Abstract
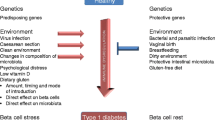
The initial development and maintenance of tolerance to dietary antigens is a complex process that, when prevented or interrupted, can lead to human disease. Understanding the mechanisms by which tolerance to specific dietary antigens is attained and maintained is crucial to our understanding of the pathogenesis of diseases related to intolerance of specific dietary antigens. Two diseases that are the result of intolerance to a dietary antigen are celiac disease (CD) and dermatitis herpetiformis (DH). Both of these diseases are dependent upon the ingestion of gluten (the protein fraction of wheat, rye, and barley) and manifest in the gastrointestinal tract and skin, respectively. These gluten-sensitive diseases are two examples of how devastating abnormal immune responses to a ubiquitous food can be. The well-recognized risk genotype for both is conferred by either of the HLA class II molecules DQ2 or DQ8. However, only a minority of individuals who carry these molecules will develop either disease. Also of interest is that the age at diagnosis can range from infancy to 70–80 years of age. This would indicate that intolerance to gluten may potentially be the result of two different phenomena. The first would be that, for various reasons, tolerance to gluten never developed in certain individuals, but that for other individuals, prior tolerance to gluten was lost at some point after childhood. Of recent interest is the concept of non-celiac gluten sensitivity, which manifests as chronic digestive or neurologic symptoms due to gluten, but through mechanisms that remain to be elucidated. This review will address how animal models of gluten-sensitive disorders have substantially contributed to a better understanding of how gluten intolerance can arise and cause disease.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CD:
-
Celiac disease
- DH:
-
Dermatitis herpetiformis
- T1D:
-
Type 1 diabetes
- NOD:
-
Non-obese diabetic
- IDD:
-
Insulin dependent diabetes
- GFC:
-
Gluten-free chow
- GCC:
-
Gluten-containing chow
References
Farrell RJ, Kelly CP (2002) Celiac sprue. N Eng J Med 346:180–188. doi:10.1056/NEJMra010852
Fry L (2002) Dermatitis herpetiformis: problems, progress and prospects. Eur J Dermatol: EJD 12:523–531
March JB (2003) High antigliadin IgG titers in laboratory rabbits fed a wheat-containing diet: a model for celiac disease? Dig Dis Sci 48:608–610
Gass J, Vora H, Bethune MT, Gray GM, Khosla C (2006) Effect of barley endoprotease EP-B2 on gluten digestion in the intact rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 318:1178–1186. doi:10.1124/jpet.106.104315
Cinova J, De Palma G, Stepankova R, Kofronova O, Kverka M, Sanz Y, Tuckova L (2011) Role of intestinal bacteria in gliadin-induced changes in intestinal mucosa: study in germ-free rats. PLoS One 6:e16169. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0016169
van der Kolk JH, van Putten LA, Mulder CJ, Grinwis GC, Reijm M, Butler CM, von Blomberg BM (2012) Gluten-dependent antibodies in horses with inflammatory small bowel disease (ISBD). Vet Q. doi:10.1080/01652176.2012.675636
Batt RM, Carter MW, McLean L (1984) Morphological and biochemical studies of a naturally occurring enteropathy in the Irish setter dog: a comparison with coeliac disease in man. Res Vet Sci 37:339–346
Hall EJ, Batt RM (1992) Dietary modulation of gluten sensitivity in a naturally occurring enteropathy of Irish setter dogs. Gut 33:198–205
Polvi A, Garden OA, Houlston RS, Maki M, Batt RM, Partanen J (1998) Genetic susceptibility to gluten sensitive enteropathy in Irish setter dogs is not linked to the major histocompatibility complex. Tissue Antigens 52:543–549
