Abstract.
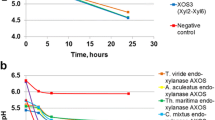
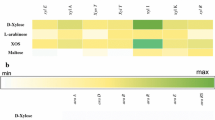
Fermentation of xylooligosaccharides by 11 strains of Selenomonas ruminantium was examined. Xylooligosaccharides were prepared by the partial hydrolysis of oat spelt xylan in dilute phosphoric acid (50 mM, 121°C, 15 min) and were added to a complex, yeast extract-Trypticase-containing medium. Strains of S. ruminantium varied considerably in their capacity to ferment xylooligosaccharides. Strains GA192, GA31, H18, and D used arabinose, xylose, and the oligosaccharides xylobiose through xylopentaose, as well as considerable quantities of larger, unidentified oligosaccharides. Other strains of S. ruminantium (HD4, HD1, 20-21a, H6a, W-21, S23, 5-1) were able to use only the simple sugars present in the substrate mixture. The ability of S. ruminantium strains to utilize xylooligosaccharides was correlated with the presence of xylosidase and arabinosidase activities. Both enzyme activities were induced by growth on xylooligosaccharides, but no activity was detected in glucose- or arabinose-grown cultures. Xylooligosaccharide-fermenting strains of S. ruminantium exhibited considerable variation in substrate utilization patterns, and the assimilation of individual carbohydrate species also appeared to be regulated. Lactic, acetic, and propionic acids were the major fermentation end products detected.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 2 August 1997 / Accepted: 18 September 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cotta, M., Whitehead, T. Xylooligosaccharide Utilization by the Ruminal Anaerobic Bacterium Selenomonas ruminantium . Curr Microbiol 36, 183–189 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002849900291
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002849900291