Abstract
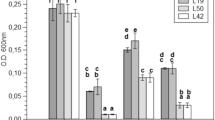
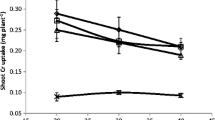
The current study aims evaluation of biosorption and symbiotic potential of horse gram plants associated with rhizobia inspite of Cobalt (Co) metal stress, and these rhizobia strains play a pivotal role in the phytoremediation of Co heavy metal-contaminated soils. Horse gram rhizobial isolates HGR-4, HGR-6, HGR-13 and HGR-25 were able to tolerate 1000 µg g−1 Co supplemented in culture media and also 100 µg g−1 in Co supplemented soil. The plants nodulated with the isolates from the study have shown higher nodulation, nitrogen and leghaemoglobin content in the potted experiment on par with the control plants. Atomic absorption spectroscopic analysis of Co content in horse gram plants inoculated with these four isolates showed maximum biosorption of Co among the bacterial root nodules. Application of these strains can be potentially aid the phytoextraction of Co from contaminated soils on association with horse gram plants.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beladi M, Habibi D, Kashani A, Paknejad F, Nooralvandi T (2011) Phytoremediation of lead and copper by Sainfoiin (Onobrychis vicifolia): role of antioxidant enzymes and biochemical biomarkers. Am Eurasian J Agric Environ Sci 3:440–449
Dary M, Chamber PMA, Palomares AJ, Pajuelo E (2010) “In situ” phytostabilisation of heavy metal polluted soils using Lupinus luteus inoculated with metal resistant plant-growth promoting rhizobacteria. J Hazard Mater 177:323–330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.12.035
Krujatz F, Haarstrick A, N€ortemann B, Greis T, (2011) Assessing the toxic effects of nickel, cadmium and EDTA on growth of the plant growth-promoting rhizobacterium Pseudomonas brassicacearum. Water Air Soil Pollut. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-011-0944-0
Michalak A (2006) Phenolic compounds and their antioxidant activity in plants growing under heavy metal stress. Pol J Env Stu 15:523–530
Rodionov DA, Hebbeln P, Gelfand MS, Eitinger T (2006) Comparative and functional genomic analysis of prokaryotic nickel and cobalt uptake transporters: evidence for a novel group of ATP-binding cassette transporters. J Bacteriol 188:317–327. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.188.1.317-327.2006
Macomber L, Hausinger RP (2011) Mechanisms of nickel toxicity in microorganisms. Metallomics 3:1153–1162. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1mt00063b
Pilon-Smits EA, Quinn CF, Tapken W, Malagoli M, Schiavon M (2009) Physiological functions of beneficial elements. Curr Opin Plant Biol 12:267–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2009.04.009
Zohny EA (2002) Cobalt in alluvial Egyptian soils as affected by industrial activities. J Environ Sci 14:34–38
Abd-Alla MH, Bagy MK, EI-Enany AE, Bashoudy SR (2014) Activation of R. Tibeticum with flavonoid enhances nodulation, nitrogen fixation and growth of fenugreek (Trigonella foenumgraecum L.) grown in cobalt polluted soil. Arch Environ Contamin Toxicol 66:303–315. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-013-9980-7
Oves M, Khan S, Qari H, Felemban N, Almeelbi T (2016) Heavy metals: biological importance and detoxification strategies. J Bioremed Biodegrad 7:334. https://doi.org/10.4172/2155-6199.1000334
Hao X, Taghavi S, Xie P, Orbach MJ, Alwathnani HA, Rensing C, Wei GH (2014) Phytoremediation of heavy and transition metals aided by legume-rhizobia Symbiosis. Int J Phytoremediat 16:179–202. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2013.773273
Ike A, Sriprang R, Ono H, Murooka Y, Yamashita M (2007) Bioremediation of cadmium contaminated soil using symbiosis between leguminous plant and recombinant rhizobia with the MTL4 and the PCS genes. Chemosphere 66:1670–1676. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.Chemosphere.2006.07.058
Vincent JM (1970) A manual for a practical study of root nodule bacteria. Blackwell Publications, Oxford
Edulamudi P, Antony Masilamani AJ, Vanga UR, Divi VRS, Konada VM (2021) Nickel tolerance and biosorption potential of rhizobia associated with horse gram [Macrotyloma uniflorum (Lam.) Verdc.]. Int J Phytoremediat 23:1184–1190. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2021.1884182
