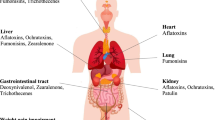
Abstract
Aflatoxins are toxic secondary metabolic products, which exert great hazards to human and animal health. Decontaminating aflatoxins from food ingredients to a threshold level is a prime concern for avoiding risks to the consumers. Biological decontamination processes of aflatoxins have received widespread attention due to their mild and environmental-friendly nature. Many reports have been published on the decontamination of aflatoxins by microorganisms, especially lactic acid bacteria (LAB), a well-explored probiotic and generally recognized as safe. The present review aims at updating the decontamination of produced aflatoxins using LAB, with an emphasis on the decontamination mechanism and influence factors for decontamination. This comprehensive analysis provides insights into the binding mechanisms between LAB and aflatoxins, facilitating the theoretical and practical application of LAB for decontaminating hazardous substances in food and agriculture.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Serra R, Braga A, Venâncio A (2005) Mycotoxin-producing and other fungi isolated from grapes for wine production, with particular emphasis on ochratoxin A. Res Microbiol 156(4):515–521
Mateo R, Medina A, Gimeno-Adelantado JV, Jiménez M (2004) An overview on the status of toxigenic fungi and mycotoxins in Spain. In: Logrieco A, Visconti A (eds) An overview on toxigenic fungi and mycotoxins in Europe. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 219–235
Medina Á, Valle-Algarra FM, Mateo R, Gimeno-Adelantado JV, Mateo F, Jiménez M (2006) Survey of the mycobiota of Spanish malting barley and evaluation of the mycotoxin producing potential of species of Alternaria, Aspergillus and Fusarium. Int J Food Microbiol 108(2):196–203
Kara GN, Ozbey F, Kabak B (2015) Co-occurrence of aflatoxins and ochratoxin A in cereal flours commercialised in Turkey. Food Control 54:275–281
Klich M, Mullaney E, Daly C, Cary J (2000) Molecular and physiological aspects of aflatoxin and sterigmatocystin biosynthesis by Aspergillus tamarii and A. ochraceoroseus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 53(5):605–609
Varga J, Frisvad JC, Samson R (2011) Two new aflatoxin producing species, and an overview of Aspergillus section Flavi. Stud Mycol 69:57–80
Henry SH, Bosch FX, Troxell TC, Bolger PM (1999) Reducing liver cancer–global control of aflatoxin. Science 286(5449):2453–2454
Liu Y, Wu F (2010) Global burden of aflatoxin-induced hepatocellular carcinoma: a risk assessment. Environ Health Perspect 118(6):818–824
Varsha KK, Nampoothiri KM (2016) Appraisal of lactic acid bacteria as protective cultures. Food Control 69:61–64
Liu N, Ding K, Wang J, Deng Q, Gu K, Wang J (2018) Effects of lactic acid bacteria and smectite after aflatoxin B1 challenge on the growth performance, nutrient digestibility and blood parameters of broilers. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr 102(4):953–961
Sevim S, Topal GG, Tengilimoglu-Metin MM, Sancak B, Kizil M (2019) Effects of inulin and lactic acid bacteria strains on aflatoxin M1 detoxification in yoghurt. Food Control 100:235–239
Gu X, Sun J, Cui Y, Wang X, Sang Y (2019) Biological degradation of aflatoxin M1 by Bacillus pumilus E-1-1-1. MicrobiologyOpen 8(3):e00663
Mwakinyali SE, Ming Z, Xie H, Zhang Q, Li P (2019) Investigation and characterization of myroides odoratimimus strain 3J2MO aflatoxin B1 degradation. J Agric Food Chem 67(16):4595–4602
Intanoo M, Kongkeitkajorn M, Pattarajinda V, Bernard J, Callaway T, Suriyasathaporn W, Phasuk Y (2018) Isolation and screening of aflatoxin-detoxifying yeast and bacteria from ruminal fluids to reduce aflatoxin B1 contamination in dairy cattle feed. J Appl Microbiol 125(6):1603–1613
Foroughi M, Sarabi Jamab M, Keramat J, Najaf Najafi M (2019) The use of Saccharomyces cerevisiae immobilized on activated alumina, and alumina silicate beads for the reduction of Aflatoxin M1 in vitro. J Food Process Preserv 43(2):e13876
