Abstract
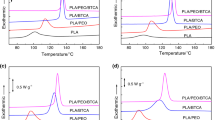
Crystallization, melting, hydrolytic degradation, and mechanical properties of poly(trimentylene terephthalate)/poly(lactic acid) (PTT/PLA) blends have been investigated. The blends show a single and composition-dependent glass-transition temperature (T g) over the entire composition range, implying that these blends are fully miscible in the amorphous state. The observed T g is found to increase with increasing PLA content and fitted well with the Gordon–Taylor equation, with the fitting parameter k being 0.91. The cold-crystallization peak temperature increases, while the melt-crystallization peak decreases with increasing the PLA content. Both the pure PTT and PTT/PLA blends cannot accomplish the crystallization during the cooling procedure and the recrystallization occurs again on the second heating. Therefore, on the thermogram recorded, there is exothermal peak followed by endothermal peak with a shoulder. However, to pure PLA, no crystallization takes place during cooling from the melt, therefore, no melting endothermic peak is found on the second heating curve. WAXD analysis indicates PLA and PTT components do not co-crystallize and the crystalline phase of the blends is that of their enriched pure component. With increasing PLA content, the hydrolytic degradation of the blend films increases, while both the tensile strength and the elongation at break of the blend films decrease. That is to say, the hydrolytic degradation of the PTT/PLA blends increases with the introduction of PLA at the cost of the decrease of the flexibility of PTT.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhuvanesh G, Nilesh R, Hilbornb J (2007) Poly(lactic acid) fiber: an overview. Prog Polym Sci 32:455–482
Ikada Y, Tsuji H (2000) Biodegradable polyesters for medical and ecological applications. Macromol Rapid Commun 21:117–132
Anderson JM, Shive MS (1997) Biodegradation and biocompatibility of PLA and PLGA microspheres. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 28:5–24
Jamshidi K, Hyon SH, Ikada Y (1988) Thermal characterizaton of polylactides. Polymer 29:2229–2234
Acar I, Özgümüş S, Kaşgöz A (2006) Nonisothermal crystallization kinetics and morphology of poly(ethylene terephthalate) modified with poly(lactic acid). Polym Plast Technol 45:351–359
Anderson KS, Hillmyer MA (2004) The influence of block copolymer microstructure on the toughness of compatibilized polylactide/polyethylene blends. Polymer 45:8809–8823
Narendra R, Digvijay N, Yang YQ (2008) Polylactic acid/polypropylene polyblend fibers for better resistance to degradation. Polym Degrad Stab 93:233–241
Biresaw G, Carriere C (2002) Interfacial tension of polylactic acid/polystyrene blends. J Polym Sci B Polym Phys 40:2248–2258
Hu Y, Rogunov M, Topolkaraev V et al (2003) Aging of poly(lactide)/poly(ethylene glycol) blends. Part 1. Poly(lactide) with low stereoregularity. Polymer 44:5701–5710
Xu H, Wang LH, Teng CQ et al (2008) Biodegradable composites: ramie fibre reinforced PLLA–PCL composite prepared by in situ polymerization process. Polym Bull 61:663–670
Zhang GB, Zhang JM, Wang SG et al (2003) Miscibility and phase structure of binary blends of polylactide and poly(methyl methacrylate). J Polym Sci Part B Polym Phys 41:23–30
Su ZZ, Guo WH, Liu YJ et al. (2009) Non-isothermal crystallization kinetics of poly(lactic acid)/modified carbon black composite. Polym Bull 62:629–642
Fathilah A, Chang YW, Kang SC (2009) Thermal, mechanical and rheological properties of poly(lactic acid)/epoxidized soybean oil blends. Polym Bull 62:91–98
Guerric EG, Eguiazábal JI, Nazabal (2007) Influence of compatibilization on the mechanical behavior of poly(trimethylene terephthalate)/poly(ethylene-octene) blends. J Eur Polym 43:1027–1037
Run MT, Wang YJ, Yao CG et al (2006) Non-isothermal crystallization kinetics of poly(trimethylene terephthalate)/poly(ethylene 2,6-naphthalate) blends. Thermochim Acta 447:13–21
Krutphun P, Supaphol P (2005) Thermal and crystallization characteristics of poly(trimethylene terephthalate)/poly(ethylene naphthalate) blends. Eur Polym J 41:1561–1568
Jafari SH, Yavari A, Asadinezhad A et al (2005) Correlation of morphology and rheological response of interfacially modified PTT/m–LLDPE blends with varying extent of modification. Polymer 46:5082–5093
Huang JM (2003) Polymer blends of poly(trimethylene terephthalate) and polystyrene compatibilized by styrene–glycidyl methacrylate copolymers. J Appl Polym Sci 88:2247–2252
Xue ML, Sheng J, Chuah HH et al (2004) Miscibility, morphology, and crystallization behavior of PTT/PC blends. J Macromol Sci Part B Polym Phys 43:1045–1061
Liang H, Xie F, Guo FQ et al (2008) Non-isothermal crystallization behavior of poly(ethylene terephthalate)/poly(trimethylene terephthalate) blends. Polym Bull 60:115–127
Liang H, Xie F, Chen B et al (2008) Miscibility and melting behavior of poly(ethylene terephthalate)/poly(trimethylene terephthalate) blends. J Appl Polym Sci 107:431–437
Brostow W, Chiu R, Kalogeras MI (2008) Prediction of glass transition temperatures: binary blends and copolymers. Mater Lett 62:3152–3155
Sirmoaon P, Dangseeyun N, Supaphol P (2004) Multiple melting behavior in isothermally crystallized poly(trimethylene terephthalate). Eur Polym J 40:599–608
Li HD, Nie W, Deng C (2009) Crystalline morphology of poly(L-lactic acid) thin films. Eur Polym J 45:123–130
Acar I, Durmuş A, Özgümüş S (2007) Nonisothermal crystallization kinetics and morphology of poly(ethylene terephthalate) modified with poly(lactic acid). J Appl Polym Sci 106:4180–4191
Supaphol P, Dangseeyun N, Thanomkiat P (2004) Thermal, crystallization, mechanical, and rheological characteristics of poly(trimethylene terephthalate)/poly(ethylene terephthalate) blends. J Polym Sci Polym Phys 42:676–686
Peesan M, Supaphol P, Rujiravanit R (2005) Preparation and characterization of hexanoyl chitosan/polylactide blend films. Carbohydr Polym 60:343–350
Acknowledgments
The financial support from the Scientific Research Foundation of Hubei Provincial Education Department (No: B200717003) and the Research Foundation of Wuhan University of Science and Engineering in China (No. 20073202) is greatly appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zou, H., Yi, C., Wang, L. et al. Crystallization, hydrolytic degradation, and mechanical properties of poly (trimethylene terephthalate)/poly(lactic acid) blends. Polym. Bull. 64, 471–481 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-009-0191-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-009-0191-3