Abstract
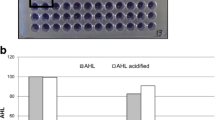
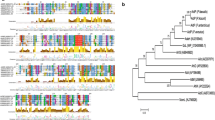
Enzymatic disruption of quorum-sensing (QS) pathways in pathogenic organisms is a promising anti-infection therapeutic strategy. AHL-lactonase, a potent tool for biocontrol, can hydrolyze QS signal molecule N-acyl-homoserine lactones (AHLs) into inactive products, thereby blocking the QS systems. A marine bacterial isolate Y2, identified as a Bacillus cereus subsp., was found capable of inactivating AHLs. The aiiA gene encoding the AHL-degrading enzyme from bacterial strain Y2 was cloned and expressed in Escherichia coli. The 28-kDa recombinant Y2-AiiA protein was purified and showed strong AHL-degrading activity. Sequence comparisons of Y2-aiiA with known AHL-lactonases revealed high identities in the deduced amino-acid sequences. Functional determination of a potential catalytic residue Tyr-194 of AHL-lactonases was performed by site-directed mutagenesis. As judged by AHL-degrading bioassay, substitution of Tyr-194 with Ala resulted in a dramatic decrease of activity compared with wild-type (WT) recombinant Y2-AiiA, although the expression level of the mutated Y2-AiiA protein was equivalent to that of WT Y2-AiiA. These results suggested that the conserved residue Tyr-194 is critical for catalytic function of the novel AHL-lactonase.




Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Cao JG, Meighen EA (1989) Purification and structural identification of an autoinducer for the luminescence system of Vibrio harveyi. J Biol Chem 264:21670–21676
de la Sierra-Gallay IL, Pellegrini O, Condon C (2005) Structural basis for substrate binding, cleavage and allostery in the tRNA maturase RNase Z. Nature 433:657–661
Dessaux Y, Petit A, Ellis JG, Legrain C, Demarez M, Wiame JM, et al. (1989) Ti plasmid-controlled chromosome transfer in Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J Bacteriol 171:6363–6366
Dong YH, Xu JL, Li XC, Zhang LH (2000) AiiA, an enzyme that inactivates the acyl homoserine lactone quorum-sensing signal and attenuates the virulence of Erwinia carotovora. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:3526–3531
Dong YH, Zhang XF, Xu JL, Zhang LH (2004) Insecticidal Bacillus thuringiensis silences Erwinia carotovora virulence by a new form of microbial antagonism, signal interference. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:954–960
Dong YH, Zhang LH (2005) Quorum sensing and quorum-quenching enzymes. J Microbiol 43:101–109
Eberhard A, Burlingame AL, Eberhard C, Kenyon GL, Nealson KH, Oppenheimer NJ (1981) Structural identification of autoinducer of Photobacterium fischeri luciferase. Biochemistry 20:2444–2449
Fuqua WC, Winans SC, Greenberg EP (1994) Quorum sensing in bacteria: The LuxR-LuxI family of cell density-responsive transcriptional regulators. J Bacteriol 176:269–275
Fuqua WC, Winans SC (1996) Conserved cis-acting promoter elements are required for density-dependent transcription of Agrobacterium tumefaciens conjugal transfer genes. J. Bacteriol 178:435–440
Jones S, Yu B, Bainton NJ, Birdsall M, Bycroft BW, Chhabra SR, et al. (1993) The lux autoinducer regulates the production of exoenzyme virulence determinants in Erwinia carotovora and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. EMBO J 12:2477–2482
Kato C, Masui N, Horikoshi K (1997) Properties of obligately barophilic bacteria isolated from a sample of deep-sea sediment from Izu-Bonin trench. J Mar Biotechnol 4:96–99
Lee SJ, Park SY, Lee JJ, Yum DY, Koo BT, Lee JK (2002) Genes encoding the N-acyl homoserine lactone-degrading enzyme are widespread in many subspecies of Bacillus thuringiensis. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:3919–3924
Liu D, Lepore BW, Petsko GA, Stone EM, Fast W, Ringe D (2005) Three-dimensional structure of the quorum-quenching N-acyl homoserine lactone hydrolase from Bacillus thuringiensis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:11882–11887
Lone G, Hans-Peter G, Andrea S, Thomas K (2002) Possible quorum sensing in marine snow bacteria: Production of acylated homoserinelactones by Roseobacter strains isolated from marine snow. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:4111–4116
Maidak BL, Cole JR, Parker CT, Garrity GM, Larsen N, Li B, et al. (1999) A new version of the RDP (Ribosomal Database Project). Nucleic Acids Res 27:171–173
Passador L, Cook JM, Gambello MJ, Rust L, Iglewski BH (1993) Expression of Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence genes requires cell-to-cell communication. Science 260:1127–1130
Reimmann C, Ginet N, Michel L, Keel C, Michaux P, Krishnapillai V, et al. (2002) Genetically programmed autoinducer destruction decreases virulence gene expression and swarming motility in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. Microbiology 148:923–932
Uroz S, D’Angelo-Picard C, Carlier A, Elasri M, Sicot C, Petit A, et al. (2003) Novel bacteria degrading N-acylhomoserine lactones and their use as quenchers of quorum-sensing-regulated functions of plant-pathogenic bacteria. Microbiology 149:1981–1989
Zhu J, Chai Y, Zhong Z, Li S, Winans SC (2003) Agrobacterium bioassay strain for ultrasensitive detection of N-acylhomoserine lactone-type quorum-sensing molecules: Detection of autoinducers in Mesorhizobium huakuii. Appl Environ Microbiol 69: 6949–6953
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, X., Yuan, Y., Xue, XL. et al. Identification of the Critical Role of Tyr-194 in the Catalytic Activity of a Novel N-Acyl-Homoserine Lactonase from Marine Bacillus cereus Strain Y2. Curr Microbiol 53, 346–350 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-006-0224-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-006-0224-1