Hall EJ, Carter SD, Barnes A, Batt RM (1992) Immune responses to dietary antigens in gluten-sensitive enteropathy of Irish setters. Res Vet Sci 53:293–299
Bethune MT, Borda JT, Ribka E, Liu MX, Phillippi-Falkenstein K, Jandacek RJ, Doxiadis GG, Gray GM, Khosla C, Sestak K (2008) A non-human primate model for gluten sensitivity. PLoS One 3:e1614. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0001614
Bethune MT, Ribka E, Khosla C, Sestak K (2008) Transepithelial transport and enzymatic detoxification of gluten in gluten-sensitive rhesus macaques. PLoS One 3:e1857. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0001857
Sestak K, Mazumdar K, Midkiff CC, Dufour J, Borda JT, Alvarez X (2011) Recognition of epidermal transglutaminase by IgA and tissue transglutaminase 2 antibodies in a rare case of <em> rhesus</em> dermatitis. J Visualized Exp: JoVE. doi:10.3791/3154
Powrie F, Leach MW, Mauze S, Menon S, Caddle LB, Coffman RL (1994) Inhibition of Th1 responses prevents inflammatory bowel disease in SCID mice reconstituted with CD45RBhi CD4+ T cells. Immunity 1:553–562
Freitag TL, Rietdijk S, Junker Y, Popov Y, Bhan AK, Kelly CP, Terhorst C, Schuppan D (2009) Gliadin-primed CD4+ CD45RBlowCD25− T cells drive gluten-dependent small intestinal damage after adoptive transfer into lymphopenic mice. Gut 58:1597–1605. doi:10.1136/gut.2009.186361
Dickey W, Hughes DF (2004) Histology of the terminal ileum in coeliac disease. Scand J Gastroenterol 39:665–667. doi:10.1080/00365520410004901
Black KE, Murray JA, David CS (2002) HLA-DQ determines the response to exogenous wheat proteins: a model of gluten sensitivity in transgenic knockout mice. J Immunol 169:5595–5600
Verdu EF, Huang X, Natividad J, Lu J, Blennerhassett PA, David CS, McKay DM, Murray JA (2008) Gliadin-dependent neuromuscular and epithelial secretory responses in gluten-sensitive HLA-DQ8 transgenic mice. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 294:G217–G225. doi:10.1152/ajpgi.00225.2007
de Kauwe AL, Chen Z, Anderson RP, Keech CL, Price JD, Wijburg O, Jackson DC, Ladhams J, Allison J, McCluskey J (2009) Resistance to celiac disease in humanized HLA-DR3-DQ2-transgenic mice expressing specific anti-gliadin CD4+ T cells. J Immunol 182:7440–7450. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.0900233
Hovhannisyan Z, Weiss A, Martin A, Wiesner M, Tollefsen S, Yoshida K, Ciszewski C, Curran SA, Murray JA, David CS, Sollid LM, Koning F, Teyton L, Jabri B (2008) The role of HLA-DQ8 beta57 polymorphism in the anti-gluten T-cell response in coeliac disease. Nature 456:534–538. doi:10.1038/nature07524
Vader W, Kooy Y, Van Veelen P, De Ru A, Harris D, Benckhuijsen W, Pena S, Mearin L, Drijfhout JW, Koning F (2002) The gluten response in children with celiac disease is directed toward multiple gliadin and glutenin peptides. Gastroenterology 122:1729–1737
Korponay-Szabo IR, Halttunen T, Szalai Z, Laurila K, Kiraly R, Kovacs JB, Fesus L, Maki M (2004) In vivo targeting of intestinal and extraintestinal transglutaminase 2 by coeliac autoantibodies. Gut 53:641–648
Esposito C, Paparo F, Caputo I, Rossi M, Maglio M, Sblattero D, Not T, Porta R, Auricchio S, Marzari R, Troncone R (2002) Anti-tissue transglutaminase antibodies from coeliac patients inhibit transglutaminase activity both in vitro and in situ. Gut 51:177–181
Zone JJ, Egan CA, Taylor TB, Meyer LJ (2004) IgA autoimmune disorders: development of a passive transfer mouse model. J invest Dermatol Symp Proc / Soc Invest Dermatol, Inc [and] Eur Soc Dermatol Res 9:47–51. doi:10.1111/j.1087-0024.2004.00840.x
Zone JJ, Taylor TB, Kadunce DP, Meyer LJ (1990) Identification of the cutaneous basement membrane zone antigen and isolation of antibody in linear immunoglobulin A bullous dermatosis. J Clin Invest 85:812–820. doi:10.1172/JCI114508
