Abstract
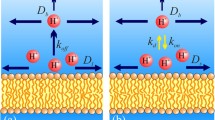
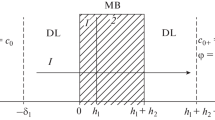
The phenomenological model developed in our recent publications [9,10] is used to investigate the kinetics of proton diffusion from a source to a detector on the membrane surface. In most cases the observed kinetics shows a single diffusional maximum with the exponential ascending front and the power-law descending tail. The kinetics depends on the distance between the source and the detector. If the detector is located inside the proton collecting antenna, the kinetics corresponds to the surface diffusion at the times near the maximum and shortly thereafter, and it turns into the bulk diffusion kinetics at longer times, after the equilibrium is established between the membrane surface and the bulk solution. If the detector is located outside the antenna, the kinetics corresponds to the bulk diffusion at all times where the signal is nonvanishing. What is seen at locations near the antenna radius depends on the exchange regime. In the regime of fast exchange between the surface and the bulk as compared to the bulk diffusion, the kinetics shows a single peak whose location is intermediate between the peaks for the surface and bulk diffusion. In the regime of slow exchange there are two maxima corresponding to the surface and bulk diffusion. In buffered solutions the antenna radius decreases with increasing buffer concentration, which changes the kinetics from the surface to bulk diffusion. The theory is applied to interprete recent experiments on a phospholipid membrane [25]. It is found that (i) the fast exchange regime is operating since only a single maximum is observed; (ii) the shift of the maximum toward longer times with increasing buffer concentration is a manifestation of the transition from the surface to bulk diffusion kinetics.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexiev, U., Marti, T., Heyn, M.P., Khorana, H.G., Scherrer, P.: Covalently bound pH-indicator dyes at selected extracellular or cytoplasmic sites in bacteriorhodopsin. 2. Rotational orientation of helices D and E and kinetic correlation between M formation and proton release in bacteriorhodopsin. Biochemistry 33, 13693–13699 (1994)
Alexiev, U., Mollaaghababa, R., Scherrer, P., Khorana, H.G., Heyn, M.P.: Rapid long-range proton diffusion along the surface and delayed proton transfer into the bulk. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92, 372–376 (1995)
Antonenko, Y.N., Pohl, P.: Coupling of proton source and sink via H+-migration along the membrane surface as revealed by double-patch clamp experiments. FEBS Lett. 429, 197–200 (1998)
Antonenko, Y.N., Pohl, P.: Unpublished results
Brandsburg-Zabary, S., Fried, O., Marantz, Y., Nachliel, E., Gutman, M.: Biophysical aspects of intra-protein tranfer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1458, 120–134 (2000)
Cherepanov, D.A., Junge, W., Mulkidjanian, A.Y.: Proton transfer dynamics at the membrane/water interface: Dependence on the fixed and mobile pH buffers, on the size and form of membrane particles, and on the interfacial potential barrier. Biophys. J. 86, 665–680 (2004)
Gabriel, B., Prats, M., Teissié, J.: Proton lateral conduction along a lipid monolayer spread on a physiological subphase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1186, 172–176 (1994)
Gabriel, B., Teissié, J.: Proton long-range migration along protein monolayers and its consequences on membrane coupling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93, 14521–14525 (1996)
Georgievskii, Y., Medvedev, E.S., Stuchebrukhov, A.A.: Proton transport via the membrane surface. Biophys. J. 82, 2833–2846 (2002)
Georgievskii, Y., Medvedev, E.S., Stuchebrukhov, A.A.: Proton transport via coupled surface and bulk diffusion. J. Chem. Phys. 116, 1692–1699 (2002)
Gradshteyn, I.S., Ryzhik, I.M.: Table of Integrals, Series, and Products. Academic Press, San Diego, 1994, Eq. 6.631.4
Gutman, M., Nachliel, E.: The dynamic aspects of proton transfer processes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1015, 391–414 (1990)
Gutman, M., Nachliel, E.: The dynamics of proton exchange between bulk and surface groups. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1231, 123–138 (1995)
Gutman, M., Nachliel, E.: Time resolved dynamics of proton transfer in proteous systems. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 48, 329–356 (1997)
Heberle, J., Dencher, N.A.: Surface-bound optical probes monitor proton translocation and surface potential charges during bacteriorhodopsin photocycle. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89, 5996–6000 (1992)
Heberle, J., Rielsle, J., Thiedemann, G., Oesterhelt, D., Dencher, N.A.: Proton migration along the membrane surface. Nature 370, 379–382 (1994)
Heberle, J.: Proton tranfer reactions across bacteriorhodopsin and along the membrane. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1458, 135–147 (2000)
Marantz, Y., Nachliel, E., Aagaard, A., Brzezinski, P., Gutman, M.: The proton collecting function of the inner surface of cytochrome c oxidase from Rhodobacter sphaeroides. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 8590–8595 (1998)
Nachliel, E., Gutman, M.: Quantitative evaluation of the dynamics of proton transfer from photoactivated bacteriorhodopsin to the bulk. FEBS Lett. 393, 221–225 (1996)
Nachliel, E., Gutman, M., Kiryati, S., Dencher, N.A.: Protonation dynamics of the extracellular and cytoplasmic surface of bacteriorhodopsin in the purple membrane. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93, 10747–10752 (1996)
Nemukhin, A.V., Grigorenko, B.L., Topol, I.A., Burt, S.K.: Quantum chemical simulations of the proton transfer in water wires attached to molecular walls. J. Phys. Chem. B 107, 2958-2965 (2003)
Pomès, R., Roux, B.: Molecular mechanism of H+ conduction in the single-file water chain of the gramicidin channel. Biophys. J. 82, 2304–2316 (2002)
Scherrer, P., Alexiev, U., Marti, T., Khorana, H.G., Heyn, M.P.: Covalently bound pH-indicator dyes at selected extracellular or cytoplasmic sites in bacteriorhodopsin. 1. Proton migration along the surface of bacteriorhodopsin micelles and its delayed transfer from surface to bulk. Biochemistry 33, 13684–13692 (1994)
Scherrer, P.: Proton movement on membranes. Nature 374, 222 (1995)
Serowy, S., Saparov, S.M., Antonenko, Y.N., Kozlovsky, W., Hagen, V., Pohl, P.: Structural proton diffusion along lipid bilayers. Biophys. J. 84, Part 1, 1031–1037 (2003)
Slevin, C.J., Unwin, P.R.: Lateral proton diffusion rates along stearic acid monolayers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 122, 2597–2602 (2000)
Teissié, J.: Lateral proton diffusion. Nature 379, 305–306 (1996)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The authors are grateful to Yu. N. Antonenko and A. I. Kotelnikov for helpful discussions.
This work was supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research (05-03-32104), U.S. Civilian Research and Development Foundation (RUC2-2658-MO-05), U. S. National Science Foundation, and U. S. National Institutes of Health.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Medvedev, E., Stuchebrukhov, A. Kinetics of proton diffusion in the regimes of fast and slow exchange between the membrane surface and the bulk solution. J. Math. Biol. 52, 209–234 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00285-005-0354-2
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00285-005-0354-2