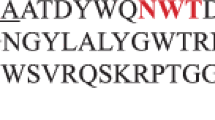Abstract
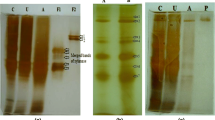
The xynA gene encoding a xylanase from the recently isolated Bacillus sp. strain BP-7 has been cloned and expressed in Escherichia coli. Recombinant xylanase A showed high activity on xylans from hardwoods and cereals, and exhibited maximum activity at pH 6 and 60°C. The enzyme remained stable after incubation at 50°C and pH 7 for 3 h, and it was strongly inhibited by Mn2+, Fe3+, Pb2+, and Hg2+. Analysis of xylanase A in zymograms showed an apparent molecular size of 24 kDa and a pI of above 9. The amino acid sequence of xylanase A, as deduced from xynA gene, shows homology to alkaline pI-low molecular weight xylanases of family 11 such as XynA from Bacillus subtilis. Analysis of codon usage in xynA from Bacillus sp. BP-7 shows that the G+C content at the first and second codon positions is notably different from the mean values found for glycosyl hydrolase genes from Bacillus subtilis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gallardo, ., Diaz, . & Pastor, . Cloning and Characterization of Xylanase A from the Strain Bacillus sp. BP-7: Comparison with Alkaline pI-Low Molecular Weight Xylanases of Family 11. Curr Microbiol 48, 276–279 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-003-4196-0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-003-4196-0