Zone JJ, Schmidt LA, Taylor TB, Hull CM, Sotiriou MC, Jaskowski TD, Hill HR, Meyer LJ (2011) Dermatitis herpetiformis sera or goat anti-transglutaminase-3 transferred to human skin-grafted mice mimics dermatitis herpetiformis immunopathology. J Immunol 186:4474–4480. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1003273
Sardy M, Karpati S, Merkl B, Paulsson M, Smyth N (2002) Epidermal transglutaminase (TGase 3) is the autoantigen of dermatitis herpetiformis. J Exp Med 195:747–757
Di Niro R, Ziller F, Florian F, Crovella S, Stebel M, Bestagno M, Burrone O, Bradbury AR, Secco P, Marzari R, Sblattero D (2007) Construction of miniantibodies for the in vivo study of human autoimmune diseases in animal models. BMC Biotechnol 7:46. doi:10.1186/1472-6750-7-46
Di Niro R, Sblattero D, Florian F, Stebel M, Zentilin L, Giacca M, Villanacci V, Galletti A, Not T, Ventura A, Marzari R (2008) Anti-idiotypic response in mice expressing human autoantibodies. Mol Immunol 45:1782–1791. doi:10.1016/j.molimm.2007.09.025
Molberg O, McAdam S, Lundin KE, Kristiansen C, Arentz-Hansen H, Kett K, Sollid LM (2001) T cells from celiac disease lesions recognize gliadin epitopes deamidated in situ by endogenous tissue transglutaminase. Eur J Immunol 31:1317–1323. doi:10.1002/1521-4141(200105)31:5<1317::AID-IMMU1317>3.0.CO;2-I
Yokoyama S, Watanabe N, Sato N, Perera PY, Filkoski L, Tanaka T, Miyasaka M, Waldmann TA, Hiroi T, Perera LP (2009) Antibody-mediated blockade of IL-15 reverses the autoimmune intestinal damage in transgenic mice that overexpress IL-15 in enterocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:15849–15854. doi:10.1073/pnas.0908834106
Boscolo S, Lorenzon A, Sblattero D, Florian F, Stebel M, Marzari R, Not T, Aeschlimann D, Ventura A, Hadjivassiliou M, Tongiorgi E (2010) Anti transglutaminase antibodies cause ataxia in mice. PLoS One 5:e9698. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0009698
Rashtak S, Marietta EV, Murray JA (2009) Celiac sprue: a unique autoimmune disorder. Expert Rev Clin Immunol 5:593–604. doi:10.1586/eci.09.30
Schuppan D, Junker Y, Barisani D (2009) Celiac disease: from pathogenesis to novel therapies. Gastroenterology 137:1912–1933. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2009.09.008
Dubois PC, Trynka G, Franke L, Hunt KA, Romanos J, Curtotti A, Zhernakova A, Heap GA, Adany R, Aromaa A, Bardella MT, van den Berg LH, Bockett NA, de la Concha EG, Dema B, Fehrmann RS, Fernandez-Arquero M, Fiatal S, Grandone E, Green PM, Groen HJ, Gwilliam R, Houwen RH, Hunt SE, Kaukinen K, Kelleher D, Korponay-Szabo I, Kurppa K, MacMathuna P, Maki M, Mazzilli MC, McCann OT, Mearin ML, Mein CA, Mirza MM, Mistry V, Mora B, Morley KI, Mulder CJ, Murray JA, Nunez C, Oosterom E, Ophoff RA, Polanco I, Peltonen L, Platteel M, Rybak A, Salomaa V, Schweizer JJ, Sperandeo MP, Tack GJ, Turner G, Veldink JH, Verbeek WH, Weersma RK, Wolters VM, Urcelay E, Cukrowska B, Greco L, Neuhausen SL, McManus R, Barisani D, Deloukas P, Barrett JC, Saavalainen P, Wijmenga C, van Heel DA (2010) Multiple common variants for celiac disease influencing immune gene expression. Nat Genet 42:295–302. doi:10.1038/ng.543
Ludvigsson JF, Ludvigsson J, Ekbom A, Montgomery SM (2006) Celiac disease and risk of subsequent type 1 diabetes: a general population cohort study of children and adolescents. Diabetes Care 29:2483–2488. doi:10.2337/dc06-0794
Barera G, Bonfanti R, Viscardi M, Bazzigaluppi E, Calori G, Meschi F, Bianchi C, Chiumello G (2002) Occurrence of celiac disease after onset of type 1 diabetes: a 6-year prospective longitudinal study. Pediatrics 109:833–838
Maki M, Hallstrom O, Huupponen T, Vesikari T, Visakorpi JK (1984) Increased prevalence of coeliac disease in diabetes. Arch Dis Child 59:739–742
