Abstract
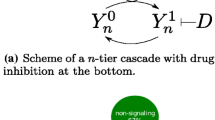
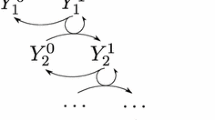
In this work, cellular signal transduction in an open cascade with forward activation was studied. By proposing a generic model which captures the common features of major existing models in the literature, it is showed how signaling profile changes during the propagation along the cascade. In particular, a typical OFF–ON–OFF switch-like transient behavior with prolonged temporary ON state is revealed, where OFF and ON represent the states of low level and high level concentrations, respectively. Analytically this phenomenon is closely related to uniform convergence of the active protein concentration of downstream cycles in the finite time range and its failure in the entire time domain. Consequently a classification of open signaling cascade which can sustain OFF–ON–OFF behavior in the far downstream cycles is accessible. Relevant biological issues, such as delayed activation of downstream reaction cycles, signal amplification and prolonged signal duration, to the generic model is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alon U (2007) An introduction to systems biology: design principles of biological circuits. Chapman & Hall/CRC, London
Arkin A (2000) Signal processing by biochemical reaction network. In: Wallczek J (eds) Self Organized biodynamics and nonlinear control. Cambridge University Press, London, pp 112–144
Behar M, Hao N, Dohlman H, Elston T (2007) Mathematical and computational analysis of adaptation via feedback inhibition in signal transduction pathways. Biophys J 93(3): 806–821
Berg HC, Brown DA (1972) Chemotaxis in escherichia coli analysed by three-dimensional tracking. Nature 239: 500–504
Chaves M, Sontag ED, Dinerstein RJ (2004) Optimal length and signal amplification in weakly activated signal transduction cascades. J Phys Chem B 108(39): 15311–15320
Chock P, Stadtman E (1977) Superiority of interconvertible enzyme cascades in metabolic regulation: analysis of multicyclic systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74(7): 2766–2770
Feldstein A, Iserles A, Levin D (1995) Embedding of delay equations into an infinite-dimensional ode system. J Differ Equ 117(1): 127–150
Goldbeter A (1991) A minimal cascade model for the mitotic oscillator involving cyclin and cdc2 kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88: 9107–9111
Goldbeter A, Koshland DE (1981) An amplified sensitivity arising from covalent modification in biological systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 78(11): 6840–6844
Gonze D, Goldbeter A (2000) A model for a network of phosphorylation-dephosphorylation cycles displaying the dynamics of dominoes and clocks. J Theor Biol 210: 167–186
Grubelnik V, Dugonik B, Osebik D, Marhl M (2009) Signal amplification in biological and electrical engineering systems: universal role of cascades. Biophys Chem 143(3): 132–138
Hale JK (1980) Ordinary differential equations, 2nd edn. Robert E. Krieger Publishing Co. Inc., Huntington
Hao N, Behar M, Parnell SC, Torres MP, Borchers CH, Elston TC, Dohlman HG (2007) A systems-biology analysis of feedback inhibition in the sho1 osmotic-stress-response pathway. Curr Biol 17(8): 659–667
Heinrich R, Neel BG, Rapoport TA (2002) Mathematical models of protein kinase signal transduction. Mol Cell 9(5): 957–970
Hohmann S (2002) Osmotic stress signaling and osmoadaptation in yeasts. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 66(2): 300–372
Li Y, Srividhya J (2010) Goldbeter-Koshland model for open signaling cascades: a mathematical study. J Math Biol 61: 781–803
Ma H, Zhao XM, Yuan YJ, Zeng AP (2004) Decomposition of metabolic network into functional modules based on the global connectivity structure of reaction graph. Bioinformatics 20(12): 1870–1876
Ma W, Trusina A, El-Samad H, Lim WA, Tang C (2009) Defining network topologies that can achieve biochemical adaptation. Cell 138(4):760–773. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2009.06.013. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0092867409007120
MacKeigan JP, Murphy LO, Dimitri CA, Blenis J (2005) Graded mitogen-activated protein kinase activity precedes switch-like c-fos induction in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol 25(11): 4676–4682
Magan S, Alon U (2003) Structure and function of the feed-forward loop network motif. Proc Natl Acad Sci 100(21): 11980–11985
Marhl M, Grubelnik V (2007) Role of cascades in converting oscillatory signals into stationary step-like responses. BioSystems 87: 58–67
Matthews HR, Reisert J (2003) Calcium, the two-faced messenger of olfactory transduction and adaptation. Curr Opin Neurobiol 13(4): 469–475
Michaelis L, Menten ML (1913) Die kinetik der invertinwirkung. Biochem Z 49(333–369): 352
Okamoto M, Takeda Y, Aso Y, Hayashi K (1983) Steady-state approximation of enzyme activation and inhibition. Biotechnol Bioeng 25(6): 1453–1463
Ossareh HR, Ventura AC, Merajver SD, Vecchio DD (2011) Long signaling cascades tend to attenuate retroactivity. Biophys J 100(7): 1617–1626
Qu Z, Vondriska TM (2009) The effects of cascade length, kinetics and feedback loops on biological signal transduction dynamics in a simplified cascade model. Phys Biol 6(1): 016007
Segel IH (1975) Enzyme Kinetics. Behavior and analysis of rapid-equilibrium and steady-state enzyme systems. Wiley-Interscience, New York
Smith HL (1995) Monotone dynamical systems: an introduction to the theory of competitive and cooperative systems. Math Surv Monogr 41: 174
Srividhya J, Gopinathan M, Schnell S (2007) The effects of time delays in a phosphorylation–dephosphorylation pathway. Biophys Chem 125(2-3): 286–297
Srividhya J, Li Y, Pomerening J (2010) Open cascades as simple solutions to providing ultrasensitivity and adaptation in cellular signaling. Phys Biol 61: 781–803
Tyson J (1975) Classification of instabilities in chemical reaction systems. J Chem Phys 62: 1010
Ventura AC, Sepulchre JA, Merajver SD (2008) A hidden feedback in signaling cascades is revealed. PLoS Comput Biol 4(3): e1000041
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y. A generic model for open signaling cascades with forward activation. J. Math. Biol. 65, 709–742 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00285-011-0480-y
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00285-011-0480-y