Abstract
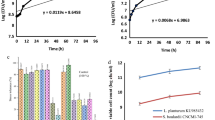
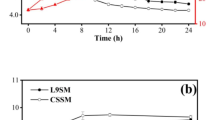
Tofu is one of the main foods made with soybeans. The aim of this work was to evaluate the effect of L. plantarum and L. fermentum on the volatile compounds and sensorial profile of fermented tofu during ripening. The soy milk was fermented separately with two native strains (L. plantarum or L. fermentum) until reaching a pH of 5.5, and the fermented tofu was obtained. The tofu obtained by acidification with lactic acid was used as a control and was characterized by microbial survival (L. plantarum, L. fermentum, and P. freudenreichii) for 0, 20, and 40 days of storage at 15 °C. Moreover, the lactic and acetic acid content was determined by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), and the volatile compounds were evaluated by gas. Chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC–MS). The results were analyzed by an ANOVA test (P < 0.05). After storage, the lactic acid bacteria (LAB) survived in the fermented tofu at a concentration higher than 8.0 log CFU/g after 40 days of storage. The shelf life of fermented tofu obtained by acidification was fewer than 20 days because of the presence of fungi and yeasts. The hexanal content was reduced by approximately 96% (P < 0.05) in the tofu obtained by fermentation compared with the control. This process for fermented tofu production employing two native strains could be used for industrial purposes.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The authors declare that the data supporting the findings of this study are available in the manuscript figures and tables.
References
Day L (2013) Proteins from land plants-potential resources from human nutrition and food security. Trends Foods Sci Tech 32(1):25–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2013.05.005
Prabhakaran MP, Conrad OP, Suresh V (2006) Effect of different coagulants on the isoflavones levels and physical properties of prepared firm tofu. Food Chem 99(3):492–499. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2005.08.011
Li C, Rui X, Zhang Y, Cai F, Chen XJ, Jiang M (2017) Production of tofu by lactic acid bacteria isolated from naturally fermented soy whey and evaluation of its quality. LWT Food Sci Technol 82:227–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2017.04.054
Cao FH, Li XJ, Luo SZ, Mu DD, Zhong XY, Jiang ST, Zheng Z, Zhao YY (2017) Effects of organic acid coagulants on the physical properties of and chemical interactions in tofu LWT-Food. Sci Technol 85:58–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2017.07.005
Chen K, Huang Y, Li X, Wu Y, Liu Y, Wang F (2021) Textural properties of firm tofu as affected by calcium coagulants. Food Measure 15:4508–4516. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-021-01031-4
Wang Y, Gao Y, Liang W, Liu Y, Gao H (2020) Identification and analysis of the flavor characteristics of unfermented stinky tofu brine during fermentation using SPME-GC–MS, e-nose, and sensory evaluation. Food Measure 14:597–612. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-019-00351-w
Lancetti R, Sciarini L, Pérez GT, Salvucci E (2021) Technological performance and selection of lactic acid bacteria isolated from Argentinian grains as starters for wheat sourdough. Curr Microbiol 78:255–264. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-020-02250-6
Merabti R, Madec MN, Chuat V, Becila FZ, Boussekine R, Bekhouche F, Valence F (2019) First insight into the technological features of lactic acid bacteria isolated from Algerian fermented wheat lemzeiet. Curr Microbiol 76:1095–1104. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-019-01727-3
Serrazanetti DI, Ndagijimana M, Miserocchi C, Perillo L, Guerzoni ME (2013) Fermented tofu: enhancement of keeping quality and sensorial properties. Food Control 34(2):336–346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2013.04.047
Riciputi Y, Serrazanetti DI, Verardo V, Vannini L, Caboni MF, Lanciotti R (2016) Effect of fermentation on the content of bioactive compounds in tofu-type products. Funct Foods 27:131–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2016.08.041
Granato D, Branco GF, Nazzarro F, Cruz AG, Faria JA (2010) Functional foods and nondairy probiotic food-development: trends, concepts and products. Compr Rev Food Sci F 9(3):292–302. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1541-4337.2010.00110.x
Mohammadi R, Mortazavian AM (2011) Review article: technological aspects of prebiotics in probiotic fermented milks. Food Rev Int 27(2):192–212. https://doi.org/10.1080/87559129.2010.535235
Tiwari BK, Valdramidis VP, O’Donnell CP, Muthukumarappan K, Bourke P, Cullen P (2009) Application of natural antimicrobials for food preservation. J Agric Food Chem 57(14):5987–6000. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf900668n
Mendoza-Avendaño C, Meza-Gordillo R, Ovando-Chacón S, Luján-Hidalgo MC, Ruiz-Cabrera MA, Grajales-Lagunes A, Ruiz-Valdiviezo VM, Gutiérrez-Miceli F, Abud-Archila M (2019) Evaluation of bioactive and anti-nutritional compounds during soymilk fermentation with Lactobacillus plantarum BAL-03-ITTG and Lactobacillus fermentum BAL-21-ITTG. Rev Mex Ing Quím 18(3):967–978. https://doi.org/10.24275/uam/izt/dcbi/revmexingquim/2019v18n3/Mendoza
Ramírez-Pérez JI, Álvarez-Gutiérrez PE, Luján-Hidalgo MC, Ovando-Chacón SL, Soria-Guerra RE, Ruiz-Cabrera MA, Grajales-Lagunes A, Abud-Archila M (2022) Effect of linear and branched fructans on growth and probiotic characteristics of seven Lactobacillus spp. isolated from an autochthonous beverage from Chiapas, Mexico. Arch Microbiol 204(7):364. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-022-02984-w
NOM-121-SSA1-1994. Bienes y servicios. Quesos: frescos, madurados y procesados. Especificaciones sanitarias.