Song J, Zhang S, Xie Y, Li Q (2019) Purification and characteristics of an aflatoxin B1 degradation enzyme isolated from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. FEMS Microbiol Lett 366(5):fnz034
Branà MT, Sergio L, Haidukowski M, Logrieco AF, Altomare C (2020) Degradation of aflatoxin B1 by a sustainable enzymatic extract from spent mushroom substrate of Pleurotus eryngii. Toxins 12(1):49
Ismail A, Gonçalves BL, de Neeff DV, Ponzilacqua B, Coppa CF, Hintzsche H, Sajid M, Cruz AG, Corassin CH, Oliveira CA (2018) Aflatoxin in foodstuffs: occurrence and recent advances in decontamination. Food Res Int 113:74–85
Hassanpour M, Rezaie MR, Baghizadeh A (2019) Practical analysis of aflatoxin M1 reduction in pasteurized Milk using low dose gamma irradiation. J Environ Health Sci Eng 17:863–872
Li H, Xiong Z, Gui D, Pan Y, Xu M, Guo Y, Leng J, Li X (2019) Effect of ozonation and UV irradiation on aflatoxin degradation of peanuts. J Food Process Preserv 43(4):e13914
Hwang J, Lee K (2006) Reduction of aflatoxin B1 contamination in wheat by various cooking treatments. Food Chem 98(1):71–75
Rastegar H, Shoeibi S, Yazdanpanah H, Amirahmadi M, Khaneghah AM, Campagnollo FB, Sant’Ana AS (2017) Removal of aflatoxin B1 by roasting with lemon juice and/or citric acid in contaminated pistachio nuts. Food Control 71:279–284
Ismail A, Akhtar S, Levin RE, Ismail T, Riaz M, Amir M (2016) Aflatoxin M1: prevalence and decontamination strategies in milk and milk products. Crit Rev Microbiol 42(3):418–427
Wang G, Xi Y, Lian C, Sun Z, Zheng S (2019) Simultaneous detoxification of polar aflatoxin B1 and weak polar zearalenone from simulated gastrointestinal tract by zwitterionic montmorillonites. J Hazard Mater 364:227–237
Chen WL, Zhou Q, Xing D (2007) Chemical detoxification of AflatoxinB1 in rice by several solutions through fluorescence spectral experiment. Key Eng Mater 364–366:1032–1036
Zavala-Franco A, Arámbula-Villa G, Ramírez-Noguera P, Salazar AM, Sordo M, Marroquín-Cardona A, de Dios F-Cárdenas J, Méndez-Albores A (2020) Aflatoxin detoxification in tortillas using an infrared radiation thermo-alkaline process: cytotoxic and genotoxic evaluation. Food Control 112:107084
Rustom IY (1997) Aflatoxin in food and feed: occurrence, legislation and inactivation by physical methods. Food Chem 59(1):57–67
ParK DL, Lee LS, Price RL, Pohland AE (1988) Review of the decontamination of aflatoxins by ammoniation: current status and regulation. J Assoc Off Anal Chem 71(4):685–703
Vijayanandraj S, Brinda R, Kannan K, Adhithya R, Vinothini S, Senthil K, Chinta RR, Paranidharan V, Velazhahan R (2014) Detoxification of aflatoxin B1 by an aqueous extract from leaves of Adhatoda vasica Nees. Microbiol Res 169(4):294–300
Pankaj S, Shi H, Keener KM (2018) A review of novel physical and chemical decontamination technologies for aflatoxin in food. Trends Food Sci Technol 71:73–83
Porto YD, Trombete FM, Freitas-Silva O, De Castro IM, Direito GM, Ascheri JLR (2019) Gaseous ozonation to reduce aflatoxins levels and microbial contamination in corn grits. Microorganisms 7(8):220
Jalili M, Jinap S, Son R (2011) The effect of chemical treatment on reduction of aflatoxins and ochratoxin A in black and white pepper during washing. Food Addit Contam A 28(4):485–493
Li X, Yuan H, Li L, Xiao D (2014) Electrogenerated chemiluminescence of magnesium chlorophyllin a aqueous solution and its sensitive response to the carcinogen aflatoxin B1. Biosens Bioelectron 55:350–354
Herzallah S, Alshawabkeh K, Fataftah AA (2008) Aflatoxin decontamination of artificially contaminated feeds by sunlight, γ-radiation, and microwave heating. J Appl Poult Res 17(4):515–521
Kamber U, Gülbaz G, Aksu P, Doğan A (2017) Detoxification of aflatoxin B1 in red pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) by ozone treatment and its effect on microbiological and sensory quality. J Food Process Preserv 41(5):e13102
