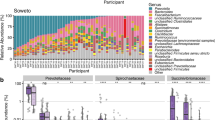
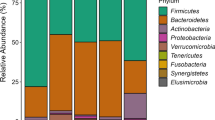
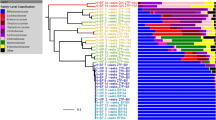
Abstract
Understanding the transmission of the human microbiota from mother to child is of major importance. Although we are gaining knowledge using 16S rRNA gene analyses, the resolution of this gene is not sufficient to determine transmission patterns. We therefore developed an Illumina deep sequencing approach targeting the 16–23S rRNA Internal Transcribed Spacer (ITS) for high-resolution microbiota analyses. Using this approach, we analyzed the composition and potential mother to child transmission patterns of the microbiota (milk and stool) in a longitudinal cohort of 20 mother/child pairs. Our results show overlap in the infant stool microbiota with both mother’s milk and stool, and that the overlap with stool increases with age. We found an Operational Taxonomic Unit resembling Streptococcus gordonii as the most widespread colonizer of both mothers and their children. In conclusion, the increased resolution of 16–23S rRNA ITS deep sequencing revealed new knowledge about potential transmission patterns of human-associated bacteria.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avershina E, Rudi K (2013) Is it who you are or what you do that is important in the human gut? Benef Microbes 4(3):219–222. doi:10.3920/BM2013.0016
Avershina E, Storro O, Oien T, Johnsen R, Pope P, Rudi K (2014) Major faecal microbiota shifts in composition and diversity with age in a geographically restricted cohort of mothers and their children. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 87(1):280–290. doi:10.1111/1574-6941.12223
Cabrera-Rubio R, Collado MC, Laitinen K, Salminen S, Isolauri E, Mira A (2012) The human milk microbiome changes over lactation and is shaped by maternal weight and mode of delivery. Am J Clin Nutr 96(3):544–551. doi:10.3945/ajcn.112.037382
D’Elia TV, Cooper CR, Johnston CG (2007) Source tracking of Escherichia coli by 16S-23S intergenic spacer region denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE) of the rrnB ribosomal operon. Can J Microbiol 53(10):1174–1184. doi:10.1139/W07-083
Dec M, Urban-Chmiel R, Gnat S, Puchalski A, Wernicki A (2014) Identification of Lactobacillus strains of goose origin using MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry and 16S-23S rDNA intergenic spacer PCR analysis. Res Microbiol 165(3):190–201. doi:10.1016/j.resmic.2014.02.003
Dotterud CK, Storro O, Johnsen R, Oien T (2010) Probiotics in pregnant women to prevent allergic disease: a randomized, double-blind trial. Br J Dermatol 163(3):616–623. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2010.09889.x
Douglas CWI, Heath J, Hampton KK, Preston FE (1993) Identity of viridans streptococci isolated from cases of infective endocarditis. J Med Microbiol 39(3):179–182. doi:10.1099/00222615-39-3-179
Jeurink PV, van Bergenhenegouwen J, Jimenez E, Knippels LM, Fernandez L, Garssen J, Knol J, Rodriguez JM, Martin R (2013) Human milk: a source of more life than we imagine. Benef Microbes 4(1):17–30. doi:10.3920/BM2012.0040
Khodayar-Pardo P, Mira-Pascual L, Collado MC, Martinez-Costa C (2014) Impact of lactation stage, gestational age and mode of delivery on breast milk microbiota. J Perinatol 34(8):599–605. doi:10.1038/jp.2014.47
Kim CM, Song ES, Jang HJ, Kim HJ, Lee S, Shin JH, Kim SJ, Jeong SH, Jeong J, Koh K, Choi GE, Lee EY, Chang CL (2010) Development and evaluation of oligonucleotide chip based on the 16S-23S rRNA gene spacer region for detection of pathogenic microorganisms associated with sepsis. J Clin Microbiol 48(5):1578–1583. doi:10.1128/JCM.01130-09
Lee SF (2003) Oral colonization and immune responses to Streptococcus gordonii: potential use as a vector to induce antibodies against respiratory pathogens. Curr Opin Infect Dis 16(3):231–235. doi:10.1097/01.qco.0000073772.11390.ae
