Abstract
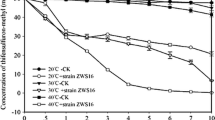
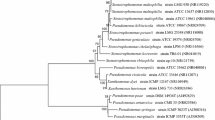
A fluoroglycofen ethyl-degrading bacterium, MBWY-1, was isolated from the soil of an herbicide factory. This isolated strain was identified as Mycobacterium phocaicum based on analysis of its 16S rRNA gene sequence and its morphological, physiological, and biochemical properties. The strain was able to utilize fluoroglycofen ethyl as its sole source of carbon for growth and could degrade 100 mg l−1 of fluoroglycofen ethyl to a non-detectable level within 72 h. The optimum temperature and pH for fluoroglycofen ethyl degradation by strain MBWY-1 were 30°C and 7.0, respectively. Five metabolites produced during the degradation of fluoroglycofen ethyl and were identified by mass spectrometry as {5-[2-chloro-4-(trifluoromethyl) phenoxy]-2-nitrophenylacyl} hydroxyacetic acid, acifluorfen, 5-[2-chloro-4-(trifluoromethyl) phenoxy]-2-nitrobenzoate, 5-[2-chloro-4-(trifluoromethyl) phenoxy]-2-hydroxyl, and 3-chloro-4-hydroxyl benzotrifluoride. Identification of the metabolites allowed to propose the degradation pathway of fluoroglycofen ethyl by strain MBWY-1. The inoculation of strain MBWY-1 into soil treated with fluoroglycofen ethyl resulted in a higher fluoroglycofen ethyl degradation rate than in uninoculated soil regardless of whether the soil was sterilized or nonsterilized.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahrens WH (ed) (1994) Herbicide handbook. Weed Science Society of America, Champaign
Aldo L, Giovanna F, Laura F, Alessandra M, Matteo M (2000) Determination of diphenyl-ether herbicides and metabolites in natural waters using high-performance liquid chromatography with diode array tandem mass spectrometric detection. Anal Chim Acta 414:79–94
Böger P, Wakabayashi K (1999) Peroxidizing herbicides. J Pesticide Sci 352-353
Bo L, Lu P, Li H, Li R, Li S, Huang X (2009) Biodegradation of fomesafen by strain Lysinibacillus sp. ZB-1 isolated from soil. Chemosphere 77:1614–1619
Karpouzas DG, Walker A (2000) Factors influencing the ability of Pseudomonas putida epI to degrade ethoprophos in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 32:1753–1762
Key BD, Howell RD, Criddle CS (1997) Fluorinated organics in the biosphere. Environ Sci Technol 31(9):2445–2454
Li R, Guo X, Chen K, Zhu JC, Li SP, Jiang J (2009) Isolation of an isocarbophos-degrading strain of arthrobacter sp. scl-2 and identification of the degradation pathway. J Microbiol Biotechnol 19:1439–1446
Li R, Zheng JW, Wang R, Song Y, Chen QM, Yang XJ, Li SP, Jiang JD (2010) Biochemical degradation pathway of dimethoate by Paracoccus sp. Lgjj-3 isolated from treatment wastewater. Int Biodeter Biodegr 1:21–57
Li XH, He J, Li SP (2007) Isolation of a chlorpyrifos-degrading bacterium, Sphingomonas sp. strain Dsp-2, and cloning of the mpd gene. Res Microbiol 158:143–149
Maloney SE, Maule A, Smith ARW (1988) Microbial transformation of the pyrethroid insecticides: permethrin, deltamethrin, fastac, fenvalerate, and fluvalinate. Appl Environ Microb 54:2874–2876
Tallur PN, Megadi VB, Ninnekar HZ (2008) Biodegradation of cypermethrin by Micrococcus sp. strain CPN 1. Biodegradation 19:77–82
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeamougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The Clustal_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882
Tomotada I, Masao N (2001) Current bioremediation practice and perspective. J Biosci Bioeng 1:1–8
Wang BZ, Guo P, Hang BJ, Li L, He J, Li SP (2009) Cloning of a novel pyrethroid-hydrolyzing carboxylesterase gene from Sphingobium sp. strain JZ-1 and characterization of the gene product. Appl Environ Microb 17:5496–5500
Wang F, Grundmann S, Schmid M, Dorfler U, Roherer S, Munch JC, Hartmann A, Jiang X, Schroll R (2007) Isolation and characterization of 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene mineralizing Bordetella sp. and its bioremediation potential in soil. Chemosphere 67:896–902
Wu LY, Tao CJ, Pu XY, Jiang H, Li XF, Wang CJ (2006) Residue analysis and degradation dynamics of fluoroglycofen-ethyl in soils. J Agro Environ Sci 25:1659–1662
Wu LY, Tao CJ, Zong FL, Pu XY, Jiang H, Li XF, Wang CJ (2007) Degradation dynamics of fluoroglycofen ethyl in water. Chin J Pestic Sci 9:96–99
Wu PC, Liu YH, Wang ZY, Zhang XY, Li H, Liang WQ, Luo N, Hu JM, Lu JQ, Luan TG, Cao LX (2006) Molecular cloning, purification, and biochemical characterization of a novel pyrethroid-hydrolyzing esterase from Klebsiella sp. strain ZD112. J Agric Food Chem 54:836–842
Yu HF (2001) Biological characteristics of fluoroglycofen ethyl. Pesticide 40:31–36
Yu H, Zhou Q (2005) Biological transformation of organofluorine compounds. Sichuan Environ 24(4):54–58
Zhang HB, Lin AJ, Liu S, Qiao M, Feng L, Hojae Shim, Jing JH (2010) Identification of pyrene degrading strains and the degrading characteristics research. Environ Sci 31:243–248
Zhang XH, Zhang GS, Zhang ZH, Xu JH, Li SP (2006) Isolation and characterization of a dichlorvos-degrading strain DDV-1 of Ochrobactrum sp. Pedosphere 16:64–71
Zhang YB, Qian YY (2002) Structure speciality and researching development survey of pesticide containing fluorine. Jiangsu Chem Ind 30:13–15
Zhang ZG, Hong Q, Xu JH, Zhang XZ, Li S (2006) Isolation of fenitrothiondegrading strain Burkholderia sp. FDS-1 and cloning of mpd gene. Biodegradation 17:275–283
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge Dr. Shichao Xu of the Nanjing Science and Technology University for excellent assistance with MS analysis. This study was supported by the Provincial Environmental Protection Scientific Research Projects of Jiangsu Provience (2009001) and National Technology Support Project (2008BAD96B05).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, L., Cai, T. & Wang, Q. Characterization of Fluoroglycofen Ethyl Degradation by Strain Mycobacterium phocaicum MBWY-1. Curr Microbiol 62, 1710–1717 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-011-9918-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-011-9918-0