Maurano F, Mazzarella G, Luongo D, Stefanile R, D'Arienzo R, Rossi M, Auricchio S, Troncone R (2005) Small intestinal enteropathy in non-obese diabetic mice fed a diet containing wheat. Diabetologia 48:931–937. doi:10.1007/s00125-005-1718-2
Sanjeevi CB, Sedimbi SK, Landin-Olsson M, Kockum I, Lernmark A (2008) Risk conferred by HLA-DR and DQ for type 1 diabetes in 0-35-year age group in Sweden. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1150:106–111. doi:10.1196/annals.1447.061
Jabri B, Sollid LM (2006) Mechanisms of disease: immunopathogenesis of celiac disease. Nat Clin Pract Gastroenterol Hepatol 3:516–525
Kagnoff MF (2007) Celiac disease: pathogenesis of a model immunogenetic disease. J Clin Invest 117:41–49. doi:10.1172/JCI30253
Fox CJ, Paterson AD, Mortin-Toth SM, Danska JS (2000) Two genetic loci regulate T cell-dependent islet inflammation and drive autoimmune diabetes pathogenesis. Am J Hum Genet 67:67–81. doi:10.1086/302995
Rajagopalan G, Mangalam AK, Sen MM, Cheng S, Kudva YC, David CS (2007) Autoimmunity in HLA-DQ8 transgenic mice expressing granulocyte/macrophage-colony stimulating factor in the beta cells of islets of Langerhans. Autoimmunity 40:169–179. doi:10.1080/08916930701201083
Fox CJ, Danska JS (1998) Independent genetic regulation of T-cell and antigen-presenting cell participation in autoimmune islet inflammation. Diabetes 47:331–338
Marietta E, Black K, Camilleri M, Krause P, Rogers RS 3rd, David C, Pittelkow MR, Murray JA (2004) A new model for dermatitis herpetiformis that uses HLA-DQ8 transgenic NOD mice. J Clin Invest 114:1090–1097. doi:10.1172/JCI21055
Sababi M, Hallgren A, Nylander O (1996) Interaction between prostanoids, NO, and VIP in modulation of duodenal alkaline secretion and motility. Am J Physiol 271:G582–G590
Nylander O, Hallgren A, Sababi M (2001) COX inhibition excites enteric nerves that affect motility, alkaline secretion, and permeability in rat duodenum. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 281:G1169–G1178
D'Arienzo R, Maurano F, Lavermicocca P, Ricca E, Rossi M (2009) Modulation of the immune response by probiotic strains in a mouse model of gluten sensitivity. Cytokine 48:254–259. doi:10.1016/j.cyto.2009.08.003
Natividad JM, Huang X, Slack E, Jury J, Sanz Y, David C, Denou E, Yang P, Murray J, McCoy KD, Verdu EF (2009) Host responses to intestinal microbial antigens in gluten-sensitive mice. PLoS One 4:e6472. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0006472
Siegel M, Strnad P, Watts RE, Choi K, Jabri B, Omary MB, Khosla C (2008) Extracellular transglutaminase 2 is catalytically inactive, but is transiently activated upon tissue injury. PLoS One 3:e1861. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0001861
de Koning BA, van Dieren JM, Lindenbergh-Kortleve DJ, van der Sluis M, Matsumoto T, Yamaguchi K, Einerhand AW, Samsom JN, Pieters R, Nieuwenhuis EE (2006) Contributions of mucosal immune cells to methotrexate-induced mucositis. Int Immunol 18:941–949. doi:10.1093/intimm/dxl030
DePaolo RW, Abadie V, Tang F, Fehlner-Peach H, Hall JA, Wang W, Marietta EV, Kasarda DD, Waldmann TA, Murray JA, Semrad C, Kupfer SS, Belkaid Y, Guandalini S, Jabri B (2011) Co-adjuvant effects of retinoic acid and IL-15 induce inflammatory immunity to dietary antigens. Nature 471:220–224. doi:10.1038/nature09849
Zanzi D, Stefanile R, Santagata S, Iaffaldano L, Iaquinto G, Giardullo N, Lania G, Vigliano I, Vera AR, Ferrara K, Auricchio S, Troncone R, Mazzarella G (2011) IL-15 interferes with suppressive activity of intestinal regulatory T cells expanded in Celiac disease. Am J Gastroenterol 106:1308–1317. doi:10.1038/ajg.2011.80