Bagley E (1979) Decontamination of corn containing aflatoxin by treatment with ammonia. J Am Oil Chem Soc 56(9):808–811
Gao SS, Chen XY, Zhu RZ, Choi BM, Kim BR (2010) Sulforaphane induces glutathione S-transferase isozymes which detoxify aflatoxin B1-8, 9-epoxide in AML 12 cells. BioFactors 36(4):289–296
Pokharel YR, Han EH, Kim JY, Oh SJ, Kim SK, Woo E-R, Jeong HG, Kang KW (2006) Potent protective effect of isoimperatorin against aflatoxin B 1-inducible cytotoxicity in H4IIE cells: bifunctional effects on glutathione S-transferase and CYP1A. Carcinogenesis 27(12):2483–2490
Mathur S, Singh R (2005) Antibiotic resistance in food lactic acid bacteria—a review. Int J Food Microbiol 105(3):281–295
Yang E, Fan L, Yan J, Jiang Y, Doucette C, Fillmore S, Walker B (2018) Influence of culture media, pH and temperature on growth and bacteriocin production of bacteriocinogenic lactic acid bacteria. AMB Express 8(1):10
Liu Z, Peng Z, Huang T, Xiao Y, Li J, Xie M, Xiong T (2019) Comparison of bacterial diversity in traditionally homemade paocai and Chinese spicy cabbage. Food Microbiol 83:141–149
Abushelaibi A, Al-Mahadin S, El-Tarabily K, Shah NP, Ayyash M (2017) Characterization of potential probiotic lactic acid bacteria isolated from camel milk. LWT Food Sci Technol 79:316–325
Liu A, Jia Y, Zhao L, Gao Y, Liu G, Chen Y, Zhao G, Xu L, Shen L, Liu Y (2018) Diversity of isolated lactic acid bacteria in Ya’an sourdoughs and evaluation of their exopolysaccharide production characteristics. LWT Food Sci Technol 95:17–22
de Lima AL, da Silva MS, Flores DRM, Athayde DR, Ruviaro AR, da Silva BD, Batista VSF, de Oliveira MR, de Menezes CR, Campagnol PCB (2018) Effect of ultrasound on the physicochemical and microbiological characteristics of Italian salami. Food Res Int 106:363–373
Kumar N, Kumari V, Ram C, Thakur K, Tomar SK (2018) Bio-prospectus of cadmium bioadsorption by lactic acid bacteria to mitigate health and environmental impacts. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102(4):1599–1615
Zhang Y, Xu D, Liu J, Zhao X (2014) Enhanced degradation of five organophosphorus pesticides in skimmed milk by lactic acid bacteria and its potential relationship with phosphatase production. Food Chem 164:173–178
Zhu Y, Yang C, Luo B, Zhou K, Liu S (2017) Efficiency of dairy strains of lactic acid bacteria to bind bisphenol A in phosphate buffer saline. Food Control 73:1203–1209
Wang L, Yue T, Yuan Y, Wang Z, Ye M, Cai R (2015) A new insight into the adsorption mechanism of patulin by the heat-inactive lactic acid bacteria cells. Food Control 50:104–110
Taheur FB, Kouidhi B, Al Qurashi YMA, Salah-Abbès JB, Chaieb K (2019) Biotechnology of mycotoxins detoxification using microorganisms and enzymes. Toxicon 160:12–22
Assaf JC, Nahle S, Chokr A, Louka N, Atoui A, El Khoury A (2019) Assorted methods for decontamination of aflatoxin M1 in milk using microbial adsorbents. Toxins 11(6):304
Zhao L, Wei J, Zhao H, Zhu B, Zhang B (2018) Detoxification of cancerogenic compounds by lactic acid bacteria strains. Crit Rev Food Sci 58(16):2727–2742
Adebo O, Njobeh P, Gbashi S, Nwinyi O, Mavumengwana V (2017) Review on microbial degradation of aflatoxins. Crit Rev Food Sci 57(15):3208–3217
Verheecke C, Liboz T, Mathieu F (2016) Microbial degradation of aflatoxin B1: current status and future advances. Int J Food Microbiol 237:1–9
Zhang G, Li J, Lv J, Liu L, Li C, Liu L (2019) Decontamination of aflatoxin M1 in yogurt using Lactobacillus rhamnosus LC-4. J Food Saf 39(5):e12673
Topcu A, Bulat T, Wishah R, Boyacı IH (2010) Detoxification of aflatoxin B1 and patulin by Enterococcus faecium strains. Int J Food Microbiol 139(3):202–205
Ismail A, Levin RE, Riaz M, Akhtar S, Gong YY, de Oliveira CA (2017) Effect of different microbial concentrations on binding of aflatoxin M1 and stability testing. Food Control 73:492–496
