Abstract
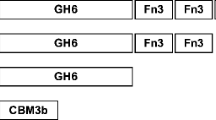
The modular endocellulase Cel9 of the bicistronic operon cel9-cel48 of Myxobacter sp. AL-1 shares not only amino acid sequence similarity but also biochemical properties similar to those of Thermobifida fusca endo/exocellulase E4. Amino acid alignments of a T. fusca E4 cellulase subfamily of family 9 cellulases revealed that Asp446 of Myxobacter sp. AL-1 Cel9, a putatively noncatalytic residue, is highly conserved in one of the catalytic domains of this subfamily. Directed mutagenesis of residue aspartate (Asp446) to alanine generated a Cel9 mutant that lost more than 99% of its activity, suggesting that Asp446 plays an essential structural role in Cel9 during cellulose degradation. Owing to its high degree of conservation and essential role, we propose that Asp446 of Myxobacter sp. AL-1 Cel9 is a good landmark that distinguishes members of the E4 subfamily of family 9 cellulases.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 4 May 2002 / Accepted: 5 July 2002
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Téllez-Valencia, A., Sandoval, A. & Pedraza-Reyes, M. The Non-Catalytic Amino Acid Asp446 Is Essential for Enzyme Activity of the Modular Endocellulase Cel9 from Myxobacter sp. AL-1. Curr Microbiol 46, 0307–0310 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-002-3862-y
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-002-3862-y