Abstract
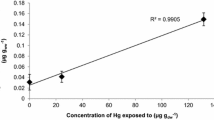
Twenty-nine bacterial isolates representing eight genera from the gastrointestinal tracts of feral brook trout Salvelinus fontinalis (Mitchell) demonstrated multiple maximal antibiotic resistances and concomitant broad-spectrum mercury (Hg) resistance. Equivalent viable plate counts on tryptic soy agar supplemented with either 0 or 25 μM HgCl2 verified the ubiquity of mercury resistance in this microbial environment. Mercury levels in lake water samples measured 1.5 ng L−1; mercury concentrations in fish filets ranged from 81.8 to 1,080 ng g−1 and correlated with fish length. The presence of similar antibiotic and Hg resistance patterns in multiple genera of gastrointestinal microflora supports a growing body of research that multiple selective genes can be transferred horizontally in the presence of an unrelated individual selective pressure. We present data that bioaccumulation of non-point source Hg pollution could be a selective pressure to accumulate both antibiotic and Hg resistant bacteria.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abo-Rady MD (1983) Concentration of heavy metals in brook trout in comparison to aquatic plants and sediments. Z Lebensm Unters Forsch 177(5):339–344
Akinbowale OL, Peng H, Grant P, Barton MD (2007) Antibiotic and heavy metal resistance in motile aeromonads and pseudomonads from rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) farms in Australia. Int J Antimicrob Agents 30:177–182
al-Hashimi AH, al-Zoerba MA (1991) Mercury in some commercial fish from Kuwait: a pilot study. Sci Total Environ 106(1–2):71–82
Allen HK, Donato J, Wang HH, Cloud-Hansen KA, Davies J, Handelsman J (2010) Call of the wild: antibiotic resistance genes in natural environments. Nat Rev Microbiol 8:251–259
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215(3):403–410
American Veterinary Medical Association (AVMA) (2001) 2000 Report of the AVMA Panel on Euthanasia. J Am Vet Med Assoc 218(5):669–696
Baker-Austin C, Wright MS, Stepanauskas R, McArthur JV (2006) Co-selection of antibiotic and metal resistance. Trends Microbiol 14:176–182
Barkay T, Miller SM, Summers AO (2003) Bacterial mercury resistance from atoms to ecosystems. FEMS Microbiol Rev 27(2–3):355–384
Barkay T, Smets BF (2005) Horizontal gene flow in microbial communities: synthesis across scientific disciplines. Am Soc Microbiol News 71:412–419
Cahill MM (1990) Bacterial flora of fishes: a review. Microb Ecol 19(1):21–41
Chen CY, Stemberger RS, Kamman NC, Brandon MM, Folt CL (2004) Patterns of Hg bioaccumulation and transfer in aquatic food webs across multi-lake studies in the northeast US. Ecotoxicology 14:135–147
D’Costa VM, McGrann KM, Hughes DW, Wright GD (2006) Sampling the antibiotic resistome. Science 311:374–377
Evers DC, Han Y-J, Driscoll CT, Kamman NC, Goodale MW, Lambert KF, Holsen TM, Chen CY, Clair TA, Butler T (2007) Biological mercury hotspots in the Northeastern United States and Southeastern Canada. Biosci Rep 57(1):29–43
Fricke WF, Welch TJ, McDermott PF, Mammel MK, LeClerc JE, White DG, Cebula TA, Ravel J (2009) Comparative genomics of the IncA/C multidrug resistance plasmid family. J Bacteriol 191(15):4750–4757. doi:10.1128/JB.00189-09
Hamlett NV, Poindexter JS, Reznikoff WS (1981) Selective pressures exerted by sewage sludge fertilization of chemoheterotrophic bacterial communities in the Great Sippewisett Marsh. Biol Bull Mar Biol Lab Woods Hole 161:326–327
Heuer OE, Kruse H, Grave K, Collignon P, Karanasager L, Angulo F (2009) Human health consequences of use of antimicrobial agents in aquaculture. Clin Infect Dis 49:1248–1253
