Abstract
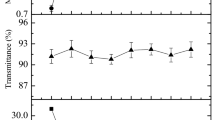
A novel and thin polyolefin hazy film with high haze (>75%), low gloss, and high light transmittance was prepared by the blending polyethylene (PE) with polypropylene (PP) rather than the reverse applying measurements which improved clarity, although Chen and Lue et al. (Annual Technical Conference Proceedings of SPE (2004), pp 2117–2121 and 2140–2143) employed blending to reduce haze. This study also presents the low melt flow rate, high density PE1 blending with PP1, and the blending ratio of 50/50 (wt/wt), are the key factors to prepare the novel polyolefin hazy film. The major origin of total haze of the hazy film was explored. It is found that surface haze is the overwhelming majority of total haze, which is opposite to earlier works about the source of total haze of the films prepared from polymer blend. That rough surface textures was the intrinsic source yielding surface haze, and also huge surface roughness degree (Ra) was the reason of the excellent haze properties in the hazy film, was confirmed based on haze measurement, surface topology images and Ra data from haze instrument, optical microscopy, and atomic force microscope, respectively.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Huck ND, Clegg PL (1961) The effect of extrusion variables on the fundamental properties of tubular polythene film. SPE Trans 1:121–132
Perron PJ, Lederman PB (1972) The effect of molecular weight distribution on polyethylene film properties. Polym Eng Sci 12:340–345
Minoru R (1979) Influence of shearing history on the rheological properties and processability of branched polymers. J Appl Polym Sci 23:463–471
Ashizawa H, Spruiell JE, White JL (1984) Investigation of optical clarity and crystalline orientation in polyethylene tubular film. Polym Eng Sci 24:1035–1042
Patel R, Ratta V, Saavedra P et al (2005) Surface haze and surface morphology of blown film compositions. J Plast Film Sheeting 21:217–231
Fatahi S, Ajji A, Lafleur PG (2005) Correlation between structural parameters and property of PE blown films. J Plast Film Sheeting 21:281–305
Khanarian G (2000) Rubber toughened and optically transparent blends of cyclic olefin copolymers. Polym Eng Sci 40:2590–2601
Trezza TA, Krochta JM (2001) Specular reflection, gloss, roughness and surface heterogeneity of biopolymer coatings. J Appl Polym Sci 79:2221–2229
Darncholvichit M (2003) Haze band formation and morphological composition in blown film extrusion. University of Massachusetts Lowell, Lowell
Wang L, Kamal MR, Rey AD (2001) Light transmission and haze of polyethylene blown thin films. Polym Eng Sci 41:358–372
Rinker JW (1979) Surface properties of blown low density polyethylene films. Paper Synthetics Conference, Proceedings of the Technical Association of the Pulp and Paper Industry, Washington, DC, USA, pp 129–136
Stehing FC, Speed CS, Westerman L (1981) Causes of haze of low-density polyethylene blown films. Macromolecules 14:698–708
Hobbs SY, Pratt CF (1982) Development of surface texture in blown polypropylene film. Polym Eng Sci 22:594–600
Audureau J, Morese-Seguela B, Constantin D et al (1986) Prediction and improvement of surface properties of tubular low density polyethylene films. J Plast Film Sheeting 2:298–309
Bheda JH, Spruiell JE (1986) Effect of process and polymer variables on the light transmission properties of polypropylene tubular blown films. Polym Eng Sci 26:736–745
Pucci MS, Shroff RN (1986) Correlation of blown film optical properties with resin properties. Polym Eng Sci 26:569
White JL, Cakmak M (1988) Orientation, crystallization, and haze development in tubular film extrusion. Adv Polym Technol 8:27–61
Tse A, Laakso R, Baer EHA (1991) Translucent blends of chlorinated polyethylene with poly(vinyl chloride). J Appl Polym Sci 42:1205–1211
