Abstract
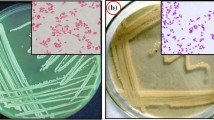
A Gram-stain negative, strictly aerobic, non-spore forming, non-motile, rod-shaped bacterium, designated TBBPA-24T, was isolated from tetrabromobisphenol A-contaminated soil in China. Phylogenetic analysis based on the 16S rRNA gene sequences showed that strain TBBPA-24T was most closely related to Pedobacter nanyangensis Q4T (96.5%) and Pedobacter ‘zeaxanthinifaciens’ TDMA-5T (96.1%). Chemotaxonomic analysis revealed that strain TBBPA-24T possessed MK-7 as the major respiratory quinone and lipid, aminolipid, phospholipid, phosphatidylethanolamine, and phosphoaminolipid as the major polar lipid. The major fatty acids were iso-C15:0 (40.2%), summed feature 3 (C16:1ω6c and/or C16:1ω7c, 25.6%) and iso-C17:0 3-OH (16.4%). The genomic DNA G+C content of strain TBBPA-24T was 43.9 mol%. Based on the phylogenetic, phenotypic characteristics, and chemotaxonomic data, strain TBBPA-24T is considered a novel species of the genus Pedobacter, for which the name Pedobacter pollutisoli sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain TBBPA-24T (= KCTC 62314T = CCTCC AB 2017244T) is proposed.

Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
The GenBank/EMBL/DDBJ accession number for the 16S rRNA gene sequence of Pedobacter pollutisoli TBBPA-24T is MG768961 and the DPD number is TA00619.
References
An DS, Kim SG, Ten LN, Cho CH (2009) Pedobacter daechungensis sp. nov., from freshwater lake sediment in South Korea. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:69–72
Asker D, Beppu T, Ueda K (2008) Nubsella zeaxanthinifaciens gen. nov., sp. nov., a zeaxanthin-producing bacterium of the family Sphingobacteriaceae isolated from freshwater. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:601–606
Baik KS, Park YD, Kim MS, Park SC, Moon EY, Rhee MS, Choi JH, Seong CN (2007) Pedobacter koreensis sp. nov., isolated from fresh water. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:2079–2083
Bernardet JF, Nakagawa Y, Holmes B (2002) Proposed minimal standards for describing new taxa of the family Flavobacteriaceae and emended description of the family. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 52:1049–1070
Buck JD (1982) Nonstaining (KOH) method for determination of gram reactions of marine bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 44:992–993
Collins MD, Pirouz T, Goodfellow M, Minnikin DE (1977) Distribution of menaquinones in actinomycetes and corynebacteria. J Gen Microbiol 100:221–230
Felsenstein J (1981)) Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. J Mol Evol 17:368–376
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791
Gallego V, Garcıà MT, Ventosa A (2006) Pedobacter aquatilis sp. nov., isolated from drinking water, and emended description of the genus Pedobacter. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:1853–1858
Gordon NS, Valenzuela A, Adams SM, Ramsey PW, Pollock JL, Holben WE, Gannon JE (2009) Pedobacter nyackensis sp. nov., Pedobacter alluvionis sp. nov. and Pedobacter borealis sp. nov., isolated from Montana flood-plain sediment and forest soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:1720–1726
Hall TA (1999) BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser 41:95–98
Hoang VA, Kim YJ, Nguyen NL, Min JW, Yang DC (2013) Pedobacter ginsengiterrae sp. nov., isolated from soil of a ginseng field. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:1273–1279
Hwang CY, Choi DH, Cho BC (2006) Pedobacter roseus sp. nov., isolated from a hypertrophic pond, and emended description of the genus Pedobacter. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:1831–1836
Kim OS, Cho YJ, Lee K, Yoon SH, Kim M, Na H, Park SC, Jeon YS, Lee JH, Yi H, Won S, Chun J (2012) Introducing EzTaxon-e: a prokaryotic 16S rRNA gene sequence database with phylotypes that represent uncultured species. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:716–721
Kook MC, Park YJ, Yi TH (2014) Pedobacter jejuensis sp. nov., isolated from soil of a pine grove, and emended description of the genus Pedobacter. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:1789–1794
Lane DL (1991) 16S/23S rRNA sequencing. In: Stackebrandt ER, Goodfellow M (eds) Nucleic acid techniques in bacterial systematics. Wiley, Chichester, pp 115–175
Li R, Zheng JW, Wang R, Song Y, Chen Q, Yang X, Li SP, Jiang JD (2010) Biochemical degradation pathway of dimethoate by Paracoccus sp. Lgjj-3 isolated from treatment wastewater. Int J Biodeterior Biodegrad 64:51–57
