Abstract
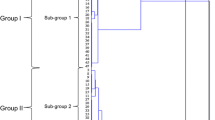
Due to unsatisfying attempts to fingerprint Auricularia polytricha, two different molecular maker systems—Inter-Simple Sequence Repeats (ISSR) and Sequence-related amplified polymorphism (SRAP)—were established and tested to quantify molecular diversity among 19 strains of this fungus. A total of 202 (99.0%) and 459 (95.9%) polymorphic bands were detected by 13 ISSR primers and 14 SRAP primer combinations, respectively. By parsimony method, a phylogenetic tree was constructed based on each analysis; the two trees show that 19 A. polytricha strains were distributed into five or four groups. These results demonstrated that both methods were suitable for discriminating among strains of A. polytricha, and the novel SRAP markers are more efficient and preferable. The result also indicated the high level of genetic diversity of A. polytricha and their relationship between each other. These findings would benefit future research in A. polytricha, especially in breeding and medicine development. It also gives a useful method for fingerprinting of other fungi.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hokama Y, Hokama JL (1981) In vitro inhibition of platelet aggregation with low dalton compounds from aqueous dialysates of edible fungi. Res Commun Chem Patho Pharmacol 31:177–180
Hokama Y, Cripps C, Hokama JL, et al. (1983) A potent naturally occurring low-molecular weight blastogenic inhibitory factor from edible black tree fungus. Res Commun Chem Patho Pharmacol 41:157–160
Wu CM, Chen QH (1991) Anticoagulation and antihyperlipidemia action of the polysaccharide from Auricularia polytricha. J China Pharm Univ 22:164–166
Sheu F, Chien PJ, Chien AL (2004) Isolation and characterization of an immunomodulatory protein (APP) from the Jew’s Ear mushroom Auricularia polytricha. Food Chem 87:593–600
Koyama K, Akiba M, Imaizumi T (2002) Antinociceptive constituents of Auricularia polytricha. Planta Med 68:284–285
Mau JL, Chao GR, Wu KT (2001) Antioxidant properties of methanolic extracts from several ear mushrooms. J Agric Food Chem 49:5461–5467
Zhang D, Zheng YL, Wang B (2004) Fruiting experiment of Basidiomycetous Auricularia polytricha of the main cultivated strains in Sichuan province. J Sichuan Agric Univ 22:353–355
Zhang D, Gao JW, Zheng YL (2006) Analysis on esterase isozyme of Auricularia polytricha. Biotechnol Bull (suppl) z1:483–489
Zhang D, Zheng YL, Wang B (2007) Studies on germplasm resources of Auricularia polytricha by random amplified polymorphic DNA. Biotechnol Bull 18:117–123
Zietkiewicz E, Rafalski A, Labuda D (1994) Genome fingerprinting by simple sequence repeat (SSR)-anchored polymerase chain reaction amplification. Genomics 20:176–183
Luque C, Legal L, Staudter H (2002) ISSR (Inter Simple Sequence Repeats) as genetic markers in Noctuids (Lepidoptera). Hereditas 136:251–253
Gryta H, Carriconde F, Charcosset JY (2006) Population dynamics of the ectomycorrhizal fungal species Tricholoma populinum and Tricholoma scalpturatum associated with black poplar under differing environmental conditions. Environ Microbiol 8:773–786
Li G, Qurios CF (2001) Sequence-related amplified polymorphism (SRAP), a new marker system based on a simple PCR reaction: its application to mapping and gene tagging in Brassica. Theo Appl Genet 103:455–461
Ferriol M, Picó B, Nuez F (2003) Genetic diversity of a germplasm collection of Cucurbita pepo using SRAP and AFLP marker. Theor Appl Genet 107:271–282
Dellaporta SL, Wood J, Hicks JB (1983) A plant DNA minipreparation version II. Plant Mol Biol Rep 4:19–21
Bassam BJ, Caetano-Anolles G, Gresshoff PM (1991) Fast and sensitive silver staining of DNA in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem 196:80–88
Nei M, Li WH (1979) Mathematical model for studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endonucleases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 76:5269–5273
Swofford DL (1998) PAUP: phylogenetic analysis using Parsimony, version 4. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland
Herrero R, Asins MJ, Carbonell EA, et al. (1996) Genetic diversity in the orange subfamily Aurantioideae. I. Intraspecies and intragenus genetic variability. Theor Appl Genet 92:599–609
Wen YL, Cao H, Pan YJ (2005) Application of ERIC Method to the affinity among Auricularia strains. Mycosystema 24:53–60
Sun SJ, Gao W, Lin SQ (2006) Analysis of genetic diversity in Ganoderma population with a novel molecular marker SRAP. Appl Microbiol Biot 72:537–543
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Dinghong Jia for providing A. polytricha strains and invaluable suggestions for this work, and to Wei Wei for expert technical assistance and advice.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, M., Ma, B., Luo, X. et al. Molecular Diversity of Auricularia polytricha Revealed by Inter-Simple Sequence Repeat and Sequence-Related Amplified Polymorphism Markers. Curr Microbiol 56, 240–245 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-007-9067-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-007-9067-7