Abstract
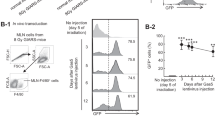
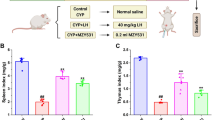
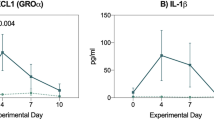
It has been reported that treatment with methotrexate (MTX) induces intestinal bacterial translocation; however, the definitive evidence of intestinal bacterial translocation induced by MTX has been lacking. The aim of this study was to confirm the intestinal bacterial translocation caused by MTX and to evaluate the preventive effect of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) on intestinal bacterial translocation caused by MTX. Sprague-Dawley rats were treated with MTX (3.5 mg/kg) for 3 days to induce intestinal bacterial translocation; with gavaged Escherichia coli TG1 labeled with green fluorescent protein (GFP) for 2 days to track intestinal bacterial translocation; and with G-CSF (10 μg/kg) for 4 days to prevent intestinal bacterial translocation. Representative tissue specimens from the mesenteric lymph nodes, spleen, liver, and kidney were aseptically harvested for bacteria culture in ampicillin-supplemented medium. The bacteria labeled with GFP were detected in tissue specimens harvested from the rats treated with MTX but not detected in the rats that were not treated with MTX. G-CSF significantly ameliorated the situation of intestinal bacterial translocation.


Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Berg RD, Garlington AW (1979) Translocation of certain indigenous bacteria from the gastrointestinal tract to the mesenteric lymph nodes and other organs in a gnotobiotic mouse model. Infect Immun 23:403–411
Cruz N, Alvarez X, Berg R, Deitch EA (1994) Bacterial translocation across enterocytes: Results of a study of bacterial-enterocyte interactions utilizing Caco-2 cells. Shock 1:67–72
Berg R (1999) Bacterial translocation from the gastrointestinal tract. Adv Exp Med Biol 473:11–30
Carneiro-Filho BA, Lima IP, Araujo DH, Cavalcante MC, Carvalho GH, Brito GA, et al. (2004) Intestinal barrier function and secretion in methotrexate-induced rat intestinal mucositis. Digest Dis Sci 49:65–72
Mao Y, Kasravi B, Nobaek S, Wang LQ, Adawi D, Roos G, et al. Pectin-supplemented enteral diet reduces the severity of methotrexate induced enterocolitis in rats. Scand J Gastroenterol 31:558–567
Ortega M, Gomez-de-Segura IA, Vazquez I, Lopez JM, de Guevara CL, De-Miguel E (2001) Effects of growth hormone plus a hyperproteic diet on methotrexate-induced injury in rat intestines. Acta Oncol 40:615–621
Cubitt AB, Heim R, Adams SR, Boyd AE, Gross LA, Tsien RY (1995) Understanding, improving and using green fluorescent proteins. Trends Biochem Sci 20:448–455
Chalfie M, Tu Y, Euskirchen G, Ward WW, Prashe DC (1994) Green fluorescent protein as a marker for gene expression. Science 263:802–805
Wiehart RH, Gasson JC, Golde DW (1989) Colony stimulating factors and host defense. Ann Intern Med 110:297–303
Crawford J, Ozer H, Stoller R, Johnson D, Lyman G, Tabbara I, et al. (1991) Reduction by granulocyte colony-stimulating factor of fever and neutropenia induced by chemotherapy in patients with small-cell lung cancer. New Engl J Med 325:164–170
Nelson S (1994) Role of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in the immune response to acute bacterial infection in the nonneutropenic host: An overview. Clin. Infect Dis 2:197–204
Colak T, Ipek T, Paksoy M, Polat E, Uygun N, Kayabasi B (2001) The effects of cefephim, g-csf, and sucralfate on bacterial translocation in experimentally induced acute pancreatitis. Surg Today 31:502–506
Akin L, Batkin A, Celenk T, Nogay A, Gunduz M (1997) Effects of granulocyte colony stimulating factor and vitamin E on bacterial translocation in complete mechanical intestinal obstructions in an experimental study. Br J Surg 84(Suppl. 2):67
Sambrook J, Fritsch E, Maniatis T. (1989) Molecular cloning: A laboratory manual, 2nd ed. Cold Spring Harbor, NY, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory
Maejima K, Deitch E, Berg R (1984) Promotion by burn stress of the translocation of bacteria from the gastrointestinal tracts of mice. Arch Surg 119:166–172
Maejima K, Deitch EA, Berg RD (1984) Bacterial translocation from the gastrointestinal tracts of rats receiving thermal injury. Infect Immun 43:6–10
Baker JW, Deitch EA, Li M, Berg RD, Specian RD (1988) Hemorrhagic shock induces bacterial translocation from the gut. J Trauma 28:896–906
Deitch EA, Berg R, Specian R (1987) Endotoxin promotes the translocation of bacteria from the gut. Arch Surg 122:185–190
Deitch EA, Ma W-J, Ma L, Berg R, Specian RD (1989) Endotoxin-induced bacterial translocation: A study of mechanisms. Surgery 106:292–300
Deitch EA (1989) Simple intestinal obstruction causes bacterial translocation in man. Arch Surg 124:699–701
Berg RD, Wommack E, Deitch EA (1988) Immunosuppression and intestinal bacterial overgrowth synergistically promote bacterial translocation. Arch Surg 123:1359–1364
Ambrose NS, Johnson M, Burdon DW, Keighley MR (1984) Incidence of pathogenic bacteria from mesenteric lymph nodes and ileal serosa during Crohn’s disease surgery. Br J Surg 71:623–625
Alverdy JC, Aoys E, Moss GS (1988) Total parenteral nutrition promotes bacterial translocation from the gut. Surgery 104:185–190
Rao R, Prinz RA, Kazantsev GB, Hecht D, Gattuso P, Jacobs HK, et al. (1996) Effects of granulocyte colony stimulating factor in severe pancreatitis. Surgery 119:657–663
Redan JA, Rush BF, Lysz TW, Smith S, Machiedo GW (1990) Organ distribution of gut-derived bacteria caused by bowel manipulation or ischemia. Am J Surg 159:85–190
Alexander JW, Gianotti L, Pyles T, Carey MA, Babcock GF (1991) Distribution and survival of Escherichia coli translocating from the intestine after thermal injury. Ann Surg 213:558–567
Gennari R, Alexande JW, Eaves-Pyles T (1994) IFN-gamma decreases translocation and improves survival following transfusion and thermal injury. J Surg Res 56:530–537
Wells CL, Maddaus MA, Simmons RL (1987) Role of the macrophage in the translocation of intestinal bacteria. Arch Surg 122:48–53
Kazantsev GB, Hecht DW, Fedorak IJ, Gattuso P, Thompson K, Djuricin G, et al. (1994) Plasmid labeling confirms bacterial translocation in pancreatitis. Am J Surg 167:201–207
Acknowledgments
We thank Zichun Hua, Dongping Wei, Jing Zhang, and Yunzi Chen for their contributions to the study. This study was supported by grants from the Nature Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 30271263) and the National Basic Research Program of China (Grant No. 2003CB515502).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, D., Shi, B., Xue, H. et al. Green Fluorescent Protein Labeling Escherichia coli TG1 Confirms Intestinal Bacterial Translocation in a Rat Model of Chemotherapy. Curr Microbiol 52, 69–73 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-005-0177-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-005-0177-9