Mandel M, Marmur J (1968) Use of ultraviolet absorbance-temperature profile for determining the guanine plus cytosine content of DNA. Methods Enzymol 12B:195–206
Mccarthy AJ, Cross T (1984) A taxonomic study of Thermomonospora and other monosporic Actinomycetes. Microbiol-SGM 130:5–25
Muurholm S, Cousin S, Päuker O, Brambilla E, Stackebrandt E (2007) Pedobacter duraquae sp. nov. Pedobacter westerhofensis sp. nov., Pedobacter metabolipauper sp. nov., Pedobacter hartonius sp. nov. and Pedobacter steynii sp. nov., isolated from a hard-water rivulet. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:2221–2227
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 3rd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor
Sasser M (1990) Identification of bacteria by gas chromatography of cellular fatty acids. MIDI Technical Note 101. Newark, DE: MIDI
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Steyn PL, Segers P, Vancanneyt M, Sandra P, Kersters K, Joubert JJ (1998) Classification of heparinolytic bacteria into a new genus, Pedobacter, comprising four species: Pedobacter heparinus comb. nov. Pedobacter piscium comb. nov., Pedobacter africanus sp. nov. and Pedobacter saltans sp. nov. Proposal of the family Sphingobacteriaceae fam. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 48:165–177
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using Maximum Likelihood, evolutionary Distance, and Maximum Parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evo 28:2731–2739
Ten LN, Liu QM, Im WT, Lee M, Yang DC, Lee ST (2006) Pedobacter ginsengisoli sp. nov., a DNase-producing bacterium isolated from soil of a ginseng field in South Korea. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:2565–2570
Tindall BJ (1990) A comparative study of the lipid composition of Halobacterium saccharovorum from various sources. Syst Appl Microbiol 13:128–130
Tindall BJ (1990) Lipid composition of Halobacterium lacusprofundi. FEMS Microbiol Lett 66:199–202
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL-X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882
Roh SW, Quan ZX, Nam YD, Chang HW, Kim KH, Kim MK, Im WT, Jin L, Kim SH (2008) Pedobacter agri sp. nov., from soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:1640–1643
Oh HW, Kim BC, Park DS, Jeong WJ, Kim H, Lee KH, Kim SU (2013) Pedobacter luteus sp. nov., isolated from soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:1304–1310
Yang DJ, Hong JK (2017) Pedobacter solisilvae sp. nov., isolated from forest soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:4814–4819
Yang JE, Son HM, Lee JM, Shin HS, Park SY, Lee DG, Kook MC, Yi TH (2013) Pedobacter ginsenosidimutans sp. nov., with ginsenoside-converting activity. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:4396–4401
Zhang DC, Schinner F, Margesin R (2010) Pedobacter bauzanensis sp. nov., isolated from soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:2592–2595
Zhang B, Liu ZQ, Zheng YG (2017) Pedobacter quisquiliarum sp. nov., isolated from activated sludge. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.002531
Zhang H, Zhang J, Song M, Cheng MG, Wu YD, Guo SH, Li Q, Hong Q, Huang X (2015) Pedobacter nanyangensis sp. nov., isolated from herbicide-contaminated soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 65:3517–3521
Zhou Z, Jiang F, Wang S, Peng F, Dai J, Li W, Fang C (2012) Pedobacter arcticus sp. nov., a facultative psychrophile isolated from Arctic soil, and emended descriptions of the genus Pedobacter, Pedobacter heparinus, Pedobacter daechungensis, Pedobacter terricola, Pedobacter glucosidilyticus and Pedobacter lentus. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:1963–1969
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported through grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31600080) and the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province, China (ZR2016CB29).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Research Involving Human Participants and/or Animals
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mu, Y., Ke, Z., Feng, CX. et al. Pedobacter pollutisoli sp. nov., Isolated from Tetrabromobisphenol A-Contaminated Soil. Curr Microbiol 76, 442–447 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-019-01643-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-019-01643-6