Huber I, Spanggaard B, Appel KF, Rossen L, Nielsen T, Gram L (2004) Phylogenetic analysis and in situ identification of the intestinal microbial community of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss, Walbaum). J Appl Microbiol 96(1):117–132
Johnels AG, Westermark T, Berg W, Persson PI, SjoAN strand B (1967) Pike (Esox lucius L.) and some other aquatic organisms in Sweden as indicators of mercury contamination in the environment. Oikos 18:323–333
Kamman NC, Burgess NM, Driscoll CT, Simonin HA, Goodale W, Linehan J, Estabrook R, Hutcheson M, Major A, Scheuhammer AM, Scruton DA (2004) Mercury in freshwater fish of northeast America: a geographic perspective based on fish tissue monitoring databases. Ecotoxicology 14:163–180
Lester SC, del Pilar Pla M, Wang F, Pere Schael I, Jiang H, O’Brien TF (1990) The carriage of Escherichia coli resistant to antibiotic agents by healthy children in Boston, in Caracas, Venezuela and in Qin Pu, China. N Engl J Med 323:285–289
Levy SB, Marshall B, Schleuderberg S, Rowse D, Davis J (1988) High frequency of antibiotic resistance in human fecal flora. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 32:1801–1806
Li H, Toleman MA, Bennett PM, Jones RN, Walsh TR (2008) Complete sequence of p07-406, a 24,179-base-pair plasmid harboring the blaVIM-7 metallo-beta-lactamase gene in a Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolate from the United States. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 52(9):3099–3105
Marshall BM, Ochieng DJ, Levy SB (2009) Commensals: underappreciated reservoir of antibiotic resistance. Microbe 4:231–238
Mathema VB, Thakuri BC, Sillanpaa M (2011) Bacterial mer operon-mediated detoxification of mercurial compounds: a short review. Arch Microbiol 193(12):837–844. doi:10.1007/s00203-011-0751-4
Mazel D, Dychinco B, Webb VA, Davies J (2000) Antibiotic resistance in the ECOR collection: integrons and identification of a novel aad gene. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 44(6):1568–1574
McArthur JV, Tuckfield RC (2000) Spatial patterns in antibiotic resistance among stream bacteria: effects of industrial pollution. Appl Environ Microbiol 66(9):3722–3726
McIntosh D, Cunningham M, Ji B, Fekete FA, Parry EM, Clark SE, Zalinger ZB, Gilg IC, Danner GR, Johnson KA, Beattie M, Ritchie R (2008) Transferable, multiple antibiotic and mercury resistance in Atlantic Canadian isolates of Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. salmonicida is associated with carriage of an IncA/C plasmid similar to the Salmonella enterica plasmid pSN254. J Antimicrob Chemother 61(6):1221–1228
Muyzer G, de Waal EC, Uitterlinden AG (1993) Profiling of complex microbial populations by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of polymerase chain reaction-amplified genes coding for 16S rRNA. Appl Environ Microbiol 59(3):695–700
NCCLS (2002) Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing; twelfth informational supplement. NCCLS Document M100-S12, twelfth edition. National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards, Wayne, PA
Nemergut DR, Martin AP, Schmidt S (2004) Integron diversity in heavy-metal-contaminated mine tailings and inferences about integron evolution. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:1160–1168
Ng SP, Davis B, Palombo EA, Bhave M (2009) A Tn5051-like mer-containing transposon identified in a heavy metal tolerant strain Achromobacter sp. AO22. BMC Res Notes 7:38
Ni Chadhain SM, Schaefer JK, Crane S, Zylstra GJ, Barkay T (2006) Analysis of mercuric reductase (merA) gene diversity in an anaerobic mercury-contaminated sediment enrichment. Environ Microbiol 8(10):1746–1752
Nieto TP, Toranzo AE, Barja JL (1984) Comparison between the bacterial flora associated with fingerling rainbow trout cultured in two different hatcheries in the north-west of Spain. Aquaculture 42(3–4):193–206