Tu JC, Ford RE, Garu CR (1970) Some factors affecting the nodulation and nodule efficiency in Soy beans infected by soybean mosaic virus. Phytopathology 60:1653–1656. https://doi.org/10.1094/Phyto-60-1653
AOAC (1978) Official and tentative methods of analysis. Association of official Agricultural Chemists, Washington
Nicholas DJD, Maruyama Y, Fisher DJ (1962) The effect of cobalt deficiency on the utilization of nitrate nitrogen in Rhizobium. Biochem Biophys Acta 56:623
Mysliva-Kurdziel B, Prasad MNV, Strzalka K (2004) Photosynthesis in heavy metal stressed plants. In: Prasad MNV (ed) Heavy metal stress in plants: from biomolecules to ecosystems. Springer, Berlin, pp 146–181
Lipskaya A (1972) Accumulation of chlorophyll in chloroplasts of cucumber leaves under the effect of cobalt and manganese applied separately and together. Biol Nauki 15:90–94
Minz A, Asha KS, Rakesh K, Kumar B, Kumar R (2018) A review on importance of cobalt in crop growth and production. Int J Curr Microbiol Appl Sci 7:2978–2984
Vaseer SG, Rasheed M, Ansar M, Bibi Y, Shah S, Hassan A, Durani LA, Asif M, Husnain Z (2020) Cobalt application improves the growth and development of mung bean. Pak J Agric Res 33:303–310. https://doi.org/10.17582/journal.pjar/2020/33.2.303.310
Awomi TA, Singh AK, Kumar M, Bordoloi LJ (2012) Effect of phosphorus, molybdenum and cobalt nutrition on yield and quality of mungbean (Vigna radiata L.) in acidic soil of Northeast India. Indian J Hill Farm 25(2):22–26
Ali B, Hayat S, Hayat Q, Ahmad A (2010) Cobalt stress affects nitrogen metabolism, photosynthesis and antioxidant system in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). J Plant Interact 3:223–231. https://doi.org/10.1080/17429140903370584
Akbar FM, Zafar M, Hamid A, Ahmed M, Khaliq A, Riaz Khan M, Rehman Z (2013) Interactive effect of cobalt and nitrogen on growth, nodulation, yield and protein content of field grown pea. Hortic Environ Biotechnol 54:465–474. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13580-013-0001-6
Atta-Aly MM (1998) Soaking summer squash seeds in low concentration of cobalt solution before sowing increased plant growth, femaleness and fruit yield via increasing plant ethylene level. J Plant Growth Regul 17:25–32. https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00007008
Bakken AK, Synnes OM, Hansen S (2004) Nitrogen fixation by red clover as related to the supply of cobalt and molybdenum from some Norwegian soils. Acta Agric Scand Sect B 54:97–101. https://doi.org/10.1080/09064710410024408
Arshiya A, Ajmat J (2020) Role of cobalt in plants: its stress and alleviation. In: Naeem M, Ansari A, Gill S (eds) Contaminants in agriculture. Springer, Cham
Yadav DV, Khanna SS (1988) Role of cobalt in nitrogen fixation: a review. Agric Rev 9:180–182
Mathur N, Singh J, Bohra A, Vyas A (2006) Effect of soil compaction potassium and cobalt on growth and yield of Moth Bean. Int J Soil Sci 1:269–271. https://doi.org/10.3923/ijss.2006.269.271
Balai CM, Majumdar SP, Kumawat BL (2005) Effect of soil compaction, potassium and cobalt on growth and yield of cowpea. Indian J Pulses Res 18(1):38–39
Younis M (2007) Responses of Lablab purpureus rhizobium symbiosis to heavy metals in pot and field experiments. World J Agric Sci 3(1):111–122
Abdel Wahab AM, Abd-Alla MH, El-Enany AE (1996) Stimulation of nodulation, nitrogen fixation and plant growth of Faba bean by cobalt and copper additions. In: Rodriguez-Barrueco C (ed) Fertilizers and environment. Springer, Dordrecht, p 66. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-009-1586-2-23
Hala K (2007) Effect of cobalt fertilizer on growth, yield and nutrients status of Faba bean (Vicia faba L.) plants. J App Sci Res 3(9):867–872
Yadav DV, Khanna SS (2002) Role of cobalt in nitrogen fixation -a review. Agricultural-Reviews 9:180–182
Mengel K, Kirkby EA (2001) Principles of plant nutrition, 5th edn. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, p 849. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-010-1009-2
Abd El-Moez MR, Gad N (2002) Effect of organic cotton compost and cobalt application on cowpea plants growth and mineral composition. Egypt J Appl Sci 17:426–440
