Abstract
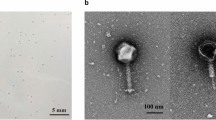
Ralstonia solanacearum is a soil-borne phytopathogen, and it can cause bacterial wilt disease in a variety of key crops around the world, thus resulting in enormous financial losses. However, there is a lack of effective, green, and safe prevention and control measures against increasingly devastating bacterial wilt disease. Bacteriophages (phages) are considered as potential biocontrol agents against bacterial wilt disease. Although many phages infecting R. solanacearum have been isolated, so far, these Ralstonia phages are still insufficient to deal with the diversity of the bacteria of R. solanacearum. In this study, a novel lytic bacteriophage vB_RsoP_BMB50 infecting multiple R. solanacearum was isolated from tomato fields in Dalian, China. Transmission electron microscopy and genomics analysis indicated that vB_RsoP_BMB50 belonged to the subfamily Okabevirinae, Autographiviridae family, and order Caudovirales, and it comprised a double-stranded DNA with a full length of 43,665 bp and a mean G+C content of 61.79%, containing 53 open reading frames (ORFs). This novel phage exhibited a large burst size, high temperature stability (4–50 °C), and strong pH tolerance (pH 5–10). Comparative analyses and phylogenetic analyses revealed that vB_RsoP_BMB50 represented a novel Ralstonia phage genus since it exhibited a low sequence similarity to other phages in the GenBank database. Due to its broad lytic spectrum, high thermal stability, and strong pH tolerance, vB_RsoP_BMB50 is considered as an effective candidate biocontrol agent against bacterial wilt disease caused by R. solanacearum.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The complete genome sequence of phage vB_RsoP_BMB50 was deposited in the GenBank database under the accession number MW965453.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
References
Peeters N, Guidot A, Vailleau F, Valls M (2013) Ralstonia solanacearum, a widespread bacterial plant pathogen in the post-genomic era. Mol Plant Pathol 14:651–662
Genin S, Denny TP (2012) Pathogenomics of the Ralstonia solanacearum species complex. Annu Rev Phytopathol 50:67–89
Abdurahman A, Parker ML, Kreuze J, Elphinstone JG, Struik PC, Kigundu A, Arengo E, Sharma K (2019) Molecular epidemiology of Ralstonia solanacearum species complex strains causing bacterial wilt of potato in Uganda. Phytopathology 109:1922–1931
Prior P, Ailloud F, Dalsing BL, Remenant B, Sanchez B, Allen C (2016) Genomic and proteomic evidence supporting the division of the plant pathogen Ralstonia solanacearum into three species. BMC Genomics 17:90
Mansfield J, Genin S, Magori S, Citovsky V, Sriariyanum M, Ronald P, Dow M, Verdier V, Beer SV, Machado MA et al (2012) Top 10 plant pathogenic bacteria in molecular plant pathology. Mol Plant Pathol 13:614–629
Paudel S, Dobhal S, Alvarez AM, Arif M (2020) Taxonomy and phylogenetic research on Ralstonia solanacearum species complex: a complex pathogen with extraordinary economic consequences. Pathogens 9:1
Jiang G, Wei Z, Xu J, Chen H, Zhang Y, She X, Macho AP, Ding W, Liao B (2017) Bacterial wilt in China: history, current status, and future perspectives. Front Plant Sci 8:1549
Doss J, Culbertson K, Hahn D, Camacho J, Barekzi N (2017) A review of phage therapy against bacterial pathogens of aquatic and terrestrial organisms. Viruses 9:1
Alvarez B, Lopez MM, Biosca EG (2019) Biocontrol of the major plant pathogen Ralstonia solanacearum in irrigation water and host plants by novel waterborne lytic bacteriophages. Front Microbiol 10:2813
Wang X, Wei Z, Yang K, Wang J, Jousset A, Xu Y, Shen Q, Friman VP (2019) Phage combination therapies for bacterial wilt disease in tomato. Nat Biotechnol 37:1513–1520
Trotereau A, Boyer C, Bornard I, Pecheur MJB, Schouler C, Torres-Barcelo C (2021) High genomic diversity of novel phages infecting the plant pathogen Ralstonia solanacearum, isolated in Mauritius and Reunion islands. Sci Rep 11:5382
Alvarez B, Biosca EG (2017) Bacteriophage-based bacterial wilt biocontrol for an environmentally sustainable agriculture. Front Plant Sci 8:1218