Galipeau HJ, Rulli NE, Jury J, Huang X, Araya R, Murray JA, David CS, Chirdo FG, McCoy KD, Verdu EF (2011) Sensitization to gliadin induces moderate enteropathy and insulitis in nonobese diabetic-DQ8 mice. J Immunol 187:4338–4346. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1100854
Fehniger TA, Suzuki K, Ponnappan A, VanDeusen JB, Cooper MA, Florea SM, Freud AG, Robinson ML, Durbin J, Caligiuri MA (2001) Fatal leukemia in interleukin 15 transgenic mice follows early expansions in natural killer and memory phenotype CD8+ T cells. J Exp Med 193:219–231
Ohta N, Hiroi T, Kweon MN, Kinoshita N, Jang MH, Mashimo T, Miyazaki J, Kiyono H (2002) IL-15-dependent activation-induced cell death-resistant Th1 type CD8 alpha beta + NK1.1+ T cells for the development of small intestinal inflammation. J Immunol 169:460–468
Yokoyama S, Takada K, Hirasawa M, Perera LP, Hiroi T (2011) Transgenic mice that overexpress human IL-15 in enterocytes recapitulate both B and T cell-mediated pathologic manifestations of celiac disease. J Clin Immunol 31:1038–1044. doi:10.1007/s10875-011-9586-7
Du Pre MF, Kozijn AE, van Berkel LA, ter Borg MN, Lindenbergh-Kortleve D, Jensen LT, Kooy-Winkelaar Y, Koning F, Boon L, Nieuwenhuis EE, Sollid LM, Fugger L, Samsom JN (2011) Tolerance to ingested deamidated gliadin in mice is maintained by splenic, type 1 regulatory T cells. Gastroenterology 141:610–620. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2011.04.048, 620 e611-612
Collado MC, Donat E, Ribes-Koninckx C, Calabuig M, Sanz Y (2008) Imbalances in faecal and duodenal Bifidobacterium species composition in active and non-active coeliac disease. BMC Microbiol 8:232. doi:10.1186/1471-2180-8-232
Collado MC, Donat E, Ribes-Koninckx C, Calabuig M, Sanz Y (2009) Specific duodenal and faecal bacterial groups associated with paediatric coeliac disease. J Clin Pathol 62:264–269. doi:10.1136/jcp.2008.061366
Kopecny J, Mrazek J, Fliegerova K, Fruhauf P, Tuckova L (2008) The intestinal microflora of childhood patients with indicated celiac disease. Folia Microbiol 53:214–216. doi:10.1007/s12223-008-0028-8
Di Cagno R, De Angelis M, De Pasquale I, Ndagijimana M, Vernocchi P, Ricciuti P, Gagliardi F, Laghi L, Crecchio C, Guerzoni ME, Gobbetti M, Francavilla R (2011) Duodenal and faecal microbiota of celiac children: molecular, phenotype and metabolome characterization. BMC Microbiol 11:219. doi:10.1186/1471-2180-11-219
Hoorfar J, Buschard K, Dagnaes-Hansen F (1993) Prophylactic nutritional modification of the incidence of diabetes in autoimmune non-obese diabetic (NOD) mice. Br J Nutr 69:597–607
Beales PE, Elliott RB, Flohe S, Hill JP, Kolb H, Pozzilli P, Wang GS, Wasmuth H, Scott FW (2002) A multi-centre, blinded international trial of the effect of A(1) and A(2) beta-casein variants on diabetes incidence in two rodent models of spontaneous Type I diabetes. Diabetologia 45:1240–1246. doi:10.1007/s00125-002-0898-2
Schmid S, Koczwara K, Schwinghammer S, Lampasona V, Ziegler AG, Bonifacio E (2004) Delayed exposure to wheat and barley proteins reduces diabetes incidence in non-obese diabetic mice. Clin Immunol 111:108–118. doi:10.1016/j.clim.2003.09.012
Funda DP, Kaas A, Bock T, Tlaskalova-Hogenova H, Buschard K (1999) Gluten-free diet prevents diabetes in NOD mice. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 15:323–327. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1520-7560(199909/10)15:5<323::AID-DMRR53>3.0.CO;2-P
Karges W, Hammond-McKibben D, Cheung RK, Visconti M, Shibuya N, Kemp D, Dosch HM (1997) Immunological aspects of nutritional diabetes prevention in NOD mice: a pilot study for the cow's milk-based IDDM prevention trial. Diabetes 46:557–564
Hummel S, Ziegler AG (2011) Early determinants of type 1 diabetes: experience from the BABYDIAB and BABYDIET studies. Am J Clin Nutr. doi:10.3945/ajcn.110.000646