Yilmazer U (1991) Effects of the processing conditions and blending with linear low-density polyethylene on the properties of low-density polyethylene films. J Appl Polym Sci 42:2379–2384
Larena A, Gabriel P (1993) Effect of surface roughness and crystallinity on the light scattering of polyethylene tubular blown films. Polym Eng Sci 33:742–747
Paul DR, Bucknall CB (2002) Polymer blends: performance, vol 2. Science Press, Beijing (simplified Chinese edition)
Sukhadia AM, Rohlfing DC, Johnson MB et al (2002) A comprehensive investigation of the origins of surface roughness and haze in polyethylene blown films. J Appl Polym Sci 85:2396–2411
Lue CT, Kwalk TH, Li D et al (2004) Haze improvement with addition of HP-LDPE or HDPE part I—Blown film property comparison: Annual Technical Conference Proceedings of SPE, Chicago, IL, United States, pp 2140–2143
He J, Fan Y (1997) Control of surface gloss of plastic products. Plastics 26:38–43 (simplified Chinese)
Clampitt BH, German DE, Anspon HD (1969) Techniques for measuring surface and bulk optical properties of polyethylene films. Anal Chem 41:1306–1309
Speed CS (1982) Formulating blends of LLDPE and LDPE to design better film. Plast Eng 12:39–42
Alcia L, Gabriel P (1995) The effect of crystallinity on the light scattering of regenerated cellulose tubular films. Polym Eng Sci 35:1155–1160
Khan MB, Keener C (1996) An investigation of the spatial and optical behavior of biaxially drawn PET film. Polym Eng Sci 36:1290–1299
Smith PF, Chun I, Liu G et al (1996) Studies of optical haze and surface morphology of blown polyethylene films using atomic force microscopy. Polym Eng Sci 36:2129–2134
Kojima M, Magill JH, Lin JS et al (1997) Structure and morphology of biaxially oriented films of polyethylenes. Chem Mater 9:1145–1153
Alexander-Katz R, Barrera RG (1998) Surface correlation effects on gloss. J Polym Sci B Polym Phys 36:1321–1334
Johnson MB, Wilkes GL, Sukhadia AM et al (2000) Optical properties of blown and cast polyethylene films: surface versus bulk structural considerations. J Appl Polym Sci 77:2845–2864
Wang L, Huang T, Kamal MR et al (2000) Surface topography and gloss of polyolefin blown films. Polym Eng Sci 40:747–760
Bafna A, Beaucage G, Mirabella F et al (2001) Optical properties and orientation in polyethylene blown films. J Polym Sci B Polym Phys 39:2923–2936
Andreassen E, Larsen A, Nord-Varhaug K et al (2002) Haze of polyethylene films-effects of material parameters and clarifying agents. Polym Eng Sci 42:1082–1097
McLeod MA, Mier R (2004) Film blowing of a narrow molecular weight polyethylene. J Plast Film Sheeting 20:261
Maruhashi Y, Iida S (2001) Transparency of polymer blends. Polym Eng Sci 41:1987–1995
Chen HY, Li J, Sammler RL et al (2004) Haze improvement with addition of HP-LDPE or HDPE part II—mechanistic understanding. Annual Technical Conference Proceedings of SPE, pp 2117–2121
Opdahl A, Somorjai GA (2001) Stretched polymer surfaces: atomic force microscopy measurement of the surface deformation and surface elastic properties of stretched polyethylene. J Polym Sci B Polym Phys 39:2263–2274
Gonzalez VA, Alanis M, Guerrero C et al (2004) Surface roughness in dynamically crystallized isotactic polypropylene films. J Polym Sci B Polym Phys 42:646–655
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Zhongda Group Co., Nanjing, for supplying some resins, test apparatus, and samples employed in this study, and also thank to teacher, Fang Lan, fellow, Yang Feng and schoolmates, Xiao-Feng Yu and Ya-Juan Gao for their kindly support in writing and editing this paper and operating some apparatus.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, XY., Xiang, M. Formulating of a novel polyolefin hazy film and the origins of haze thereof. Polym. Bull. 64, 925–937 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-009-0229-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-009-0229-6