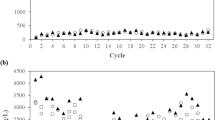
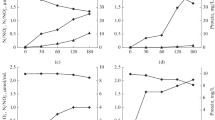
Abstract
An aerobic bacterium (BCc6), isolated from nonylphenol polyethoxylates (NPEOs)-contaminated sludge, was shown to be capable of degrading low-ethoxylated NPEO mixtures. Sequencing of 16S rRNA gene (rDNA) showed that it clustered with Stenotrophomonas nitritireducens. Fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH), performed on BCc6 strain and on the previously isolated Stenotrophomonas BCaL2, also involved in NPEO degradation but clustering with S. maltophilia, showed that strain BCc6 did not hybridize with the S. maltophilia-specific probe, and neither of the two strains hybridized with probes targeted to the Gammaproteobacteria site, rDNA analyses performed on the two strains evidenced two new polymorphisms, the first one at the 23S rRNA Gammaproteobacteria site, characterizing the known members of the Stenotrophomonas genus, and the other one at the 16S rRNA level, characteristic of S. nitritireducens. Two new FISH probes were designed accordingly, tested on control bacterial cultures, and employed for in situ monitoring of Stenotrophomonas representatives.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schäffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, et al. (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Amann RI, Binder BJ, Olson RJ, Chisholm SW, Devereux R, Stahl DA (1990) Combination of 16S rRNA-targeted oligonucleotide probes with flow cytometry for analyzing mixed microbial populations. Appl Environ Microbiol 56:1919–1925
Amann RI, Ludwig W, Schleifer KH (1995) Phylogenetic identification and in situ detection of individual microbial cells without cultivation. Microbiol Rev 59:143–169
Andreoni V, Cavalca L, Rao MA, Nocerino G, Bernasconi S, Dell’Amico E, et al. (2004) Bacterial communities and enzyme activities of PAHs polluted soils. Chemosphere 57:401–412
Anthony RM, Brown TJ, French GL (2000) Rapid diagnosis of bacteremia by universal amplification of 23S ribosomal DNA followed by hybridization to an oligonucleotide array. J Clin Microbiol 38:781–788
Barberio C, Fani R (1998) Biodiversity of an Acinetobacter population isolated from activated sludge. Res Microbiol 149:665–673
Barberio C, Pagliai L, Cavalieri D, Fani R (2001) Biodiversity and horizontal gene transfer in culturable bacteria from activated sludge enriched in nonylphenol ethoxylates. Res Microbiol 152:105–112
Bokern M, Raid P, Harms H (1998) Toxicity, uptake and metabolism of 4-n-nonylphenol in root cultures and intact plants under septic and aseptic conditions. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 5:21–27
Boonchan S, Britz ML, Stanley GA (2000) Degradation and mineralization of high-molecular-weight polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by defined fungal-bacterial cocultures. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:1007–1019
Brosius J, Dull TL, Steeter DD, Noller HF (1981) Gene organization and primary structure of a ribosomal RNA operon from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol 148:107–127
Corpet F (1988) Multiple sequence alignment with hierarchical clustering. Nucleic Acids Res 16:10881–10890
Di Cello F, Pepi M, Baldi F, Fani R (1997) Molecular characterization of an n-alkane-degrading bacterial community and identification of a new species, Acinetobacter venetianus. Res Microbiol 148:237–249
Di Corcia A, Costantino A, Crescenzi C, Marinoni E, Samperi R (1998) Characterization of recalcitrant intermediates from biotransformation of the branched alkyl side chain of nonylphenol ethoxylate surfactants. Environ Sci Technol 32:2401–2409
Di Corcia A, Cavallo R, Crescenzi C, Nazzari M (2000) Occurrence and abundance of dicarboxylated metabolites of nonylphenol polyethoxylate surfactants in treated sewages. Environ Sci Technol 34:3914–3919
Di Gioia D, Fambrini L, Coppini E, Fava F, Barberio C (2004) Aggregation-based cooperation during bacterial aerobic degradation of polyethoxylated nonylphenols. Res Microbiol 155:761–749
Duarte GF, Rosado AS, Seldin L, de Araujo W, van Elsas JD (2001) Analysis of bacterial community structure in sulfurous-oil-containing soils and detection of species carrying dibenzothiophene desulfurization (dsz) genes. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:1052–1062
Finkmann W, Altendorf K, Stackebrandt E, Lipski A (2000) Characterization of N2O- producing Xanthomonas-like isolates from biofilters as Stenotrophomonas nitritireducens sp. nov., Luteimonas mephitis gen. nov., sp. nov. and Pseudoxanthomonas broegbernensis gen. nov., sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 50:273–282