Peltonen K, El-Nezami H, Haskard C, Ahokas J, Salminen S (2001) Aflatoxin B1 binding by dairy strains of lactic acid bacteria and bifidobacteria. J Dairy Sci 84(10):2152–2156
Kabak B, Ozbey F (2012) Assessment of the bioaccessibility of aflatoxins from various food matrices using an in vitro digestion model, and the efficacy of probiotic bacteria in reducing bioaccessibility. J Food Compos Anal 27(1):21–31
Gratz S, Mykkänen H, El-Nezami H (2005) Aflatoxin B1 binding by a mixture of Lactobacillus and Propionibacterium: in vitro versus ex vivo. J Food Prot 68(11):2470–2474
Oatley JT, Rarick MD, Ji GE, Linz JE (2000) Binding of aflatoxin B1 to bifidobacteria in vitro. J Food Prot 63(8):1133–1136
Panwar R, Kumar N, Kashyap V, Ram C, Kapila R (2019) Aflatoxin M1 detoxification ability of probiotic Lactobacilli of Indian Origin in in vitro digestion model. Probiotics Antimicrob 11(2):460–469
Haskard CA, El-Nezami HS, Kankaanpää PE, Salminen S, Ahokas JT (2001) Surface binding of aflatoxin B1 by lactic acid bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 67(7):3086–3091
Haskard C, Binnion C, Ahokas J (2000) Factors affecting the sequestration of aflatoxin by Lactobacillus rhamnosus strain GG. Chem Biol Interact 128(1):39–49
Lee Y, El-Nezami H, Haskard C, Gratz S, Puong K, Salminen S, Mykkänen H (2003) Kinetics of adsorption and desorption of aflatoxin B1 by viable and nonviable bacteria. J Food Prot 66(3):426–430
Lahtinen S, Haskard C, Ouwehand A, Salminen S, Ahokas J (2004) Binding of aflatoxin B1 to cell wall components of Lactobacillus rhamnosus strain GG. Food Addit Contam A 21(2):158–164
Hernandez-Mendoza A, Guzman-de-Peña D, Garcia H (2009) Key role of teichoic acids on aflatoxin B1 binding by probiotic bacteria. J Appl Microbiol 107(2):395–403
Dalié D, Deschamps A, Richard-Forget F (2010) Lactic acid bacteria—potential for control of mould growth and mycotoxins: a review. Food Control 21(4):370–380
Chlebicz A, Śliżewska K (2019) In vitro detoxification of aflatoxin B 1, deoxynivalenol, fumonisins, T-2 toxin and zearalenone by probiotic bacteria from genus Lactobacillus and Saccharomyces cerevisiae yeast. Probiotics Antimicro 12(1): 289–301
El Khoury A, Atoui A, Yaghi J (2011) Analysis of aflatoxin M1 in milk and yogurt and AFM1 reduction by lactic acid bacteria used in Lebanese industry. Food Control 22(10):1695–1699
Martínez M, Magnoli A, Pereyra MG, Cavaglieri L (2019) Probiotic bacteria and yeasts adsorb aflatoxin M1 in milk and degrade it to less toxic AFM1-metabolites. Toxicon 172:1–7
Elsanhoty RM, Al-Turki I, Ramadan MF (2016) Application of lactic acid bacteria in removing heavy metals and aflatoxin B1 from contaminated water. Water Sci Technol 74(3):625–638
Huang L, Duan C, Zhao Y, Gao L, Niu C, Xu J, Li S (2017) Reduction of aflatoxin B1 toxicity by Lactobacillus plantarum C88: a potential probiotic strain isolated from Chinese traditional fermented food “tofu”. PloS One 12(1):e0170109
Sarlak Z, Rouhi M, Mohammadi R, Khaksar R, Mortazavian AM, Sohrabvandi S, Garavand F (2017) Probiotic biological strategies to decontaminate aflatoxin M1 in a traditional Iranian fermented milk drink (Doogh). Food Control 71:152–159
Taheur FB, Fedhila K, Chaieb K, Kouidhi B, Bakhrouf A, Abrunhosa L (2017) Adsorption of aflatoxin B1, zearalenone and ochratoxin A by microorganisms isolated from Kefir grains. Int J Food Microbiol 251:1–7
Zinedine A, Faid M, Benlemlih M (2005) In vitro reduction of aflatoxin B1 by strains of lactic acid bacteria isolated from Moroccan sourdough bread. Int J Agric Biol 7(1):67–70
Bovo F, Franco LT, Rosim RE, Trindade CSF, de Oliveira CAF (2014) The ability of Lactobacillus rhamnosus in solution, spray-dried or lyophilized to bind aflatoxin B1. J Food Res 3(2):35–42
Bovo F, Corassin CH, Rosim RE, de Oliveira CA (2013) Efficiency of lactic acid bacteria strains for decontamination of aflatoxin M 1 in phosphate buffer saline solution and in skimmed milk. Food Bioprocess Technol 6(8):2230–2234
