Abstract
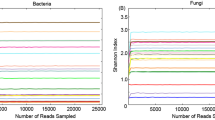
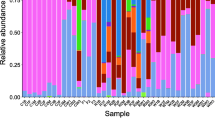
Intestinal microbiota is essential to the health and physiology of host animals. We undertook the first microbiological study of the fecal bacterial composition from critically endangered (CR) Yangtze finless porpoises (Neophocaena asiaeorientalis asiaeorientalis; YFPs) living under captive and semi-natural conditions using both high-throughput sequencing method and 16S rRNA gene clone library method. As determined by high-throughput sequencing of V3–V4 regions of the 16S rRNA gene, semi-natural samples harbored 30 and 36 operational taxonomic units (OTUs), which was more than the 22 and 27 OTUs detected from YFPs living in captivity. In captive YFPs Firmicutes was the predominant phylum, whereas this was Proteobacteria for YFPs living in semi-nature conditions. This suggests habitat-specific fecal bacterial composition of YFPs. Plesiomonas spp. and Aeromonas spp., which are potentially pathogenic, were identified in all the feces. Bacterial diversity from one porpoise living in captivity was also determined by constructing a 16S rRNA gene clone library and only 1 phylum was identified. High-throughput sequencing was more effective at determining the bacterial diversity compared to the 16S rRNA gene clone library. This study provides important information for the management and conservation of the CR YFPs.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aldape M, Bryant A, Stevens D (2006) Clostridium sordellii infection: epidemiology, clinical findings, and current perspectives on diagnosis and treatment. Clin Infect Dis 43(11):1436–1446
Bolger AM, Lohse M, Usadel B (2014) Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 30:2114–2120
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Pena AG, Goodrich JK, Gordon JI (2010) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods 7(5):335–336
Carnahan A, Fanning G, Joseph S (1991) Aeromonas jandaei (formerly genospecies DNA group 9 A. sobria), a new sucrose-negative species isolated from clinical specimens. J Clin Microbiol 29(3):560–564
Chen W, Liu F, Ling Z, Tong X, Xiang C (2012) Human intestinal lumen and mucosa-associated microbiota in patients with colorectal cancer. PLoS One 7(6):e39743
Cunha IS, Barreto CC, Costa OY, Bomfim MA, Castro AP, Kruger RH, Quirino BF (2011) Bacteria and Archaea community structure in the rumen microbiome of goats (Capra hircus) from the semiarid region of Brazil. Anaerobe 17(3):118–124
De la Fe C, Rodríguez J, Ramírez G, Hervás J, Gil J, Poveda J (2006) Sudden death associated with Clostridium sordellii in captive lions (Panthera leo). Vet Pathol 43(3):370–374
Deodhar LP, Saraswathi K, Varudkar A (1991) Aeromonas spp. and their association with human diarrheal disease. J Clin Microbiol 29(5):853–856
Dethlefsen L, Eckburg PB, Bik EM, Relman DA (2006) Assembly of the human intestinal microbiota. Trends Ecol Evol 21(9):517–523
Eckburg PB, Bik EM, Bernstein CN, Purdom E, Dethlefsen L, Sargent M, Gill SR, Nelson KE, Relman DA (2005) Diversity of the human intestinal microbial flora. Science 308(5728):1635–1638
Edgar RC (2010) Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 26(19):2460–2461
Feaster F, Nisbet R, Barber J (1978) Aeromonas hydrophila corneal ulcer. Am J Ophthalmol 85(1):114–117
Glad T, Bernhardsen P, Nielsen KM, Brusetti L, Andersen M, Aars J, Sundset MA (2010) Bacterial diversity in faeces from polar bear (Ursus maritimus) in Arctic Svalbard. BMC Microbiol 10(1):10
Gu S, Chen D, Zhang J, Lv X, Wang K, Duan L, Nie Y, Wu X (2013) Bacterial community mapping of the mouse gastrointestinal tract. PLoS One 8(10):e74957
Huber T, Faulkner G, Hugenholtz P (2004) Bellerophon: a program to detect chimeric sequences in multiple sequence alignments. Bioinformatics 20(14):2317–2319
Isaacs LT, Kan J, Nguyen L, Videau P, Anderson MA, Wright TL, Hill RT (2009) Comparison of the bacterial communities of wild and captive sponge Clathria prolifera from the Chesapeake Bay. Mar Biotechnol 11(6):758–770
Janda JM, Duffey PS (1988) Mesophilic aeromonads in human disease: current taxonomy, laboratory identification, and infectious disease spectrum. Rev Infect Dis 10(5):980–997
Janda JM, Guthertz LS, Kokka RP, Shimada T (1994) Aeromonas species in septicemia: laboratory characteristics and clinical observations. Clin Infect Dis 19(1):77–83
Kain KC, Kelly MT (1989) Clinical features, epidemiology, and treatment of Plesiomonas shigelloides diarrhea. J Clin Microbiol 27(5):998–1001
