Abstract.
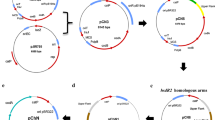
Three sporulation-specific genes (orfA, sigE, sigG) from Clostridium acetobutylicum ATCC 824 are arranged in a cluster, encoding the putative σE-processing enzyme, σE, and σG respectively. When they were transformed into Clostridium acetobutylicum while on a plasmid functional in this organism, transformants did not survive. Three kinds of recombinations were then attempted with nonreplicative plasmids: duplication of orfA and sigE, replacement of all of the three genes, and inactivation of orfA. While the wild-type strain ceased to grow and produce solvents in batch cultures after approximately 24 h, mutant strains were isolated that showed sustained growth for a much longer time and produced a threefold increase in acetone and butanol in test tube cultures. In addition, one of the derived strains showed a significantly higher growth rate. Features of the restriction maps of the recombinants did not correlate with expected maps, indicating possible complications occurring during the recombination events.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wong, J., Bennett, G. Recombination-Induced Variants of Clostridium acetobutylicum ATCC 824 with Increased Solvent Production. Curr Microbiol 32, 349–356 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002849900062
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002849900062