Abstract
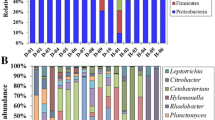
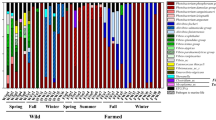
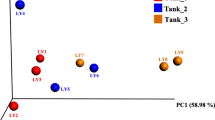
Enteritis comprises one of the most common diseases affecting the survival of farmed yellow seahorse (Hippocampus kuda), an important economic fish species cultured worldwide. Although there are several studies describing bacteria associated with seahorse, the microbial alternations associated with enteritis in seahorse has not been extensively investigated. In the present study, high-throughput 16S rRNA gene sequencing was used to explore the changes in the intestinal microbiota of seahorse suffering from enteritis. The results showed that the diversity, structure, and function of intestinal microbiota were significantly different between healthy and diseased seahorse. Particularly, significant increase was observed in Brevinema, Mycobacterium, and Vibrio, as well as significant decrease in Psychrobacter, Bacillus, and Shewanella in diseased seahorse (P < 0.05). In addition, PICRUSt predictions revealed that the intestinal microbiota significantly changed the specific metabolic pathways (related to metabolic diseases, replication and repair, transport and catabolism, infectious diseases and immune system) in diseased seahorse (P < 0.05). Altogether, our findings point out the association between changes of the intestinal microbiota and enteritis in seahorse, which provide basic information useful for optimization of breeding regimes and improvements in the health of this endangered species in captivity.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Job SD, Dob HH, Meeuwigc JJ et al (2002) Culturing the oceanic seahorse, Hippocampus kuda. Aquaculture 214:333–341
Foster SJ, Vincent ACJ (2004) Life history and ecology of seahorses: implications for conservation and management. J Fish Biol 65:1–61
Vincent ACJ, Foster SJ, Koldewey HJ (2011) Conservation and management of seahorses and other Syngnathidae. J Fish Biol 78:1681–1724
Lepage V, Young J, Dutton CJ et al (2015) Diseases of captive yellow seahorse Hippocampus kuda bleeker, pot-bellied seahorse Hippocampus abdominalis Lesson and weedy seadragon Phyllopteryx taeniolatus (lacépède). J Fish Dis 38:439–450
Gómez GD, Balcázar JL (2008) A review on the interactions between gut microbiota and innate immunity of fish. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 52:145–154
Tingting L, Dong Z, Xin L et al (2016) Variations of immune parameters in the lined seahorse Hippocampus erectus after infection with enteritis pathogen of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Fish Shellfish Immunol 50:247–254
Haidong Li, Hushan S, Xuefeng B et al (2016) HC2 of Pseudomonas sp. induced enteritis in Hippocampus japonicus. Aquacult Res 47:2027–2030
Xin W, Yixinya Z, Geng Q et al (2015) A novel pathogenic bacteria (Vibrio fortis) causing enteritis in cultured seahorses, Hippocampus erectus perry, 1810. J Fish Dis 39:765
Balcazar JL, Gallo-Bueno A, Planas M et al (2010) Isolation of Vibrio alginolyticus and Vibrio splendidus from captive-bred seahorses with disease symptoms. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 97:207–210
Akayli T, Erkan M, Çanak Ö et al (2017) Formation of pinocytic activity in cultured common dentex (Dentex dentex) larvae intestine. Isr Aquacult-Bamid 69:1–7
Bolger AM, Lohse M, Usadel B (2014) Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 30:2114–2120
Magoč T, Salzberg SL (2011) FLASH: fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 27:2957–2963
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J et al (2010) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Meth 7:335–336
Langille MGI, Zaneveld J, Caporaso JG et al (2013) Predictive functional profiling of microbial communities using 16S rRNA marker gene sequences. Nat Biotechnol 31(9):814–821
Zhiguang G, Bomin G, Renyuan G et al (2015) Microbiota disbiosis is associated with colorectal cancer. Front Microbiol 6:20
Tran NT, Jing Z, Fan X et al (2018) Altered gut microbiota associated with intestinal disease in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus). World J Microbiol Biotech 34(6):2–9
Tongtong Li, Long M, Ji C et al (2016) Alterations of the gut microbiome of largemouth bronze gudgeon (Coreius guichenoti) suffering from furunculosis. Sci Rep 6:30606
Wei S, Lingzhi Li, Hongliang H et al (2016) The gut microbial community of Antarctic fish detected by 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis. BioMed Res Int 2016:1–7
Bruni L, Pastorelli R, Viti C et al (2018) Characterisation of the intestinal microbial communities of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) fed with, Hermetia illucens, (black soldier fly) partially defatted larva meal as partial dietary protein source. Aquaculture 487:56–63
Spor A, Koren O, Ley R (2011) Unravelling the effects of the environment and host genotype on the gut microbiome. Nat Rev Microbiol 9:279–290
