Abstract
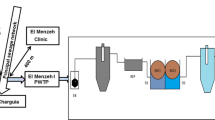
The efficiency of ultraviolet (UV) light disinfection of wastewater effluent using a large-scale pilot system was studied. The relationship between biofilm and siderophore production and UV doses received by Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain ATCC 15442 was determined. UV decreased pyoverdine production and enhanced biofilm production. Consequently external factors conditioned by both pyoverdine and biofilm may affect the UV effect on bacterial disinfection.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ankenbauer R, Sriyosachati S, Cox CD (1985) Effects of siderophores on the growth of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Human Serum and Transferrin. Infect Immun 49:132–140
Aristoteli LP, Willcox MDP (2003) Mucin degradation mechanisms by distinct Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates in vitro. Infect Immun 71:5565–5575
Brahmi M, Belhadi NH, Hamdi H, Hassen A (2010) Modeling of secondary treated wastewater disinfection by UV irradiation: effects of suspended solids content. J Environ Sci 22:1218–1224
Briner H, Croal L, Gora K, Tsokos C, Laub M (2010) Novel regulators controlling biofilm formation through the GacS/GacA two-component system in Pseudomonas aeruginosa reports. MURJ 19:46–56
Ceri H, Olson ME, Turner RJ (2010) Needed, new paradigms in antibiotic development. Expert Opin Pharmacother 11:1233–1237
Ciofu O, Tolker-Nielsen T (2010) Antibiotic tolerance and resistance in biofilms. In: Bjarnsholt T, Moser C, Jensen P, Høiby N (eds) Biofilm infections. Springer Publishing Company, New York, pp 215–229
Decho AW (1990) Microbial exopolymer secretions in ocean environments: their role(s) in food webs and marine processes. Oceanogr Mar Biol Ann Rev 28:73–153
Fallahzadeh V, Ahmadzadeh M, Sharifi R (2010) Growth and pyoverdine production kinetics of Pseudomonas aeruginosa 7NSK2 in an experimental fermentor. J Agric Technol 6:107–115
Grecz N, Rowley DB, Matsuyama A (1983) The effect of irradiation on bacteria and viruses. In: Josephson ES, Peterson MS (eds) Preservation of food by ionizing radiation. CRC Press, Boca Raton, p 167
Griffin M, Engler AJ, Barber T, Healy K, Sweeney HL, Discher D (2004) Patterning, prestress and peeling dynamics of myocytes. Biophys J 86:1209–1222
Harrison J, Ceri H, Yerly J, Stremick CA, Hu Y, Martinuzzi R, Turner RJ (2006) The use of microscopy and three-dimensional visualization to evaluate the structure of microbial biofilms cultivated in the calgary biofilm device. Biomed Life Sci 8:194–215
Hassen A, Mahrouk M, Ouzari H, Cherif M, Boudabous A, Damelincourt J (2000) UV disinfection of treated wastewater in a large scale pilot plant and inactivation of selected bacteria in a laboratory UV device. Bioresour Technol 74:141–150
Kavamura VN, Esposito E (2010) Biotechnological strategies applied to the decontamination of soils polluted with heavy metals. Biotechnol Adv 28:61–69
Kipnis E, Sawa T, Wiener-Kronish J (2006) Targeting mechanisms of Pseudomonas aeruginosa pathogenesis Thérapeutiques ciblant les mécanismes pathogéniques de Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Médecine et maladies infectieuses 36:78–91
Knobloch JKM, Bartscht K, Sabottke A, Rohde H, Feucht HH, Mack D (2001) Biofilm formation of Staphylococcus epidermidis depends on RsbU, a functional activator of the sigB operon: differential activation mechanisms due to ethanol and salt stress. J Bacteriol 183:2624–2633
Mack D, Bartscht K, Fischer C, Rohde H, de Grahl C, Dobinsky S, Horstkotte MA, Kiel K, KM Knobloch J (2001) Genetic and biochemical analysis of Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilm accumulation. Methods Enzymol 336:215–239
Meyer JM, Abdallah MA (1978) The fluorescent pigment of Pseudomonas fluorescens: biosynthesis, purification and physicochemical properties. J Gen Microbiol 107:319–328
Miller RV, Kokjohn TA (1990) General microbiology of recA: environmental and evolutionary significance. Annu Rev Microbiol 44:365–394
Moeller R, Horneck G, Facius R, Stackebrandt E (2005) Role of pigmentation in protecting Bacillus sp. endospores against environmental UV radiation. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 51:231–236
Myklestad S, Haug A, Larsen B (1972) Production of carbohydrates by the marine diatom Chaeotoceros affinis var. willei (Gran) Hustedt. 11. Preliminary investigation of the extracellular polysaccharide. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 9:137–144
Nicolella C, Van Loosdrecht MCM, Heijnen JJ (2000) Wastewater treatment with particulate biofilm reactors. J Biotechnol 80:1–33
Parker JA, Darby JL (1995) Particle-associated coliform in secondary effluents: shielding from ultraviolet light disinfection. Water Environ Res 67:1065
Spoering AL MS (2006) Gilmore quorum sensing and DNA release in bacterial biofilms. Curr Opin Microbiol 9:133–137
Süß J, Volz S, Obst Uand Schwartz T (2009) Application of a molecular biology concept for the detection of DNA damage and repair during UV disinfection. Water Res 43:3705–3716
Wimpenn JWT (2000) An overview of biofilms as functional communities. In: Allison DG, Gilbert HMLappin-Scott P, Wilson M (eds) Community structure and co operation in biofilms. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 1–24
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the European Union (Avicenna Project No. 93AVI054. Authors are grateful for Centre National Universitaire de Documentation Scientifique et Technique (CNUDST) particularly to Mr. Ahmed El Amri and Mrs. Asma Riahi. We are also grateful to Prof. Ann C. Kennedy for her assistance in revision and improvement of manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saidi, N., Kouki, S., Mehri, I. et al. Biofilm and Siderophore Effects on Secondary Waste Water Disinfection. Curr Microbiol 63, 337 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-011-9983-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-011-9983-4