Abstract
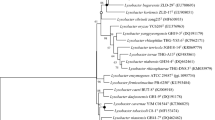
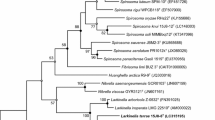
A novel bacterial strain, designated Re6T, was isolated from forest soil collected in Campbell University, North Carolina. The cells are aerobic, Gram-positive, non-motile, and rod shaped. Growth occurred at 4–42 °C (optimum, 25 °C), pH 6–9 (optimum, pH 6), and in 0–3 % NaCl (w/v). Phylogenetic analysis based on 16S rRNA gene sequences indicated that strain Re6T belonged to the genus Leucobacter and showed the highest 16S rRNA gene sequence similarities with Leucobacter iarius JCM 14736T (98.3 %), Leucobacter luti JCM 14920T (97.9 %), Leucobacter komagatae JCM 9414T (97.8 %), and Leucobacter denitrificans KACC 14055T (97.7 %). Strain Re6T contained anteiso-C15:0 (45.2 %), iso-C16:0 (17.1 %), and anteiso-C17:0 (32.6 %) as the major cellular fatty acids; MK-11 as the major respiratory quinone; l-diaminobutyric acid as the diagnostic diamine acid in cell wall peptidoglycan; and diphosphatidylglycerol and phosphatidylglycerol as the main polar lipids. The DNA G+C content of the strain Re6T was 66.6 mol%. DNA–DNA hybridization results showed similarity values less than 50 % for DNA samples from the most closely related type strains of L. iarius, L. luti, and L. komagatae. On the basis of the data from the polyphasic analysis, strain Re6T is considered to be a representative novel species in the genus Leucobacter, for which the name Leucobacter humi sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain is Re6T (KEMC 7301-006T = JCM 18638T).


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Collins MD, Jones D (1981) Distribution of isoprenoid quinone structural types in bacteria and their taxonomic implications. Microbiol Rev 45:316–354
Doetsch RN (1981) Determinative methods of light microscopy. In: Gerhardt P, Murray RGE, Costilow RN, Nester EW, Wood WA, Krieg NR, Phillips GH (eds) Manual of methods for general bacteriology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, pp 21–33
Ezaki T, Hashimoto Y, Yabuuchi E (1989) Fluorometric DNA–DNA hybridization in microdilution wells as an alternative to membrane filter hybridization in which radioisotopes are used to determine genetic relatedness among bacterial strains. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 39:224–229
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limit on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791
Hall TA (1999) BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser 41:95–98
Halpern M, Shaked T, Pukall R et al (2009) Leucobacter chironomi sp. nov., a chromate-resistant bacterium isolated from a chironomid egg mass. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:665–670
Kimura M (1983) The neutral theory of molecular evolution. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Kim HJ, Lee SS (2011) Leucobacter kyeonggiensis sp. nov., a new species isolated from dye waste water. J Microbiol 49(6):1044–1049
Kim OS, Cho YJ, Lee K, Yoon SH, Kim M, Na H, Park SC, Jeon YS, Lee JH et al (2012) Introducing EzTaxon-e: a prokaryotic 16S rRNA gene sequence database with phylotypes that represent uncultured species. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:716–721
Komagata K, Suzuki K (1987) Lipid and cell-wall analysis in bacterial systematics. Methods Microbiol 19:161–207
Kumar S, Tamura K, Nei M (2004) MEGA3: integrated software for molecular evolutionary genetics analysis and sequence alignment. Brief Bioinform 5:150–163
Lee JH, Lee SS (2012) Leucobacter margaritiformis sp. nov., isolated from bamboo extract. Curr Microbiol 64(5):441–448
Lin YC, Uemori K, de Briel DA et al (2004) Zimmermannella helvola gen. nov., sp. nov., Zimmermannella alba sp. nov., Zimmermannella bifida sp. nov., Zimmermannella faecalis sp. nov. and Leucobacter albus sp. nov., novel members of the family Microbacteriaceae. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 54:1669–1676
Marmur J (1961) A procedure for the isolation of deoxyribonucleic acid from micro- organisms. J Mol Biol 8:201–218
Martin E, Lodders N, Jäckel U, Schumann P, Kämpfer P (2010) Leucobacter aerolatus sp. nov., from the air of a duck barn. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60(12):2838–2842
Mesbah M, Premachandran U, Whitman WB (1989) Precise measurement of the G+C content of deoxyribonucleic acid by high-performance liquid chromatography. Int J Syst Bacteriol 39:159–167
Minnikin DE, O’Donnell AG, Goodfellow M et al (1984) An integrated procedure for the extraction of bacterial isoprenoid quinones and polar lipids. J Microbiol Methods 2:233–241
Morais PV, Francisco R, Branco R et al (2004) Leucobacter chromiireducens sp. nov, and Leucobacter aridicollis sp. nov., two new species isolated from a chromium contaminated environment. Syst Appl Microbiol 27:646–652
Morais PV, Paulo C, Francisco R et al (2006) Leucobacter luti sp. nov., and Leucobacter alluvii sp. nov., two new species of the genus Leucobacter isolated under chromium stress. Syst Appl Microbiol 29:414–421
Muir RE, Tan MW (2007) Leucobacter chromiireducens subsp. solipictus subsp. nov., a pigmented bacterium isolated from the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans, and emended description of L. chromiireducens. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:2770–2776
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Sasser M (1990). Identification of bacteria by gas chromatography of cellular fatty acids. MIDI Technical Note 101. Newark: MIDI Inc
Schleifer KH, Kandler O (1972) Peptidoglycan types of bacterial cell walls and their taxonomic implications. Bacteriol Rev 36:407–477
Shin NR, Kim MS, Jung MJ et al (2011) Leucobacter celer sp. nov., isolated from Korean fermented seafood. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:2353–2357
Somvanshi VS, Lang E, Schumann P et al (2007) Leucobacter iarius sp. nov., in the family Microbacteriaceae. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:682–686
Takeuchi M, Weiss N, Schumann P et al (1996) Leucobacter komagatae gen. nov., sp. nov., a new aerobic Gram-positive, nonsporulating rod with 2,4-diaminobutyric acid in the cell wall. Int J Syst Bacteriol 46:967–971
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F et al (1997) The ClustalX windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 24:4876–4882
Weisburg WG, Barns SM, Pelletier DA et al (1991) 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J Bacteriol 173:697–703
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Kyonggi University‘s Graduate Research Assistantship 2015, Korea national Environmental Microorganisms Bank (2010-0007473). This research was supported by a Grant (14CTAP-C078666-01) from infrastructure and transportation technology promotion research Program funded by Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, and Transport of Korean government.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The NCBI GenBank/EMBL/DDBJ accession number for the 16S rRNA gene sequence of strain Re6T is KC818288.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Her, J., Lee, SS. Leucobacter humi sp. nov., Isolated from Forest Soil. Curr Microbiol 71, 235–242 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-015-0820-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-015-0820-z