Desai AR, Links MG, Collins SA et al (2012) Effects of plant-based diets on the distal gut microbiome of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 350–353:134–142
Jiachao Z, Zhuang G, Zhengsheng X et al (2015) A phylo-functional core of gut microbiota in healthy young Chinese cohorts across lifestyles, geography and ethnicities. ISME J 9:1979–1990
Rosa KB, Ilhan ZE, Kang DW et al (2012) Effects of gut microbes on nutrient absorption and energy regulation. Nutr Clin Pract 27:201–214
Grillova L, Jolley K, Šmajs D et al (2019) A public database for the new MLST scheme for Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum: surveillance and epidemiology of the causative agent of syphilis. J Life Environ Sci 6:e6182
Milner JA, Sellwood R (1994) Chemotactic response to mucin by Serpulina hyodysenteriae and other porcine spirochetes: potential role in intestinal colonization. Infect Immun 62:4095–4099
Hampson DJ, Fellström C, Thomson JR (2006) Swine dysentery. In: Straw BE, Zimmerman JJ, Allaire S, Talor DJ (eds) Diseases of swine, 9th edn. Blackwell, London, pp 785–805
Prapasarakul N, Lugsomya K, Disatian S et al (2011) Faecal excretion of intestinal spirochaetes by urban dogs, and their pathogenicity in a chick model of intestinal spirochaetosis. Res Vet Sci 91:e38–e43
Yang HL, Sun YZ, Ma RL et al (2011) Probiotic Psychrobacter sp. improved the autochthonous microbial diversity along the gastrointestinal tract of grouper Epinephelus coioides. J Aquacult Res Dev S1:001
Makled SO, Hamdan AM, El-Sayed AFM et al (2017) Evaluation of marine psychrophile, Psychrobacter namhaensis SO89, as a probiotic in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) diets. Fish Shellfish Immun 61:194–200
Christopher MAC, Monica FB, Viswanath K (2010) Antagonistic activity of bacterial isolates from intestinal microbiota of Atlantic cod, Gadus morhua, and an investigation of their immunomodulatory capabilities. Aquacult Res 41:249–256
Interaminense JA, Vogeley JL, Gouveia CK et al (2018) In vitro and in vivo potential probiotic activity of Bacillus subtilis and Shewanella algae for use in Litopenaeus vannamei rearing. Aquaculture 488:114–122
Jurado J, Villasanta-González A, Tapia-Paniagua ST et al (2018) Dietary administration of the probiotic, Shewanella putrefaciens, Pdp11 promotes transcriptional changes of genes involved in growth and immunity in, Solea senegalensis, larvae. Fish Shellfish Immun 77:350–363
Brown RM, Wiens GD, Salinas I (2018) Analysis of the gut and gill microbiome of resistant and susceptible lines of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Fish Shellfish Immun 86:497–506
Aro L, Correa K, Martínez A et al (2014) Characterization of Mycobacterium salmoniphilum as causal agent of mycobacteriosis in Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar L. from a freshwater recirculation system. J Fish Dis 37:341–348
Zhang L, Jie Li, Zhengguo Z et al (2018) Mycobacterium marinum, is the causative agent of splenic and renal granulomas in half-smooth tongue sole (Cynoglossus semilaevis, Günther) in China. Aquaculture 490:203–207
Balcázar JL, Planas M, Pintado J (2014) Mycobacterium hippocampisp. nov. a rapidly growing scotochromogenic species isolated from a seahorse with tail rot. Curr Microbiol 69:329–333
Swaim LE, Connolly LE, Volkman HE et al (2006) Mycobacterium marinum infection of adult zebrafish causes caseating granulomatous tuber-culosis and is moderated by adaptive immunity. Infect Immun 74:6108–6117
Balcázar JL, Lee NM, Pintado J et al (2010) Phylogenetic characterization and in situ detection of bacterial communities associated with seahorses (Hippocampus guttulatus) in captivity. Syst Appl Microbiol 33(2):71–77
Hongye J, Tingjin C, Hengchang S et al (2017) Immune response induced by oral delivery of Bacillus subtilis spores expressing enolase of Clonorchis sinensis in grass carps (Ctenopharyngodon idellus). Fish Shellfish Immun 60:318–325
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Welfare Technology Applied Research Project of Zhejiang Province [No. LGN19C190009]; Natural Science Foundation of Ningbo Under Contract [No. 2017A610282]; Key Project of Ministry of Education, Science and Technology [No. 212070]; Discipline Opened Program of Ningbo University [No. xkzsc1508] and K C Wong Magna Fund in Ningbo University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All handling of fish was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Zhejiang Province, and performed in strict accordance with the Regulations for the Administration of Affairs Concerning Experimental Animals, under protocol license number: SYXK (ZHE) 2019 – 0005.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, R., Pan, X. & Xu, Y. Altered Intestinal Microbiota Composition Associated with Enteritis in Yellow Seahorses Hippocampus kuda (Bleeker, 1852). Curr Microbiol 77, 730–737 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-019-01859-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-019-01859-6