Abstract.
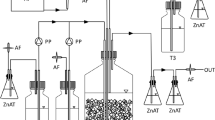
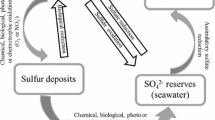
The spent caustic wastewater from the oxidation of sulfide present in offshore natural gas production mainly comprises thiosulfate and sulfate. A biocatalytic process, employing phototrophic green sulfur bacteria in symbiosis with sulfate-reducing bacteria, is described in this paper for the production of sulfur from the spent caustic wastewater, with synthetic wastewater as the model system. The process entails the conversion of thiosulfate to sulfur and sulfate by photosynthetic green sulfur bacteria Chlorobium vibrioforme f. thiosulfatophilum. Sulfate formed in turn is removed by Desulfovibrio desulfuricans to sulfide, which is further converted to sulfur by Chlorobium limicola through photooxidation. Sulfide is also oxidized to sulfur and sulfate via thiosulfate as an intermediate by Chlorobium vibrioforme f. thiosulfatophilum.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khanna, P., Rajkumar, B. & Jothikumar, N. Microbial Recovery of Sulfur from Thiosulfate-Bearing Wastewater with Phototrophic and Sulfur-Reducing Bacteria. Curr Microbiol 32, 33–37 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002849900006
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002849900006