Guenther K, Heinke V, Thiele B, Kleist E, Prast H, Raecker T (2002) Endocrine disrupting nonylphenols are ubiquitous in food. Environ Sci Technol 36:1676–1680
Ho EM, Chang HW, Kim SI, Kahng HY, Oh KH (2004) Analysis of TNT (2,4,6- trinitrotoluene)-inducible cellular responses and stress shock proteome in Stenotrophomonas sp. OK-5. Curr Microbiol 49:346–352
Hogardt M, Trebesius K, Geiger AM, Hornef M, Rosenecker J, Heesemann J (2000) Specific and rapid detection by fluorescent in situ hybridization of bacteria in clinical samples obtained from cystic fibrosis patients. J Clin Microbiol 38:818–825
John DM, White GF (1998) Mechanism for biotransformation of nonylphenol polyethoxylates to Xenoestrogens in Pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol 180:4332–4338
Juhasz AL, Stanley GA, Britz ML (2000) Microbial degradation and detoxification of high molecular weight polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia strain VUN 10,003. Lett Appl Microbiol 30:396–401
Kawai F (2002) Microbial degradation of polyethers, Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 58:30–38
Kotilainen P, Jalava J, Meurman O, Lehtonen OP, Rintala E, Seppala OP, et al. (1998) Diagnosis of meningococcal meningitis by broad-range bacterial PCR with cerebrospinal fluid. J Clin Microbiol 36:2205–2209
Kroon AGM, van Ginkel CG (2001) Complete mineralization of dodecyldimethylamine using a two-membered bacterial culture. Environ Microbiol 3:131–136
Kumar S, Tamura K, Jakobsen IB, Nei M (2001) MEGA2:Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis software. Bioinformatics 17:1244–1245
Loy A, Horn M, Wagner M (2003) probeBase—An online resource for rRNA-targeted oligonucleotide probes. Nucleic Acids Res 31:514–516
Maki H, Masuda N, Fujiwara Y, Ike M, Fujita M (1994) Degradation of alkylphenol ethoxylates by Pseudomonas sp. strain TR01. Appl Environ Microbiol 60:2265–2271
Manz W, Amann R, Ludwig W, Wagner M, Schleifer KH (1992) Phylogenetic oligodeoxynucleotide probes for the major subclasses of Proteobacteria: Problems and solutions. Syst Appl Microbiol 15:593–600
Morgan CA, Hudson A, Konopka A, Nakatsu CH (2002) Analyses of microbial activity in biomass-recycle reactors using denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis of 16S rDNA and 16S rRNA PCR products. Can J Microbiol 48:333–341
Palleroni NJ, Bradbury JF (1993) Stenotrophomonas, a new bacterial genus for Xanthomonas maltophilia (Hugh 1980) Swings et al. 1983. Int J Syst Bacteriol 43:606–609
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (eds.) (1989) Molecular cloning: A laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor, NewYork, NY, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press
Sanger F, Nicklen S, Coulson AR (1977) DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 74:5463–5467
Schaumann R, Stein K, Eckhardt C, Ackermann G, Rodloff AC (2001) Infections caused by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia–A prospective study. Infection 29:205–208
Soares A, Guieysse B, Delgado O, Mattiasson B (2003) Aerobic biodegradation of nonylphenol by cold-adapted bacteria. Biotechnol Lett 25:731–738
Thibaut R, Debrauwer L, Rao D, Cravedi JP (1999) Urinary metabolites of 4-n -nonylphenol in rainbow trout (Oncorhyncus mykiss). Sci Tot Environ 233:193–200
van Ginkel CG (1996) Complete degradation of xenobiotic surfactants by consortia of aerobic microorganisms. Biodegradation 7:151–164
Wagner M, Amann R, Lemmer H, Schleifer KH (1993) Probing activated sludge with oligonucleotides specific for Proteobacteria: Inadequacy of culture-dependent methods for describing microbial community structure. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:1520–1525
Whitby PW, Carter KB, Burns JL, Royall JA, LiPuma JJ, Stull TL (2000) Identification and detection of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia by rRNA-directed PCR. J Clin Microbiol 38:4305–4309
Woese CR (1987) Bacterial evolution. Microbiol Rev 5l:221–271
Yeates C, Saunders AM, Crocetti GR, Blackall L (2003) Limitations of the widely used GAM42a and BET42a probes for targeting bacteria in the Gammaproteobacteria radiation. Microbiol 149:1239–1247
Yuan SY, Yu CH, Chang BV (2004) Biodegradation of nonylphenol in river sediment. Environ Pollut 127:425–430
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salvadori, L., Gioia, D.D., Fava, F. et al. Degradation of Low-Ethoxylated Nonylphenols by a Stenotrophomonas Strain and Development of New Phylogenetic Probes for Stenotrophomonas spp. Detection. Curr Microbiol 52, 13–20 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-005-0055-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-005-0055-5