, Hernández E, Katime I (2004) Timolol maleate release from pH-sensible poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate-co-methacrylic acid) hydrogels. Eur Polym J 40:1683–1690
Pilar J, Krız J, Meissner B, Kadlec P, Pradny M (2009) Effect of structure of HEMA–DEGMA hydrogel matrix on difusión coefficients of PEG tracers. Variation of hydrogel crosslink density by change of polymer concentration. Polymer 50:4543–4551
Fornasiero F, Tang D, Boushehri A, Prausnitz J, Radke CJ (2008) Water diffusion through hydrogel membranes. A novel evaporation cell free of external mass-transfer resistance. J Membr Sci 320:423–430
Wang K, Xing B (2004) Mutual effects of cadmium and phosphate on their adsorption and desorption by goethite. Environ Pollut 127:13–20
Qin F, Wen B, Shan X-Q, Xie Y-N, Liu T, Zhang S-Z, Khan SU (2006) Mechanisms of competitive adsorption of Pb, Cu, and Cd on peat. Environ Pollut 144:669–680
Acknowledgments
Authors wish to thank specially to the Foundation Institute of Engineering in Caracas (F.I.I.) for allowing us to use the installations of the Center of Materials to make the ICP analyses. Polymer Group of Simón Bolívar University (GPUSB) for allowing the use of infrared spectrophotometer. At the same time, we wish to thank to Lic. Gleen Rodríguez from Center of Surface Engineering (C.I.S) of the Simon Bolivar University for SEM analyses. The authors also thank Decanato de Investigación y Desarrollo DID Universidad Simón Bolívar for financial support (Fondo de Trabajo PPI).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peñaranda A., J.E., Sabino, M.A. Effect of the presence of lignin or peat in IPN hydrogels on the sorption of heavy metals. Polym. Bull. 65, 495–508 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-010-0264-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-010-0264-3