Fegan M, Prior P (2005) How complex is the Ralstonia solanacearum species complex. Bacterial wilt disease and the Ralstonia solanacearum species complex 1:449–461
Van Twest R, Kropinski AM (2009) Bacteriophage enrichment from water and soil. Methods Mol Biol 501:15–21
Hyman P, Abedon ST (2009) Practical methods for determining phage growth parameters. Methods Mol Biol 501:175–202
Wang M, Du J, Zhang D, Li X, Zhao J (2017) Modification of different pulps by homologous overexpression alkali-tolerant endoglucanase in Bacillus subtilis Y106. Sci Rep 7:3321
Santos MA (1991) An improved method for the small scale preparation of bacteriophage DNA based on phage precipitation by zinc chloride. Nucleic Acids Res 19:5442
Jackman SD, Vandervalk BP, Mohamadi H, Chu J, Yeo S, Hammond SA, Jahesh G, Khan H, Coombe L, Warren RL et al (2017) ABySS 2.0: resource-efficient assembly of large genomes using a Bloom filter. Genome Res 27:768–777
Aziz RK, Bartels D, Best AA, DeJongh M, Disz T, Edwards RA, Formsma K, Gerdes S, Glass EM, Kubal M et al (2008) The RAST Server: rapid annotations using subsystems technology. BMC Genomics 9:75
Lowe TM, Chan PP (2016) tRNAscan-SE On-line: integrating search and context for analysis of transfer RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res 44:W54-57
Sullivan MJ, Petty NK, Beatson SA (2011) Easyfig: a genome comparison visualizer. Bioinformatics 27:1009–1010
Moraru C, Varsani A, Kropinski AM (2020) VIRIDIC-A novel tool to calculate the intergenomic similarities of prokaryote-infecting viruses. Viruses 12:1
Dong Z, Xing S, Liu J, Tang X, Ruan L, Sun M, Tong Y, Peng D (2018) Isolation and characterization of a novel phage Xoo-sp2 that infects Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. J Gen Virol 99:1453–1462
Kawasaki T, Shimizu M, Satsuma H, Fujiwara A, Fujie M, Usami S, Yamada T (2009) Genomic characterization of Ralstonia solanacearum phage phiRSB1, a T7-like wide-host-range phage. J Bacteriol 191:422–427
Yamada T, Satoh S, Ishikawa H, Fujiwara A, Kawasaki T, Fujie M, Ogata H (2010) A jumbo phage infecting the phytopathogen Ralstonia solanacearum defines a new lineage of the Myoviridae family. Virology 398:135–147
Wang R, Cong Y, Mi Z, Fan H, Shi T, Liu H, Tong Y (2019) Characterization and complete genome sequence analysis of phage GP4, a novel lytic Bcep22-like podovirus. Arch Virol 164:2339–2343
Addy HS, Ahmad AA, Huang Q (2019) Molecular and biological characterization of Ralstonia phage RsoM1USA, a new species of P2virus, isolated in the United States. Front Microbiol 10:267
Van Truong TB, Pham Khanh NH, Namikawa R, Miki K, Kondo A, Dang Thi PT, Kamei K (2016) Genomic characterization of Ralstonia solanacearum phage varphiRS138 of the family Siphoviridae. Arch Virol 161:483–486
Bhunchoth A, Blanc-Mathieu R, Mihara T, Nishimura Y, Askora A, Phironrit N, Leksomboon C, Chatchawankanphanich O, Kawasaki T, Nakano M et al (2016) Two asian jumbo phages, varphiRSL2 and varphiRSF1, infect Ralstonia solanacearum and show common features of varphiKZ-related phages. Virology 494:56–66
Matsui T, Yoshikawa G, Mihara T, Chatchawankanphanich O, Kawasaki T, Nakano M, Fujie M, Ogata H, Yamada T (2017) Replications of two closely related groups of jumbo phages show different level of dependence on host-encoded RNA polymerase. Front Microbiol 8:1010
Ahmad AA, Addy HS, Huang Q (2021) Biological and molecular characterization of a jumbo bacteriophage infecting plant pathogenic Ralstonia solanacearum species complex strains. Front Microbiol 12:741600
Kawasaki T, Narulita E, Matsunami M, Ishikawa H, Shimizu M, Fujie M, Bhunchoth A, Phironrit N, Chatchawankanphanich O, Yamada T (2016) Genomic diversity of large-plaque-forming podoviruses infecting the phytopathogen Ralstonia solanacearum. Virology 492:73–81
Drigues P, Demery-Lafforgue D, Trigalet A, Dupin P, Samain D, Asselineau J (1985) Comparative studies of lipopolysaccharide and exopolysaccharide from a virulent strain of Pseudomonas solanacearum and from three avirulent mutants. J Bacteriol 162:504–509
Chen D, Liu B, Zhu Y, Wang J, Chen Z, Che J, Zheng X, Chen X (2017) Complete genome sequence of Ralstonia solanacearum FJAT-1458, a potential biocontrol agent for Tomato Wilt. Genome Announc 5:1