Karlsson FH, Fåk F, Nookaew I, Tremaroli V, Fagerberg B, Petranovic D, Bäckhed F, Nielsen J (2012) Symptomatic atherosclerosis is associated with an altered gut metagenome. Nat Commun 3:1245
Kooperman N, Ben-Dov E, Kramarsky-Winter E, Barak Z, Kushmaro A (2007) Coral mucus-associated bacterial communities from natural and aquarium environments. FEMS Microbiol Lett 276(1):106–113
Kueneman JG, Parfrey LW, Woodhams DC, Archer HM, Knight R, McKenzie VJ (2014) The amphibian skin-associated microbiome across species, space and life history stages. Mol Ecol 23(6):1238–1250
Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown N, Chenna R, McGettigan PA, McWilliam H, Valentin F, Wallace IM, Wilm A, Lopez R (2007) Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 23(21):2947–2948
Lazarevic V, Whiteson K, Huse S, Hernandez D, Farinelli L, Østerås M, Schrenzel J, François P (2009) Metagenomic study of the oral microbiota by Illumina high-throughput sequencing. J Microbiol Meth 79(3):266–271
Li ZP, Liu HL, Li GY, Bao K, Wang KY, Xu C, Yang YF, Yang FH, Wright AG (2013) Molecular diversity of rumen bacterial communities from tannin-rich and fiber-rich forage fed domestic Sika deer (Cervus nippon) in China. BMC Microbiol 13(1):151
Magoč T, Salzberg SL (2011) FLASH: fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 27(21):2957–2963
McDonald R, Schreier HJ, Watts JE (2012) Phylogenetic analysis of microbial communities in different regions of the gastrointestinal tract in Panaque nigrolineatus, a wood-eating fish. PLoS One 7(10):e48018
McLaughlin RW, Chen M, Zheng J, Zhao Q, Wang D (2012) Analysis of the bacterial diversity in the fecal material of the endangered Yangtze finless porpoise, Neophocaena phocaenoides asiaeorientalis. Mol Biol Rep 39(5):5669–5676
Mei Z, Zhang X, Huang SL, Zhao X, Hao Y, Zhang L, Qian Z, Zheng J, Wang K, Wang D (2014) The Yangtze finless porpoise: on an accelerating path to extinction? Biol Conserv 172:117–123
Miller ML, Koburger JA (1985) Plesiomonas shigelloides: an opportunistic food and waterborne pathogen. J Food Protect 48(5):449–457
Muñoz P, Fernández-Baca V, Peláez T, Sánchez R, Rodríguez-Créixems M, Bouza E (1994) Aeromonas peritonitis. Clin Infect Dis 18(1):36–37
O’Hara AM, Shanahan F (2006) The gut flora as a forgotten organ. EMBO Rep 7(7):688–693
Ong K, Sordillo E, Frankel E (1991) Unusual case of Aeromonas hydrophila endocarditis. J Clin Microbiol 29(5):1056–1057
Pallen MJ, Loman NJ, Penn CW (2010) High-throughput sequencing and clinical microbiology: progress, opportunities and challenges. Curr Opin Microbiol 13(5):625–631
Parras F, Diaz M, Reina J, Moreno S, Guerrero C, Bouza E (1993) Meningitis due to Aeromonas species: case report and review. Clin Infect Dis 17(6):1058–1060
Pluske J, Durmic Z, Payne H, Mansfield J, Mullan B, Hampson D, Vercoe P (2007) Microbial diversity in the large intestine of pigs born and reared in different environments. Livest Sci 108(1):113–116
Polz MF, Cavanaugh CM (1998) Bias in template-to-product ratios in multitemplate PCR. Appl Environ Microb 64(10):3724–3730
Pope PB, Mackenzie AK, Gregor I, Smith W, Sundset MA, McHardy AC, Morrison M, Eijsink VG (2012) Metagenomics of the Svalbard reindeer rumen microbiome reveals abundance of polysaccharide utilization loci. PLoS One 7(6):e38571
Pryde SE, Duncan SH, Hold GL, Stewart CS, Flint HJ (2002) The microbiology of butyrate formation in the human colon. FEMS Microbiol Lett 217(2):133–139
Qin J, Li Y, Cai Z, Li S, Zhu J, Zhang F, Liang S, Zhang W, Guan Y, Shen D (2012) A metagenome-wide association study of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes. Nature 490(7418):55–60
Ringø E, Sperstad S, Myklebust R, Refstie S, Krogdahl Å (2006) Characterisation of the microbiota associated with intestine of Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua L.): the effect of fish meal, standard soybean meal and a bioprocessed soybean meal. Aquaculture 261(3):829–841
Ritchie LE, Steiner JM, Suchodolski JS (2008) Assessment of microbial diversity along the feline intestinal tract using 16S rRNA gene analysis. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 66(3):590–598
Roeselers G, Mittge EK, Stephens WZ, Parichy DM, Cavanaugh CM, Guillemin K, Rawls JF (2011) Evidence for a core gut microbiota in the zebrafish. ISME J 5(10):1595–1608