Hummel S, Pfluger M, Hummel M, Bonifacio E, Ziegler AG (2011) Primary dietary intervention study to reduce the risk of islet autoimmunity in children at increased risk for type 1 diabetes: the BABYDIET study. Diabetes Care 34:1301–1305. doi:10.2337/dc10-2456
Scott FW, Rowsell P, Wang GS, Burghardt K, Kolb H, Flohe S (2002) Oral exposure to diabetes-promoting food or immunomodulators in neonates alters gut cytokines and diabetes. Diabetes 51:73–78
Visser J, Hillebrands JL, Boer MW, Bos NA, Rozing J (2009) Prevention of diabetes by a hydrolysed casein-based diet in diabetes-prone biobreeding rats does not involve restoration of the defective natural regulatory T cell function. Diabetologia 52:1445–1447. doi:10.1007/s00125-009-1370-3
Visser J, Brugman S, Klatter F, Vis L, Groen H, Strubbe J, Rozing J (2003) Short-term dietary adjustment with a hydrolyzed casein-based diet postpones diabetes development in the diabetes-prone BB rat. Metab: Clin Exp 52:333–337. doi:10.1053/meta.2003.50052
MacFarlane AJ, Burghardt KM, Kelly J, Simell T, Simell O, Altosaar I, Scott FW (2003) A type 1 diabetes-related protein from wheat (Triticum aestivum). cDNA clone of a wheat storage globulin, Glb1, linked to islet damage. J Biol Chem 278:54–63. doi:10.1074/jbc.M210636200
Loit E, Melnyk CW, MacFarlane AJ, Scott FW, Altosaar I (2009) Identification of three wheat globulin genes by screening a Triticum aestivum BAC genomic library with cDNA from a diabetes-associated globulin. BMC Plant Biol 9:93. doi:10.1186/1471-2229-9-93
Sapone A, de Magistris L, Pietzak M, Clemente MG, Tripathi A, Cucca F, Lampis R, Kryszak D, Carteni M, Generoso M, Iafusco D, Prisco F, Laghi F, Riegler G, Carratu R, Counts D, Fasano A (2006) Zonulin upregulation is associated with increased gut permeability in subjects with type 1 diabetes and their relatives. Diabetes 55:1443–1449
Smecuol E, Sugai E, Niveloni S, Vazquez H, Pedreira S, Mazure R, Moreno ML, Label M, Maurino E, Fasano A, Meddings J, Bai JC (2005) Permeability, zonulin production, and enteropathy in dermatitis herpetiformis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol: Off Clin Pract J Am Gastroenterol Assoc 3:335–341
Lammers KM, Lu R, Brownley J, Lu B, Gerard C, Thomas K, Rallabhandi P, Shea-Donohue T, Tamiz A, Alkan S, Netzel-Arnett S, Antalis T, Vogel SN, Fasano A (2008) Gliadin induces an increase in intestinal permeability and zonulin release by binding to the chemokine receptor CXCR3. Gastroenterology 135:194–204. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2008.03.023
Simpson M, Mojibian M, Barriga K, Scott FW, Fasano A, Rewers M, Norris JM (2009) An exploration of Glo-3A antibody levels in children at increased risk for type 1 diabetes mellitus. Pediatr Diabetes 10:563–572. doi:10.1111/j.1399-5448.2009.00541.x
Sonier B, Strom A, Wang GS, Patrick C, Crookshank JA, Mojibian M, MacFarlane AJ, Scott FW (2011) Antibodies from a patient with type 1 diabetes and celiac disease bind to macrophages that express the scavenger receptor CD163. J Can Gastroenterol 25:327–329
Huibregtse IL, Marietta EV, Rashtak S, Koning F, Rottiers P, David CS, van Deventer SJ, Murray JA (2009) Induction of antigen-specific tolerance by oral administration of Lactococcus lactis delivered immunodominant DQ8-restricted gliadin peptide in sensitized nonobese diabetic Abo Dq8 transgenic mice. J Immunol 183:2390–2396. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.0802891
Steidler L, Hans W, Schotte L, Neirynck S, Obermeier F, Falk W, Fiers W, Remaut E (2000) Treatment of murine colitis by Lactococcus lactis secreting interleukin-10. Science 289:1352–1355
Huibregtse IL, Snoeck V, de Creus A, Braat H, De Jong EC, Van Deventer SJ, Rottiers P (2007) Induction of ovalbumin-specific tolerance by oral administration of Lactococcus lactis secreting ovalbumin. Gastroenterology 133:517–528. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2007.04.073