Lindberg E, Adlerberth I, Hesselmar B, Saalman R, Strannegard I-L, Aberg N, Wold AE (2004) High rate of transfer of Staphylococcus aureus from parental skin to infant gut flora. J Clin Microbiol 42(2):530–534
LoCascio RG, Desai P, Sela DA, Weimer B, Mills DA (2010) Broad Conservation of milk utilization genes in Bifidobacterium longum subsp. infantis as revealed by comparative genomic hybridization. Appl Environ Microbiol 76(22):7373–7381
McDonald D, Price MN, Goodrich J, Nawrocki EP, DeSantis TZ, Probst A, Andersen GL, Knight R, Hugenholtz P (2012) An improved Greengenes taxonomy with explicit ranks for ecological and evolutionary analyses of bacteria and archaea. ISME J 6 (3):610–618. http://www.nature.com/ismej/journal/v6/n3/suppinfo/ismej2011139s1.html
Naseribafrouei A, Hestad K, Avershina E, Sekelja M, Linlokken A, Wilson R, Rudi K (2014) Correlation between the human fecal microbiota and depression. Neurogastroenterol Motil. doi:10.1111/nmo.12378
Rajilic-Stojanovic M, de Vos WM (2014) The first 1000 cultured species of the human gastrointestinal microbiota. FEMS Microbiol Rev 38(5):996–1047. doi:10.1111/1574-6976.12075
Rudi K, Zimonja M, Kvenshagen B, Rugtveit J, Midtvedt T, Eggesbo M (2007) Alignment-independent comparisons of human gastrointestinal tract microbial communities in a multidimensional 16S rRNA gene evolutionary space. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(8):2727–2734
Ruegger PM, Clark RT, Weger JR, Braun J, Borneman J (2014) Improved resolution of bacteria by high throughput sequence analysis of the rRNA internal transcribed spacer. J Microbiol Methods 105:82–87. doi:10.1016/j.mimet.2014.07.001
Saruta K, Matsunaga T, Kono M, Hoshina S, Ikawa S, Sakai O, Machida K (1997) Rapid identification and typing of Staphylococcus aureus by nested PCR amplified ribosomal DNA spacer region. FEMS Microbiol Lett 146(2):271–278
Schacher B, Baron F, Rossberg M, Wohlfeil M, Arndt R, Eickholz P (2007) Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans as indicator for aggressive periodontitis by two analysing strategies. J Clin Periodontol 34(7):566–573. doi:10.1111/j.1600-051X.2007.01080.x
Sekelja M, Berget I, Naes T, Rudi K (2011) Unveiling an abundant core microbiota in the human adult colon by a phylogroup-independent searching approach. ISME J 5(3):519–531. doi:10.1038/ismej.2010.129
Takahashi Y, Takashima E, Shimazu K, Yagishita H, Aoba T, Konishi K (2006) Contribution of sialic acid-binding adhesin to pathogenesis of experimental endocarditis caused by Streptococcus gordonii DL1. Infect Immun 74(1):740–743. doi:10.1128/IAI.74.1.740-743.2006
Yu Y, Lee C, Kim J, Hwang S (2005) Group-specific primer and probe sets to detect methanogenic communities using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. Biotechnol Bioeng 89(6):670–679. doi:10.1002/bit.20347
Zeng YH, Koblizek M, Li YX, Liu YP, Feng FY, Ji JD, Jian JC, Wu ZH (2013) Long PCR-RFLP of 16S-ITS-23S rRNA genes: a high-resolution molecular tool for bacterial genotyping. J Appl Microbiol 114(2):433–447. doi:10.1111/jam.12057
Zheng L, Itzek A, Chen Z, Kreth J (2011) Environmental influences on competitive hydrogen peroxide production in Streptococcus gordonii. Appl Environ Microbiol 77(13):4318–4328. doi:10.1128/AEM.00309-11
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank the Norwegian University of Life Sciences for financial support and the team at the MiDiv Lab for fruitful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schanche, M., Avershina, E., Dotterud, C. et al. High-Resolution Analyses of Overlap in the Microbiota Between Mothers and Their Children. Curr Microbiol 71, 283–290 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-015-0843-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-015-0843-5