Salyers A, Vercellotti J, West S, Wilkins T (1977) Fermentation of mucin and plant polysaccharides by strains of Bacteroides from the human colon. Appl Environ Microb 33(2):319–322
Schloss PD, Westcott SL, Ryabin T, Hall JR, Hartmann M, Hollister EB, Lesniewski RA, Oakley BB, Parks DH, Robinson CJ (2009) Introducing mothur: open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ Microb 75(23):7537–7541
Smith MI, Yatsunenko T, Manary MJ, Trehan I, Mkakosya R, Cheng J, Kau AL, Rich SS, Concannon P, Mychaleckyj JC (2013) Gut microbiomes of Malawian twin pairs discordant for kwashiorkor. Science 339(6119):548–554
Srinivasan S, Hoffman NG, Morgan MT, Matsen FA, Fiedler TL, Hall RW, Ross FJ, McCoy CO, Bumgarner R, Marrazzo JM (2012) Bacterial communities in women with bacterial vaginosis: high resolution phylogenetic analyses reveal relationships of microbiota to clinical criteria. PLoS One 7(6):e37818
Suchodolski JS, Ruaux CG, Steiner JM, Fetz K, Williams DA (2005) Assessment of the qualitative variation in bacterial microflora among compartments of the intestinal tract of dogs by use of a molecular fingerprinting technique. Am J Vet Res 66(9):1556–1562
Suzuki MT, Giovannoni SJ (1996) Bias caused by template annealing in the amplification of mixtures of 16S rRNA genes by PCR. Appl Environ Microb 62(2):625–630
Thewissen J, Sensor JD, Clementz MT, Bajpai S (2011) Evolution of dental wear and diet during the origin of whales. Paleobiology 37(4):655–669
Tsukamoto T, Kinoshita Y, Shimada T, Sakazaki R (1978) Two epidemics of diarrhoeal disease possibly caused by Plesiomonas shigelloides. J Hyg Camb 80(02):275–280
Turnbaugh PJ, Hamady M, Yatsunenko T, Cantarel BL, Duncan A, Ley RE, Sogin ML, Jones WJ, Roe BA, Affourtit JP (2008) A core gut microbiome in obese and lean twins. Nature 457(7228):480–484
Van Bressem MF, Raga JA, Di Guardo G, Jepson PD, Duignan PJ, Siebert U, Barrett T, Santos M, Moreno IB, Siciliano S (2009) Emerging infectious diseases in cetaceans worldwide and the possible role of environmental stressors. Dis Aquat Organ 86(2):143–157
Wang D, Turvey S, Zhao X, Mei Z (2013) Neophocaena asiaeorientalis ssp. asiaeorientalis. IUCN Red List of Threatened Species Version 20131
Wang J, Frasier T, Yang S, White B (2008) Detecting recent speciation events: the case of the finless porpoise (genus Neophocaena). Heredity 101(2):145–155
Wang JY, Yang SC, Wang BJ, Wang LS (2010) Distinguishing between two species of finless porpoises (Neophocaena phocaenoides and N. asiaeorientalis) in areas of sympatry. Mammalia 74(3):305–310
Wang Q, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM, Cole JR (2007) Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl Environ Microb 73(16):5261–5267
Wu S, Gao T, Zheng Y, Wang W, Cheng Y, Wang G (2010) Microbial diversity of intestinal contents and mucus in yellow catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco). Aquaculture 303(1):1–7
Wu S, Wang G, Angert ER, Wang W, Li W, Zou H (2012) Composition, diversity, and origin of the bacterial community in grass carp intestine. PLoS One 7(2):e30440
Xing M, Hou Z, Yuan J, Liu Y, Qu Y, Liu B (2013) Taxonomic and functional metagenomic profiling of gastrointestinal tract microbiome of the farmed adult turbot (Scophthalmus maximus). FEMS Microbiol Ecol 86(3):432–443
Zu G, Yu W, Li J (2000) Diagnosis and epidemiological research on bacterial septicemia of grass carp Ctenopharyngodon idellus. Freshw Fish 30:35–37
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Chaoqun Wang and Qingzhong Zhao for their help in collecting fecal samples. We also thank Zhigang Mei and Lin Zhang for their helpful critique on an earlier version of this manuscript. Special gratitude to Prof. Erko Stackebrandt and anonymous reviewers for their valuable suggestions for improving the manuscript. This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31430080; No. 31000168), the Experimental Platform Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. CZBZX-1), and the Special Conservation Fund for the Yangtze finless porpoise from the Ministry of Agriculture of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interest declared.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wan, X., Ruan, R., McLaughlin, R.W. et al. Fecal Bacterial Composition of the Endangered Yangtze Finless Porpoises Living Under Captive and Semi-natural Conditions. Curr Microbiol 72, 306–314 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-015-0954-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-015-0954-z