Abstract
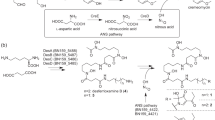
Nikkomycins are highly potent inhibitors of chitin synthase. The nikkomycin biosynthetic gene cluster has been cloned from Streptomyces asochromogenes. Two cytochrome P450 monooxygenase genes (sanQ, sanH) and one ferredoxin gene (sanI) were found in the cluster. It was reported that SanQ is involved in the hydroxylation of l-His, a key step in 4-formyl-4-imidazolin-2-one base biosynthesis. Here, we have studied the function of sanH and sanI. Disruption of sanH abolished the production of nikkomycin X and Z, but it accumulated one dominant component nikkomycin Lx, which is the nikkomycin X analog lacking the hydroxy group at the pyridyl residue. The sanI disruption mutant accumulated predominantly nikkomycin Lx in addition to nikkomycin X and Z. The nikkomycin production profile of the sanH and sanI double disruption mutant was the same as that of the sanH disruption mutant. These results confirmed that SanH is essential for the hydroxylation of pyridyl residue in nikkomycin biosynthesis of S. ansochromogenes and first demonstrated that SanI is an effective electron donor for SanH, but not for SanQ in vivo.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bierman M, Logan R, O’Brien K, et al. (1992) Plasmid cloning vectors for the conjugal transfer of DNA from Escherichia coli to Streptomyces spp. Gene 116:43–49
Bormann C, Lauer B, Kalmanczhelyi A, et al. (1999) Novel nikkomycins Lx and Lz produced by genetically engineered Streptomyces tendae Tu901. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 52:582–585
Bruntner C, Lauer B, Schwarz W, et al. (1999) Molecular characterization of co-transcribed genes from Streptomyces tendae Tu901 involved in the biosynthesis of the peptidyl moiety of the peptidyl nucleoside antibiotic nikkomycin. Mol Gen Genet 262:102–114
Chen H, Hubbard BK, O’Connor SE, et al. (2002) Formation of beta-hydroxy histidine in the biosynthesis of nikkomycin antibiotics. Chem Biol 9:103–112
Chen W, Zeng H, Tan H (2000) Cloning, sequencing, and function of sanF: A gene involved in nikkomycin biosynthesis of Streptomyces ansochromogenes. Curr Microbiol 41:312–316
Fiedler HP, Kurth R, Langhärig J, et al. (1982) Nikkomycins: microbial inhibitors of chitin synthase. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 32:271–280
Guengerich FP (1991) Reactions and significance of cytochrome P-450 enzymes. J Biol Chem 266:10,019–10,022
Healy FG, Krasnoff SB, Wach M, et al. (2002) Involvement of a cytochrome P450 monooxygenase in thaxtomin A biosynthesis by Streptomyces acidiscabies. J Bacteriol 184:2019–2029
Kieser T, Bibb MJ, Buttner MJ, et al. (2000) Practical Streptomyces genetics. The John Innes Foundation, Norwich, UK
Lauer B, Russwurm R, Bormann C (2000) Molecular characterization of two genes from Streptomyces tendae Tü901 required for the formation of the 4-formyl-4-imidazolin-2-one-containing nucleoside moiety of the peptidyl nucleoside antibiotic nikkomycin. Eur J Biochem 267:1698–1706
Lei L, Waterman MR, Fulco AJ, et al. (2004) Availability of specific reductases controls the temporal activity of the cytochrome P450 complement of Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:494–499
Liu G, Tian Y, Yang H, Tan H (2005) A pathway-specific transcriptional regulatory gene for nikkomycin biosynthesis in Streptomyces ansochromogenes that also influences colony development. Mol Microbiol 55:1855–1866
MacNeil DJ, Gewain KM, Ruby CL, et al. (1992) Analysis of Streptomyces avermitilis genes required for avermectin biosynthesis utilizing a novel integration vector. Gene 111:61–68
Niu G, Liu G, Tian Y, Tan H (2006) SanJ, an ATP-dependent picolinate-CoA ligase, catalyzes the conversion of picolinate to picolinate-CoA during nikkomycin biosynthesis in Streptomyces ansochromogenes. Metab Eng 8:183–195
O’Keefe DP, Harder PA (1991) Occurrence and biological function of cytochrome P450 monooxygenases in the actinomycetes. Mol Microbiol 5:2099–2105
Xu J, Liu G, Tan H (2003) sanC: a novel gene involved in nikkomycin biosynthesis in Streptomyces ansochromogenes. Lett Appl Microbiol 36:234–238
Xue Y, Wilson D, Zhao L, et al. (1998) Hydroxylation of macrolactones YC-17 and narbomycin is mediated by the pikC-encoded cytochrome P450 in Streptomyces venezuelae. Chem Biol 5:661–667
Zeng H, Tan H, Li J (2002) Cloning and function of sanQ: a gene involved in nikkomycin biosynthesis of Streptomyces ansochromogenes. Curr Microbiol 45:175–179
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (grant Nos. 2003CB114205, 2006AA02Z206, and 2006AA10A209) and the Chinese Academy of Sciences (grant No. KSCX2-YW-N-027).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, Z., Niu, G., Li, R. et al. Identification and Characterization of sanH and sanI Involved in the Hydroxylation of Pyridyl Residue During Nikkomycin Biosynthesis in Streptomyces ansochromogenes . Curr Microbiol 55, 537–542 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-007-9028-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-007-9028-1