Khan MR, Khan MM (2010) Effect of varying concentration of nickel and cobalt on the plant growth and yield of chickpea. Aust J Basic Appl Sci 4:1036–1046
Gad N, Mohammed AM, Bekbayeva LK (2013) Response of cowpea (Vigna Anguiculata) to cobalt nutrition. Middle East J Sci Res 14:177–184. https://doi.org/10.5829/idosi.mejsr.2013.14.2.2008
Jain V, Nainawatee H (2000) Cobalt reduces nitrate inhibition of nodulation in mung bean (Vigna radiata). Biol Fertil Soils 31:522–524. https://doi.org/10.1007/s003740000203
Basu M, Bhadoria PBS, Maha Patra SC (2006) Influence of microbial culture in combination with micronutrient in improving the groundnut productivity under alluvial soil of India. Acta Agric Slov 87:435–444
Almeida MG, Silveira CM, Guigliarelli B, Bertrand P, Moura JJ (2007) A needle in a haystack the active site of the membrane-bound complex cytochrome c nitrite reductase. FEBS Lett 581:284–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2006.12.023
Singh PK, Singh AK (2010) Response of mung bean (Vigna radiata L. Wilczek) in relation to micronutrients content and yield as affected by sulfur and cobalt application. Environ Ecol 28(1B):564–568
Jana PK, Sounda G (1994) Effect of cobalt and Rhizobium on yield, oil content and nutrient concentration in irrigated summer groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Indian J Agric Sci 64:630–632
Jayakumar K, Abdul Jaleel C, Azooz MM, Vijayarengan P, Gomathinayagam M, Panneerselvam R (2009) Effect of different concentrations of cobalt on morphological parameters and yield components of soybean. Glob J Mol Sci 4(1):10–14
Outten FW, Outten CE, Halloran T (2000) Metallo regulatory systems at the interface between bacterial metal homeostasis and resistance. In: Storz G, Hengge AR (eds) Bacterial stress responses. ASM Press, Washington, pp 29–42
Zaidi S, Usmani S, Singh BR, Musarrat J (2006) Significance of Bacillus subtilis strain SJ-101 as a bioinoculant for concurrent plant growth promotion and nickel accumulation in Brassica juncea. Chemosphere 64(6):991–997. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.12.057
Wani PA, Khan MS, Zaidi A (2008) Effect of metal-tolerant plant growth-promoting Rhizobium on the performance of pea grown in metal-amended soil. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 55(1):33–42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-007-9097-y
Nandakumar PBA, Dushenkov V, Motto H, Raskin I (1995) Phytoextraction: the use of plants to remove heavy metals from soils. Environ Sci Technol 29:232–1238. https://doi.org/10.1021/es00005a014
McIntyre T (2003) Phytoremediation of heavy metals from soils. In: Schepet T, Tsao DT (eds) Advances in biochemical engineering/biotechnology phytoremediation, vol 78. Springer, Berlin, pp 97–123. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-45991-x-4
Hornik M, Pipsika M, Vrtoch L, Augustin J, Lesny J (2005) Bioaccumulation of Cs-137 and Co-60 by Helianthus annus. Nukleonika 50:49–521
Acknowledgements
E.P is thankful to University Grants Commission (UGC), New Delhi for financial assistance towards Post-Doctoral Fellowship (PDF) under grant No. F./31-1/2017/PDFSS-2017-18-AND-14375. Thanks to the Department of Botany, ANU for necessary facilities to carry out this work.
Funding
AAS facility of the ANU and Post-Doctoral Fellowship (PDF) under Grant no. F./31-1/2017/PDFSS-2017-18-AND-14375 is acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Dr. PE: Formal analysis, Data curation, Writing—original draft, Investigation, editing, Methodology. Dr. AJAM: Formal analysis, Data curation, Statistical analysis, Review. Dr. URV: review & editing, Methodology. Prof. VRSGD: Review & editing, Data curation, Conceptualization. Prof. VMK: Methodology, Conceptualization, Data curation, work administration and Supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Ethical Approval
This study does not describe any experimental work related to humans.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Edulamudi, P., Antony Masilamani, A.J., Vanga, U.R. et al. Biosorption and Symbiotic Potential of Horse Gram Rhizobia in Soils Contaminated with Cobalt. Curr Microbiol 80, 174 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-023-03278-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-023-03278-0