Nobrega FL, Vlot M, de Jonge PA, Dreesens LL, Beaumont HJE, Lavigne R, Dutilh BE, Brouns SJJ (2018) Targeting mechanisms of tailed bacteriophages. Nat Rev Microbiol 16:760–773
Mamphogoro TP, Babalola OO, Aiyegoro OA (2020) Sustainable management strategies for bacterial wilt of sweet peppers (Capsicum annuum) and other Solanaceous crops. J Appl Microbiol 129:496–508
Yuliar NYA, Toyota K (2015) Recent trends in control methods for bacterial wilt diseases caused by Ralstonia solanacearum. Microbes Environ 30(1):1–11
Buttimer C, McAuliffe O, Ross RP, Hill C, O’Mahony J, Coffey A (2017) Bacteriophages and bacterial plant diseases. Front Microbiol 8:34
Fujiwara A, Fujisawa M, Hamasaki R, Kawasaki T, Fujie M, Yamada T (2011) Biocontrol of Ralstonia solanacearum by treatment with lytic bacteriophages. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:4155–4162
Bae JY, Wu J, Lee HJ, Jo EJ, Murugaiyan S, Chung E, Lee SW (2012) Biocontrol potential of a lytic bacteriophage PE204 against bacterial wilt of tomato. J Microbiol Biotechnol 22:1613–1620
Bhunchoth A, Phironrit N, Leksomboon C, Chatchawankanphanich O, Kotera S, Narulita E, Kawasaki T, Fujie M, Yamada T (2015) Isolation of Ralstonia solanacearum-infecting bacteriophages from tomato fields in Chiang Mai, Thailand, and their experimental use as biocontrol agents. J Appl Microbiol 118:1023–1033
de Leeuw M, Baron M, Ben David O, Kushmaro A (2020) Molecular insights into bacteriophage evolution toward its host. Viruses 12:1
Sieiro C, Areal-Hermida L, Pichardo-Gallardo A, Almuina-Gonzalez R, de Miguel T, Sanchez S, Sanchez-Perez A, Villa TG (2020) A hundred years of bacteriophages: can phages replace antibiotics in agriculture and aquaculture? Antibiotics (Basel) 9:1
Hong Y, Schmidt K, Marks D, Hatter S, Marshall A, Albino L, Ebner P (2016) Treatment of salmonella-contaminated eggs and pork with a broad-spectrum, single bacteriophage: assessment of efficacy and resistance development. Foodborne Pathog Dis 13:679–688
Wang C, Chen Q, Zhang C, Yang J, Lu Z, Lu F, Bie X (2017) Characterization of a broad host-spectrum virulent Salmonella bacteriophage fmb-p1 and its application on duck meat. Virus Res 236:14–23
Ye M, Sun M, Huang D, Zhang Z, Zhang H, Zhang S, Hu F, Jiang X, Jiao W (2019) A review of bacteriophage therapy for pathogenic bacteria inactivation in the soil environment. Environ Int 129:488–496
Ma Y, Li E, Qi Z, Li H, Wei X, Lin W, Zhao R, Jiang A, Yang H, Yin Z et al (2016) Isolation and molecular characterisation of Achromobacter phage phiAxp-3, an N4-like bacteriophage. Sci Rep 6:24776
Leon-Velarde CG, Happonen L, Pajunen M, Leskinen K, Kropinski AM, Mattinen L, Rajtor M, Zur J, Smith D, Chen S et al (2016) Yersinia enterocolitica-specific infection by bacteriophages TG1 and varphiR1-RT is dependent on temperature-regulated expression of the phage host receptor OmpF. Appl Environ Microbiol 82:5340–5353
Williamson KE, Fuhrmann JJ, Wommack KE, Radosevich M (2017) Viruses in soil ecosystems: an unknown quantity within an unexplored territory. Annu Rev Virol 4:201–219
Skurnik M, Pajunen M, Kiljunen S (2007) Biotechnological challenges of phage therapy. Biotechnol Lett 29:995–1003
Acknowledgements
We thank Professor Bo Liu (Fujian Academy of Agriculture Sciences) for donating R. solanacearum strains.
Funding
This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31970075 and 31370002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MS and DP conceived the project, DP designed the experiments. KW and QL performed the experiments. DC and PZ analyzed the data. KW wrote the manuscript. DP revised the paper. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors declared that there are no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Informed Consent
The authors grant the publisher consent to publish the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, K., Chen, D., Liu, Q. et al. Isolation and Characterization of Novel Lytic Bacteriophage vB_RsoP_BMB50 infecting Ralstonia solanacearum. Curr Microbiol 79, 245 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-022-02940-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-022-02940-3