Abstract
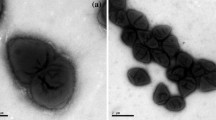
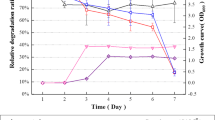
A Gram-staining-negative, oxidase-positive, catalase-positive, non-motile, non-spore-forming, and rod-shaped bacterium, designated BJQ-6T, was isolated from activated sludge of a waste-water treatment plant in Jiangsu Province, China. Phylogenetic analysis based on 16S rRNA gene sequences showed that strain BJQ-6T belonged to the genus Rhodanobacter, and shared 98.7% similarity with Rhodanobacter lindaniclasticus LMG 18385T and <97% similarities with other Rhodanobacter species. The major fatty acids were iso-C15:0 (17.6%), iso-C16:0 (19.3%), and Summed feature 9 (isoC17:1 ω9c and/or C16:0 10-methyl) (25.8%). The DNA G+C content of strain BJQ-6T was 64.8 mol%. Based on the phenotypic and phylogenetic considerations, strain BJQ-6T represents a novel species of the genus Rhodanobacter, for which the name Rhodanobacter xiangquanii sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain is BJQ-6T (=CCTCC AB 2010106T =KCTC 23100T).

Similar content being viewed by others
References
An DS, Lee HG, Lee ST, Im WT (2009) Rhodanobacter ginsenosidimutans sp nov., isolated from soil of a ginseng field in South Korea. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:691–694
Bui TPN, Kim YJ, Kim H, Yang DC (2010) Rhodanobacter soli sp. nov., isolated from soil of a ginseng field. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.019422-0
Chun J, Lee JH, Jung Y, Kim M, Kim S, Kim BK, Lim YW (2007) EzTaxon: a web-based tool for the identification of prokaryotes based on 16S ribosomal RNA gene sequences. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:2259–2261
De Clercq D, Van Trappen S, Cleenwerck I, Ceustermans A, Swings J, Coosemans J, Ryckeboer J (2006) Rhodanobacter spathiphylli sp. nov., a gammaproteobacterium isolated from the roots of Spathiphyllum plants grown in a compost-amended potting mix. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:1755–1759
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791
Im WT, Lee ST, Yokota A (2004) Rhodanobacter fulvus sp. nov., β-galactosidase-producing gammaproteobacterium. J Gen Appl Microbiol 50:143–147
Kimura M (1980) A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequence. J Mol Evol 16:111–120
Kimura M (1983) The neutral theory of molecular evolution. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Lane DJ (1991) 16S/23S rRNA sequencing. In: Stackebrandt E, Goodfellow M (eds) Nucleic acid techniques in bacterial systematics. Wiley, Chichester, pp 115–175
Lee CS, Kim KK, Aslam Z, Lee ST (2007) Rhodanobacter thiooxydans sp. nov., isolated from a biofilm on sulfur particles used in an autotrophic denitrification process. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:1775–1779
Marmur J, Doty P (1962) Determination of the base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid from its thermal denaturation temperature. J Mol Biol 5:109–118
Mergaert J, Cnockaert MC, Swings J (2002) Fulvimonas soli gen. nov., sp. nov., a c-proteobacterium isolated from soil after enrichment on acetylated starch plastic. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 52:1285–1289
Nalin R, Simonet P, Vogel TM, Normand P (1999) Rhodanobacter lindaniclasticus gen. nov., sp. nov., a lindane-degrading bacterium. Int J Syst Bacteriol 49:19–23
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory 186 manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY
Smibert RM, Krieg NR (1994) Phenotypic characterization. In: Gerhardt P, Murray RGE, Wood WA, Krieg NR (eds) Methods for general and molecular bacteriology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC, pp 607–654
Weon HY, Kim BY, Hong SB, Jeon YA, Kwon SW, Go SJ, Koo BS (2007) Rhodanobacter ginsengisoli sp. nov. and Rhodanobacter terrae sp. nov., isolated from soil cultivated with Korean ginseng. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:2810–2813
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (30970099), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province, China (BK2008331), and National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (2006AA10Z402).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The GenBank/EMBL/DDBJ accession number for the 16S rRNA gene sequence of strain BJQ-6T is EU876661.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Zheng, JW., Hang, BJ. et al. Rhodanobacter xiangquanii sp. nov., a Novel Anilofos-Degrading Bacterium Isolated from a Wastewater Treating System. Curr Microbiol 62, 645–649 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-010-9757-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-010-9757-4