Abstract
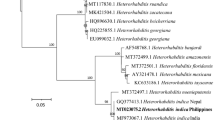
The occurrence of Heterorhabditis brevicaudis (Rhabditida: Heterorhabditidae) and its symbiotic bacteria, Photorhabdus luminescens subsp. akhurstii in Taiwan were recorded for the first time. H. brevicaudis was described by Liu in 1994, but it was unavailable and no molecular data has ever been published for it ever since. The native entomopathogenic nematode (EPN), H. brevicaudis TG01 was recovered from sandy coastal soils in moist bamboo forest, as observed in this article. The bacterial symbiont was isolated from H. brevicaudis for the first time. On the basis of biochemical tests and 16S rDNA it was identified as P. luminescens subsp. akhurstii. This is also the first report of novel nucleotide sequences of the internal transcribed spacer (ITS) from H. brevicaudis. The phylogenetic relationships of ITS sequences were established using Neighbor-Joining, Maximum Parsimony, and Maximum Likelihood methods. The inferred trees strongly support that H. brevicaudis TG01 is specifically related to H. indica and H. hawaiiensis. But the tail length of the infective juveniles (IJ) of H. brevicaudis TG01 in our study, which was less than 80 μm, shorter than that of other species indeed, fall within the original description for H. brevicaudis. Moreover, comparing with morphometrics of IJ and male of H. brevicaudis and H. indica, we recognize that the H. brevicaudis TG01 does not represent variation among populations of H. indica and H. hawaiiensis. This article will answer questions regarding the status of H. brevicaudis and would also provide this species for further investigation.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams BJ, Nguyen KB (2002) Taxonomy and systematics. In: Gaugler R (ed) Entomopathogenic nematology. CABI Press, New York, pp 1–33
Adams BJ, Burnell AM, Powers TO (1998) A phylogenetic analysis of Heterorhabditis (Nemata: Rhabditidae) based on internal transcribed spacer 1 DNA sequence data. J Nematol 30:22–39
Adams BJ, Fodor A, Koppenhofer HS, Stackebrandt E, Stock SP, Klein MG (2006) Biodiversity and systematics of nematode-bacterium entomopathogens. Biol Control 37:32–49
Bedding RA (1990) Logistics and strategies for introducing entomopathogenic nematode technology in developing countries. In: Gaugler R, Kaya HK (eds) Entomopathogenic nematodes for biological control. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 233–248
Bedding RA, Akhurst RJ (1975) A simple technique for the detection of insect parasitic Rhabditid nematodes in soil. Nematologica 21:109–110
Boemare NE (2002) Biology, taxonomy and systematics of Photorhabdus and Xenorhabdus. In: Gaugler R (ed) Entomopathogenic nematology. CABI Press, New York, pp 35–56
Boemare NE, Akhurst RJ (1988) Biochemical and physiological characterization of colony form variants in Xenorhabdus spp. (Enterobacteriaceae). J Gen Microbiol 134:751–761
Boemare NE, Akhurst RJ, Mourant RG (1993) DNA relatedness between Xenorhabdus spp. (Enterobacteriaceae), symbiotic bacteria of entomopathogenic nematodes, and a proposal to transfer Xenorhabdus luminescens to a new genus, Photorhabdus gen. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 43:249–255
Brunel B, Givaudan A, Lanois A, Akhurst RJ, Boemare N (1997) Fast and accurate identification of Xenorhabdus and Photorhabdus species by restriction analysis of PCR-amplified 16S rRNA genes. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:574–580
Ehlers RU (1996) Current and future use of nematodes in biocontrol: practice and commercial aspects in regard to regulatory policies. Biocontrol Sci Technol 6:303–316
Ehlers RU, Niemann I (1998) Molecular identification of Photorhabdus luminescens strains by amplification of specific fragments of the 16S ribosomal DNA. Syst Appl Microbiol 21:509–519
Forst S, Nealson K (1996) Molecular biology of the symbiotic-pathogenic bacteria Xenorhabdus spp. and Photorhabdus spp. Microbiol Rev 60:21–43