Oregaard G, Sorensen SJ (2007) High diversity of bacterial mercuric reductase genes from surface and sub-surface floodplain soil (Oak Ridge, USA). ISME J 1(5):453–467
Pennuto CM, Lane OP, Evers DC, Taylor RJ, Loukmas J (2005) Mercury in the northern crayfish, Orconectes virilis (Hagen), in New England, USA. Ecotoxicology 14:149–162
Rowe-Magnus DA, Mazel D (2002) The role of integrons in antibiotic resistance gene capture. Int J Med Microbiol 292:115–125
Roy PH, Tetu SG, Larouche A, Elbourne L, Tremblay S, Ren Q, Dodson R, Harkins D, Shay R, Watkins K, Mahamoud Y, Paulsen IT (2010) Complete genome sequence of the multiresistant taxonomic outlier Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA7. PLoS ONE 5(1):e8842
Rucker RR, Amend DE (1969) Absorption and retention of organic mercurials by rainbow trout and sockeye salmon. Prog Fish Culturist 31:197–201
Saye DJ, MIller RV (1989) Aquatic environment: consideration of horizontal gene transmission in a diversified habitat. In: Levy SB, Miller RV (eds) Gene transfer in the environment. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 405–420
Stepanauskas R, Glenn TC, Jagoe CH, Tuckfield RC, Lindell AH, King CJ, McArthur JV (2006) Coselection for microbial resistance to metals and antibiotics in freshwater microcosms. Environ Microbiol 8(9):1510–1514
Summers AO (2002) Generally overlooked fundamentals of bacterial genetics and ecology. Clin Infect Dis 34(Suppl 3):S85–S92
Summers AO (2006) Generally overlooked fundamentals of bacterial genetics and ecology. Clin Infect Dis 34(Suppl 3):S85–S92
Summers AO, Wireman J, Vimy MJ, Lorscheider FL, Marshall B, Levy SB, Bennett S, Billard L (1993) Mercury released from dental “silver” fillings provokes an increase in mercury- and antibiotic-resistant bacteria in oral and intestinal floras of primates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 37(4):825–834
Wang LF, Luo H, Miyoshi M, Imoto T, Hiji Y, Sasaki T (1998) Inhibitory effect of gymnemic acid on intestinal absorption of oleic acid in rats. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 76(10–11):1017–1023
Wardwell LH, Jude BA, Moody JP, Olcerst AI, Gyure RA, Nelson RE, Fekete FA (2009) Co-selection of mercury and antibiotic resistance in sphagnum core samples dating back 2,000 years. Geomicrobiol J 26:238–247
Wireman J, Liebert CA, Smith T, Summers AO (1997) Association of mercury resistance with antibiotic resistance in the gram-negative fecal bacteria of primates. Appl Environ Microbiol 63(11):4494–4503
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge Drs. A.O. Summers (University of Georgia, Athens, GA, USA), and G.M. King (Louisiana State University, Baton Rouge, LA, USA), for helpful advice and assistance in experimental design. The project was supported at Colby College by grants from the National Center for Research Resources (5P20RR016463-12) and the National Institute of General Medical Sciences (8 P20 GM103423-12) from the National Institutes of Health, Colby College Student Special Projects Fund, Colby College Natural Science Division Grant (#01.2375, F.A. Fekete), the Maine Department of Inland Fisheries & Wildlife, by the Department of Biology and the Office of Teaching and Faculty Development at Bradley University (K.A. Johnson), and by the National Science Foundation through a Research Experiences for Undergraduates supplement to EAR-0525374 (T. Barkay).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meredith, M.M., Parry, E.M., Guay, J.A. et al. Concomitant Antibiotic and Mercury Resistance Among Gastrointestinal Microflora of Feral Brook Trout, Salvelinus fontinalis . Curr Microbiol 65, 575–582 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-012-0194-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-012-0194-4