D'Arienzo R, Maurano F, Luongo D, Mazzarella G, Stefanile R, Troncone R, Auricchio S, Ricca E, David C, Rossi M (2008) Adjuvant effect of Lactobacillus casei in a mouse model of gluten sensitivity. Immunol Lett 119:78–83. doi:10.1016/j.imlet.2008.04.006
D'Arienzo R, Stefanile R, Maurano F, Mazzarella G, Ricca E, Troncone R, Auricchio S, Rossi M (2011) Immunomodulatory effects of Lactobacillus casei administration in a mouse model of gliadin-sensitive enteropathy. Scand J Immunol 74:335–341. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3083.2011.02582.x
Endo H, Higurashi T, Hosono K, Sakai E, Sekino Y, Iida H, Sakamoto Y, Koide T, Takahashi H, Yoneda M, Tokoro C, Inamori M, Abe Y, Nakajima A (2011) Efficacy of Lactobacillus casei treatment on small bowel injury in chronic low-dose aspirin users: a pilot randomized controlled study. J Gastroenterol 46:894–905. doi:10.1007/s00535-011-0410-1
Keech CL, Dromey J, Chen ZJ, Anderson RP, McCluskey J (2009) Immune tolerance induced by peptide immunotherapy in an HLA Dq2-dependent mouse model of gluten immunity. Gastroenterology 136:A57–A57
Senger S, Luongo D, Maurano F, Mazzeo MF, Siciliano RA, Gianfrani C, David C, Troncone R, Auricchio S, Rossi M (2003) Intranasal administration of a recombinant alpha-gliadin down-regulates the immune response to wheat gliadin in DQ8 transgenic mice. Immunol Lett 88:127–134
Pinier M, Verdu EF, Nasser-Eddine M, David CS, Vezina A, Rivard N, Leroux JC (2009) Polymeric binders suppress gliadin-induced toxicity in the intestinal epithelium. Gastroenterology 136:288–298. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2008.09.016
Malamut G, El Machhour R, Montcuquet N, Martin-Lanneree S, Dusanter-Fourt I, Verkarre V, Mention JJ, Rahmi G, Kiyono H, Butz EA, Brousse N, Cellier C, Cerf-Bensussan N, Meresse B (2010) IL-15 triggers an antiapoptotic pathway in human intraepithelial lymphocytes that is a potential new target in celiac disease-associated inflammation and lymphomagenesis. J Clin Invest 120:2131–2143. doi:10.1172/JCI41344
Drago S, El Asmar R, Di Pierro M, Grazia Clemente M, Tripathi A, Sapone A, Thakar M, Iacono G, Carroccio A, D'Agate C, Not T, Zampini L, Catassi C, Fasano A (2006) Gliadin, zonulin and gut permeability: effects on celiac and non-celiac intestinal mucosa and intestinal cell lines. Scand J Gastroenterol 41:408–419. doi:10.1080/00365520500235334
Gopalakrishnan S, Tripathi A, Tamiz AP, Alkan SS, Pandey NB (2012) Larazotide acetate promotes tight junction assembly in epithelial cells. Peptides. doi:10.1016/j.peptides.2012.02.016
Gopalakrishnan S, Durai M, Kitchens K, Tamiz AP, Somerville R, Ginski M, Paterson BM, Murray JA, Verdu EF, Alkan SS, Pandey NB (2012) Larazotide acetate regulates epithelial tight junctions in vitro and in vivo. Peptides. doi:10.1016/j.peptides.2012.02.015
Bergamo P, Maurano F, Mazzarella G, Iaquinto G, Vocca I, Rivelli AR, De Falco E, Gianfrani C, Rossi M (2011) Immunological evaluation of the alcohol-soluble protein fraction from gluten-free grains in relation to celiac disease. Mol Nutr Food Res 55:1266–1270. doi:10.1002/mnfr.201100132
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported in part by NIH grant DK071003 and Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research.
This article is published as part of the Special Issue on Celiac Disease [34:5]
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marietta, E.V., Murray, J.A. Animal models to study gluten sensitivity. Semin Immunopathol 34, 497–511 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00281-012-0315-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00281-012-0315-y