Gardner SL, Stock SP, Kaya HK (1994) A new species of Heterorhabditis from Hawaiian Islands. J Parasitol 80:100–106
Hsieh FC, Tzeng CY, Kao SS (2005) A new isolate of the entomopathogenic nematode, H. brevicaudis TG01 (Rhabditida: Heterorhabditidae). Taiwan Plant Prot Bull 4:263–271 (in Chinese with English summary)
Hsieh FC, Tzeng CY, Kao SS (2007) Bioactivities of Photorhabdus luminescens subsp. akhurstii, a symbiont of entomopathogenic nematode, Heterorhabditis brevicaudis. The 40th annual meeting of the Society for Invertebrate Pathology and the 1st international forum on entomopathogenic nematodes and symbiotic bacteria, August 12–16, Université Laval in Quebec City, Canada
Iraki N, Salah N, Sansour MA, Segal D, Glazer I, Johnigk SA, Hussein MA, Ehlers RU (2000) Isolation and characterization of two entomopathogenic nematode strains, Heterorhabditis indica (Nematoda, Rhabditida), from the West Bank, Palestinian Territories. J Appl Ent 124:375–380
Kaya HK, Stock SP (1997) Techniques in insect nematology. In: Lacey LA (ed) Manual of techniques in insect pathology. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 281–324
Liao CY, Tang LC, Pai CF, Hsiao WF, Briscoe BR, Hou RF (2001) A new isolate of the entomopathogenic nematode, Steinernema abbasi (Nematoda: Steinernematidae), from Taiwan. J Invertebr Pathol 77:78–80
Liu J (1994) A new species of the genus Heterorhabditis from China (Rhabditida: Heterorhabditidae). Acta Zootaxonomica Sin 19:268–272
Liu J, Berry R, Poinar G, Moldenke A (1997) Phylogeny of Photorhabdus and Xenorhabdus species and strains as determined by comparison of partial 16S rRNA gene sequences. Int J Syst Bacteriol 47:948–951
Nguyen KB, Smart GC Jr (1996) Identification of entomopathogenic nematodes in the Steinernematidae and Heterorhabditidae (Nemata: Rhabditida). J Nematol 28:286–300
Poinar GO (1976) Description and biology of a new insect parasitic Rhabditoid, Heterorhabditis bacteriophora n. gen. n. sp. (Rhabditida: Heterorhabditidae n. fam.). Nematologica 21:463–470
Poinar GO (1990) Taxonomy and biology of Steinernematidae and Heterorhabditidae. In: Gaugler R, Kaya HK (eds) Entomopathogenic nematodes in biological control. CRC Press, Florida, pp 23–61
Poinar GO, Karunakar GK, David H (1992) Heterorhabditis indicus n. sp. (Rhabditida: Nematoda) from India: separation of Heterorhabditis spp. by infective juveniles. Fundam Appl Nematol 15:467–472
Qiu XH, Han RC (2007) Entomopathogenic nematodes and advances in taxonomic techniques. Acta Entomologica Sin 50:286–296 (in Chinese with English summary)
Rainey FA, Ehlers RU, Stackebrandt E (1995) Inability of the polyphasic approach to systematics to determine the relatedness of the genera Xenorhabdus and Photorhabdus. Int J Syst Bacteriol 45:379–381
Thomas GM, Poinar GO Jr (1979) Xenorhabdus gen. nov., a genus of entomopathogenic, nematophilic bacteria of the family Enterobacteriaceae. Int J Syst Bacteriol 29:352–360
Uribe-Lorio L, Mora M, Stock SP (2005) First record of entomopathogenic nematodes (Steinernematidae and Heterorhabditidae) in Costa Rica. J Invert Pathol 88:226–231
Wu YC (1996) Studies on infection of Spodoptera litura with the entomopathogenic nematode, Steinernema carpocapsae. MS thesis, National Chung Hsing University, Taichung, Taiwan (in Chinese with English summary)
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Council of Agriculture Grant 94AS-5.2.1-PI-P1, 95AS-6.2.1-ST-a4, and National Science Council, Taiwan, Grant NSC-97-2317-B-225-001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hsieh, FC., Tzeng, CY., Tseng, JT. et al. Isolation and Characterization of the Native Entomopathogenic Nematode, Heterorhabditis brevicaudis, and its Symbiotic Bacteria from Taiwan. Curr Microbiol 58, 564–570 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-009-9371-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-009-9371-5