Abstract
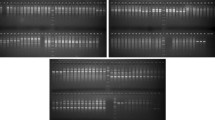
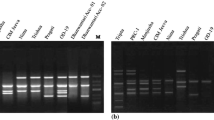
To accelerate the breeding of Agaricus bisporus, quick and reliable methods to identify the infrequent homokaryons are necessary. A new marker, inter simple sequence repeat (ISSR) fingerprinting, is described for differentiation of homo- and hetero-karyotic protoclones. Nine slow growing protoclones, two strandy and seven appressed, were analyzed for the first time with ISSR amplifications. The patterns were highly polymorphic and very reproducible. Among 40 primers tested, 7 ISSR primers were selected for the analysis of genomic DNA and generated a total of 68 ISSR fragments. ISSR fingerprinting detected 44.12% polymorphic loci. All appressed homokaryons carried a subset of ISSR markers found in the heterokaryons, and clustered separately in dendrogram. These were not able to produce a fruiting body. A test of cross-fertility and the following fruiting trial proved that 7 of the 9 protoclones with different ISSR fingerprints were homokaryons. These results demonstrated that ISSR markers provide an efficient alternate for identification of homokaryons and suggest these markers be considered as new tools for the survey of Agaricus species.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amin M, Dongmei H, Yingjie P (1995) Study on homokaryotic protoplast breeding technique in Agaricus bisporus. I. Isolation and identification of homokaryotic protoplast in Agaricus bisporus. Acta Edulis Fungi 2(3):1–5
Begin M, Spear M (1991) A novel method for inducing the expression of sectors in Agaricus bisporus. In: Maher MJ (ed) Science and cultivation of edible fungi. Balkema, Rotterdam, Netherlands, pp 105–109
Blair MW, Panaud O, Mccouch SR (1999) Inter-simple sequence repeat (ISSR) amplification for analysis of micro-satellite motif frequency and fingerprinting in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 98:780–792
Bornet B, Antoine E, Bardouil M, Baut CM (2004) ISSR as new markers for genetic characterization and evaluation of relationships among phytoplankton. J Appl Phycol 16:285–290
Callac P, Hocquart S, Imbernon M, Desmerger C, Oliver JM (1998) Bsn-t alleles from french field strains of Agaricus bisporus. Applied Environ Microbiol 64:2105–2110
Camacho FJ, Liston A (2001) Population structure and genetic diversity of Botrychium pumicola (Ophioglossaceae) based on inter-simple sequence repeats (ISSR). Am J Bot 88:1065–1070
Chen R, Chen L, Song S (2003) Identification of two thermo tolerance-related genes in Agaricus bisporus. Food Technol Biotechnol 41:339–344
Depeiges A, Goubely C, Lenoir A, Cocherel S, Picard G, Raynal M, Grellet F, Delseny M (1995) Identification of the most represented motifs in Arabidopsis thaliana microsatellite loci. Theor Appl Genet 91:160–168
Esselman EJ, Jianqiang L, Crawford DJ, Windus JL, Wolfe AD (1999) Clonal diversity in the rare Calamagrostis porteri ssp. Insperata (Poaceae): comparative results for allozymes and random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) and inter-simple sequence repeat (ISSR) markers. Mol Ecol 8:443–451
Fang DQ, Roose ML (1997) Identification of closely related citrus cultivars with inter-simple sequence repeats markers. Theor Appl Genet 95:408–417
Guan XJ, Xu L, Shao YC, Wang ZR, Chen FS, Luo XC (2008) Differentiation of commercial strains of Agaricus species in China with inter-simple sequence repeat marker. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 24:1617–1622
Kazuhisa T, Teruyuki M (2004) Strain typing of shiitake (Lentinus edodes) cultivars by AFLP analysis, focusing on a heat-dried fruiting body. Mycoscience 45:79–82
Khush RS, Becker E, Wach M (1992) DNA amplification polymorphisms of the cultivated mushroom Agaricus bisporus. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:2971–2977
Li RC, Fang XC (2002) Analysis of POD and EST isozyme of three Agaricus species. Edible Fungi (China) 21:34–36 in Chinese
Ma FY, Luo XC (2002) PCR-based restriction analysis of internal transcribed spacers of nuclear ribosomal DNA in the genus Pleurotus. Mycosystema 1:356–362
Mattioni C, Casasoli M, Gonzalez M, Ipinza R, Villani F (2002) Comparison of ISSR and RAPD markers to characterize three Chilean Nothofagus species. Theor Appl Genet 104:1064–1070
Qin LH, Song CY, Tan Q, Chen MJ, Pan YJ (2006) Use of ITS and ISSR markers to identify cultivated strains for Lentinus edodes. Mycosystema 25:94–100 (in Chinese)
Raper CA, Raper JR (1972) Genetic analysis of the life-cycle of Agaricus bisporus. Mycologia 64:1088–1117
Robert BB, Daniel RJ, Chikthimmah N (2003) Bioactive components in button mushroom Agaricus bisporus of nutritional, medicinal, and biological importance. Int J Med Mush 5:321–327
Rohlf FJ (2000) NTSYS-pc: numerical taxonomy and multivariate analysis system, Version 2.02. Exeter Publications, Setauket, NY
Roodt R, Spies JJ, Burger TH (2002) Preliminary DNA fingerprinting of the Turfgrass Cynodon dactylon (Poaceae: Cloridoideae). Bothalia 32:117–122
Sambrook J, Russel DW (2001) Rapid isolation of yeast DNA. In: Sambrook J, Russel DW (eds) Molecular cloning, a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York, pp 631–632
Singh RI, Aarti K, Singh SS (2007) Formation of interspecies fusants of Agaricus bisporus and Agaricus bitorquis mushroom by protoplast fusion. Indian J Microbiol 47:369–372
Sonnenberg AS, Wessels JG, Griensven LJ (1988) An efficient protoplasting/regeneration system for Agaricus bisporus and Agaricus bitorquis. Curr Microbiol 17:285–291
Spear MC, Royse DJ, May B (1983) A typical meiosis and joint segregation of biochemical loci in Agaricus brunnescens. J Hered 74:417–420
Summerbell RC, Castle AJ, Horgen PA, Anderson JB (1989) Inheritance of restriction fragment length polymorphisms in Agaricus brunnescens. Genetics 23:293–300
Tang LH, Xiao Y, Bian YB (2005) The orthogonal optimization of ISSR-PCR amplification system in Auricularia auricula. J Fungal Res 3:15–18 in Chinese
Williams JGK, Kubelik AR, Livak KJ, Rafalski JA, Tingey SV (1990) DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucleic Acids Res 18:6531–6535
Yadav MC, Verma RN, Dhar BL (1999) Studies on the development of improved strains and hybrids of white button mushroom Agaricus bisporus (Lange) Imbach. The 3rd international conference on mushroom biology and mushroom product (ICMBMP), Sydney, Australia, pp 1–9
Yangxinmei (1996) Cultivation of edible fungi (in Chinese), 1st edn. China’s Agricultural Public Press, Beijing, China, pp 239–241
Zhao J, Chang ST (1993) Monokaryotization by protoplasting heterothallic species of edible mushrooms. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 9:538–543
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Mushroom Spawn Center, Huazhong Agricultural University, Hubei, China, for providing the mushroom strain and excellent technical assistance during spawn run study and fruiting trials, without which this study could not have been completed.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nazrul, M.I., Yin-Bing, B. ISSR as New Markers for Identification of Homokaryotic Protoclones of Agaricus bisporus . Curr Microbiol 60, 92–98 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-009-9506-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-009-9506-8