Abstract
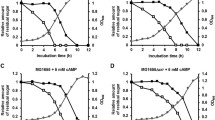
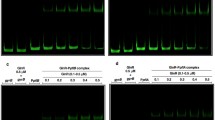
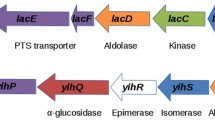
To elucidate the regulatory mechanism of catabolite control in Streptococcus bovis, we investigated the molecular properties and gene expression of the mannose-specific phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP)-dependent sugar: phosphotransferase system (PTS). The mannose PTS gene cluster (man) was found to comprise a gene encoding enzyme (E) II AB (manL) and genes encoding EIIC (manM), EIID (manN), and a putative regulator (manO). The gene cluster (man operon) was transcribed from one transcriptional start site, which was located 40 bp upstream of the manL start codon. However, two transcriptional start sites were found between manN and manO in primer extension analysis, and the manO may be transcribed independently from the man operon. The man operon and manO were constitutively transcribed without being affected by culture conditions, such as the sugar supplied (glucose, galactose, fructose, maltose, lactose, sucrose, or mannose), growth rate, or pH.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Asanuma, ., Yoshii, . & Hino, . Molecular Characteristics of Phosphoenolpyruvate: Mannose Phosphotransferase System in Streptococcus bovis . Curr Microbiol 49, 4–9 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-003-4232-0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-003-4232-0