Peredo-Lovillo A, Dorantes-Alvarez LH-S, Ribas-Aparicio RM, Cauich-Sánchez PI, Aparicio-Ozores G (2019) Functional properties and microstructure of Leuconostoc citrum and Lactobacillus casei shirota exposed to habanero pepper extract and inhibition of Staphylococcus aureus. Rev Mex Ing Quím 18(1):115–129. https://doi.org/10.24275/uam/izt/dcbi/revmexingquim/2019v18n1/Peredo
Enciso-Sáenz S, Borrás-Enriquez AJ, Ventura-Canseco LMC, Gutiérrez-Miceli F, Dendooven L, Grajales-Lagunes A, Ruiz-Cabrera MA, Ruíz-Valdiviezo V, Abud-Archila M (2018) Lemongrass (Cymbopogon citratus (DC) Stapf) essential oil encapsulation. Rev Mex Ing Quím 17(2):407–420. https://doi.org/10.24275/10.24275/uam/izt/dcbi/revmexingquim/2018v17n2/Enciso
Audisio MC, Torres MJ, Sabate DC, Ibarguren C, Apella MC (2011) Properties of different lactic acid bacteria isolated from Apis mellifera L. bee-gut. Microbiol Res 166(1):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2010.01.003
Lee S, Cho H, Lee KG (2014) Volatile compounds as markers of tofu (soybean curd) freshness during storage. J Agric Food Chem 62(3):772–779. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf404847g
Kamikaze NKK, Silva LCP, Prudencio SH (2018) Impact of soybean aging conditions on tofu sensory characteristics and acceptance. J Sci Food Agr 98(3):1132–1139. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.8564
Vannini L, Ndagijimana M, Saracino P, Vernocchi P, Corsetti A, Vallicelli M, Cappa F, Cocconcelli PS, Guerzoni ME (2007) New signaling molecules in some gram-positive and gramnegative bacteria. Int J Food Microbiol 120:25–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2007.02.028
FAO/OMS (2002) Report on drafting guidelines for the evaluation of probiotics in food. London, Ontario, Canada
Wu QQ, You HJ, Ahn HJ, Kwon B, Ji GE (2012) Changes in growth and survival of Bifidobacterium by coculture with Propionibacterium in soymilk, cow’s milk, and modified MRS medium. Int J Food Microbiol 157(1):65–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2012.04.013
Piwowarek K, Lipińska E, Hac-Szymanczuk E, Kieliszek M, Ścibisz I (2018) Propionibacterium spp.-source of propionic acid, vitamin B12, and other metabolites important for the industry. Appl Microbiol Biotech 102(2):515–538. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8616-7
Adepehin JO (2018) Safety assessment and microbiological quality of homemade soy-cheese in Nigeria. J Food Safety 38(5):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfs.12511
Her JY, Cho H, Kim MK, Lee KG (2017) Organic acids as a freshness indicator for tofu (soybean curd). J Food Sci Technol 54(11):3443–3450. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-017-2799-x
Liu DM, Li L, Yang XQ, Liang SZ, Wang JS (2006) Survivability of Lactobacillus rhamnosus during the preparation of soy cheese. Food Tech Biotech 44(3):417–422
Smit G, Smit BA, Engels WJ (2005) Flavour formation by lactic acid bacteria and biochemical flavour profiling of cheese products. FEMS Microbiol Rev 29(3):591–610. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.femsre.2005.04.002
Kaneko D, Igarashi T, Aoyama K (2014) Reduction of the off-flavor volatile generated by the yogurt starter culture including Streptococcus thermophilus and Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus in soymilk. J Agric Food Chem 62(7):1658–1663. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf404567e
Vong WC, Lui SQ (2018) Bioconversion of green volatiles in okara (soybean residue) in to esters by coupling enzyme catalysis and yeast (Lindnera saturns) fermentation. Appl Microbiol Biotech 102(23):10017–10026. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-9396-4
Frank DC, Owen CM, Patterson J (2004) Solid phase microextraction (SPME) combined with gas-chromatography and olfactometry-mass spectrometry for characterization of cheese aroma compounds. LWT Food Sci Technol 37(2):139–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0023-6438(03)00144-0
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to CONACyT for providing a doctoral scholarship to Mendoza-Avendaño.
Funding
This study was funded by Tecnológico Nacional de México (5651.19-P).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MA conducted the research, validation, data analysis, and the writing of this original draft. MG, GL, and RC actively participated in data analysis. LH, GM, and OC participated in the conceptualization and review of this manuscript. AA participated in the conceptualization of this research, as well as the validation, data analysis, and the review and editing of this manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors have no competing interest to disclose.
Ethics Approval
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mendoza-Avendaño, C., Ovando-Chacón, S.L., Luján-Hidalgo, M.C. et al. Volatile Compounds in Tofu Obtained by Soy Milk Fermentation with Lactobacillus plantarum BAL-03-ITTG and Lactobacillus fermentum BAL-21-ITTG. Curr Microbiol 79, 317 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-022-03014-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-022-03014-0