El-Nezami H, Kankaanpaa P, Salminen S, Ahokas J (1998) Ability of dairy strains of lactic acid bacteria to bind a common food carcinogen, aflatoxin B1. Food Chem Toxicol 36(4):321–326
Rahaie S, Emam-Djomeh Z, Razavi SH, Mazaheri M (2012) Evaluation of aflatoxin decontaminating by two strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Lactobacillus rhamnosus strain GG in pistachio nuts. Int J Food Sci Technol 47(8):1647–1653
Kabak B, Var I (2008) Factors affecting the removal of aflatoxin M1 from food model by Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium strains. J Environ Sci Health B 43(7):617–624
Wochner KF, Moreira MC, Kalschne DL, Colla E, Drunkler DA (2019) Detoxification of Aflatoxin B1 and M1 by Lactobacillus acidophilus and prebiotics in whole cow’s milk. J Food Saf 39(5):e12670
Liu N, Ding K, Wang J, Jia S, Wang J, Xu T (2017) Detoxification, metabolism, and glutathione pathway activity of aflatoxin B1 by dietary lactic acid bacteria in broiler chickens. J Anim Sci 95(10):4399–4406
Hernandez-Mendoza A, González-Córdova AF, Vallejo-Cordoba B, Garcia HS (2011) Effect of oral supplementation of Lactobacillus reuteri in reduction of intestinal absorption of aflatoxin B1 in rats. J Basic Microbiol 51(3):263–268
El-Nezami H, Mykkänen H, Kankaanpää P, Salminen S, Ahokas J (2000) Ability of Lactobacillus and Propionibacterium strains to remove aflatoxin B1 from the chicken duodenum. J Food Prot 63(4):549–552
Hernandez-Mendoza A, Garcia H, Steele J (2009) Screening of Lactobacillus casei strains for their ability to bind aflatoxin B1. Food Chem Toxicol 47(6):1064–1068
Bueno DJ, Casale CH, Pizzolitto RP, Salvano MA, Oliver G (2007) Physical adsorption of aflatoxin B1 by lactic acid bacteria and Saccharomyces cerevisiae: a theoretical model. J Food Prot 70(9):2148–2154
El-Nezami H, Kankaanpää P, Salminen S, Ahokas J (1998) Physicochemical alterations enhance the ability of dairy strains of lactic acid bacteria to remove aflatoxin from contaminated media. J Food Prot 61(4):466–468
Fazeli MR, Hajimohammadali M, Moshkani A, Samadi N, Jamalifar H, Khoshayand MR, Vaghari E, Pouragahi S (2009) Aflatoxin B1 binding capacity of autochthonous strains of lactic acid bacteria. J Food Prot 72(1):189–192
Ben Salah-Abbes J, Abbes S, Jebali R, Haous Z, Oueslati R (2015) Potential preventive role of lactic acid bacteria against Aflatoxin M1 immunotoxicity and genotoxicity in mice. J Immunotoxicol 12(2):107–114
Assaf JC, Khoury AE, Chokr A, Louka N, Atoui A (2019) A novel method for elimination of aflatoxin M1 in milk using Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG biofilm. Int J Dairy Technol 72(2):248–256
Antognoni F, Mandrioli R, Potente G, Saa DLT, Gianotti A (2019) Changes in carotenoids, phenolic acids and antioxidant capacity in bread wheat doughs fermented with different lactic acid bacteria strains. Food Chem 292:211–216
Poutanen K, Flander L, Katina K (2009) Sourdough and cereal fermentation in a nutritional perspective. Food Microbiol 26(7):693–699
Sarimehmetoğlu B, Küplülü Ö (2004) Binding ability of aflatoxin M1 to yoghurt bacteria. Ankara Üniversitesi Veteriner Fakültesi Dergisi 51(3):195–198
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for the funding support from the Education Bureau of Sichuan Province (No. 17ZB0337) and the contribution of Ms Xingzhe Cai and Yuxi Tan in draft preparation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, AL; Methodology, YZ, LL, SC, LH and XA; Writing-Original Draft Preparation, AL and YZ; Writing-Review & Editing, AL, SC, LH, XA, YY and SL; Supervision, YY and SL.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, A., Zheng, Y., Liu, L. et al. Decontamination of Aflatoxins by Lactic Acid Bacteria. Curr Microbiol 77, 3821–3830 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-020-02220-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-020-02220-y