Abstract
Purpose
Berberine chloride (BBC) is a well-known plant isoquinoline alkaloid derived from Berberis aristata. In this study, we aim to explore the effect of BBC on non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), and further expound the underlying mechanism of BBC induces NSCLC cell death in vitro and in vivo.
Methods
CCK-8 assay and colony formation assay were used to test the viability and colony formation ability of NSCLC cells. Apoptosis analysis was used to analyze the apoptotic cells. siRNAs were utilized to disturb the expression of Sin3A. qPCR and Western blot analysis were employed to determine mRNA and protein levels of related genes and proteins. Tumor xenografts model was used for in vivo detection.
Results
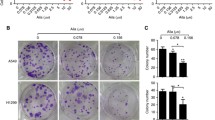
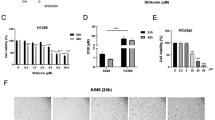
BBC inhibited the proliferation and colony formation of human NSCLC cells in a dose- and time-dependent manner. In addition, BBC induced DNA double-stranded breaks (DSBs) through downregulating TOP2B level, leading to apoptosis in human NSCLC cells. The Chip-seq data of A549 cells obtained from the ENCODE consortium indicate that Sin3A binds on the promoters of TOP2B. Knockdown of Sin3A led to downregulation of TOP2B in human NSCLC cells. Furthermore, BBC decreased Sin3A expression and shortened the half-life of Sin3A, results in downregulation of TOP2B in human NSCLC cells.
Conclusion
In this study, we demonstrated a new mechanism that BBC suppresses human NSCLC by deregulating Sin3A/TOP2B pathway, leading to DNA damage and apoptosis in human NSCLC in vitro and in vivo.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wakelee H, Kelly K, Edelman MJ (2014) 50 Years of progress in the systemic therapy of non-small cell lung cancer. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. https://doi.org/10.14694/EdBook_AM.2014.34.177
Amable L (2016) Cisplatin resistance and opportunities for precision medicine. Pharmacol Res 106:27–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2016.01.001
Feng X, Liu H, Zhang Z, Gu Y, Qiu H, He Z (2017) Annexin A2 contributes to cisplatin resistance by activation of JNK-p53 pathway in non-small cell lung cancer cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 36(1):123. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-017-0594-1
Xiao L, Lan X, Shi X, Zhao K, Wang D, Wang X, Li F, Huang H, Liu J (2017) Cytoplasmic RAP1 mediates cisplatin resistance of non-small cell lung cancer. Cell Death Dis 8(5):e2803. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2017.210
Drake FH, Zimmerman JP, McCabe FL, Bartus HF, Per SR, Sullivan DM, Ross WE, Mattern MR, Johnson RK, Crooke ST et al (1987) Purification of topoisomerase II from amsacrine-resistant P388 leukemia cells. Evidence for two forms of the enzyme. J Biol Chem 262(34):16739–16747
Cowell IG, Sondka Z, Smith K, Lee KC, Manville CM, Sidorczuk-Lesthuruge M, Rance HA, Padget K, Jackson GH, Adachi N, Austin CA (2012) Model for MLL translocations in therapy-related leukemia involving topoisomerase IIbeta-mediated DNA strand breaks and gene proximity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109(23):8989–8994. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1204406109
Austin CA, Lee KC, Swan RL, Khazeem MM, Manville CM, Cridland P, Treumann A, Porter A, Morris NJ, Cowell IG (2018) TOP2B: the first thirty years. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092765
Nitiss JL (2009) Targeting DNA topoisomerase II in cancer chemotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer 9(5):338–350. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc2607
Zhang P, Wang H, Rowe PSN, Hu B, Wang Y (2010) MEPE/OF45 as a new target for sensitizing human tumour cells to DNA damage inducers. Br J Cancer 102(5):862–866. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjc.6605572
Bansal N, David G, Farias E, Waxman S (2016) Emerging roles of epigenetic regulator Sin3 in cancer. Adv Cancer Res 130:113–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.acr.2016.01.006
Dannenberg JH, David G, Zhong S, van der Torre J, Wong WH, Depinho RA (2005) mSin3A corepressor regulates diverse transcriptional networks governing normal and neoplastic growth and survival. Genes Dev 19(13):1581–1595. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1286905
Das TK, Sangodkar J, Negre N, Narla G, Cagan RL (2013) Sin3a acts through a multi-gene module to regulate invasion in drosophila and human tumors. Oncogene 32(26):3184–3197. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2012.326
Desborough MJR, Keeling DM (2017) The aspirin story—from willow to wonder drug. Br J Haematol 177(5):674–683. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjh.14520
Rolnik DL, Wright D, Poon LC, O'Gorman N, Syngelaki A, de Paco MC, Akolekar R, Cicero S, Janga D, Singh M, Molina FS, Persico N, Jani JC, Plasencia W, Papaioannou G, Tenenbaum-Gavish K, Meiri H, Gizurarson S, Maclagan K, Nicolaides KH (2017) Aspirin versus placebo in pregnancies at high risk for preterm preeclampsia. N Engl J Med 377(7):613–622. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1704559
Nelson BS, Kremer DM, Lyssiotis CA (2018) New tricks for an old drug. Nat Chem Biol 14(11):990–991. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41589-018-0137-x
Vuddanda PR, Chakraborty S, Singh S (2010) Berberine: a potential phytochemical with multispectrum therapeutic activities. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 19(10):1297–1307. https://doi.org/10.1517/13543784.2010.517745
Cicero AF, Baggioni A (2016) Berberine and its role in chronic disease. Adv Exp Med Biol 928:27–45. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-41334-1_2
Watanabe A, Obata T, Nagashima H (1982) Berberine therapy of hypertyraminemia in patients with liver cirrhosis. Acta Med Okayama 36(4):277–281. https://doi.org/10.18926/AMO/30659
Chekalina SI, Umurzakova RZ, Saliev KK, Abdurakhmanov TR (1994) Effect of berberine bisulfate on platelet hemostasis in thrombocytopenia patients. Gematol Transfuziol 39(5):33–35
Zhao W, Xue R, Zhou ZX, Kong WJ, Jiang JD (2008) Reduction of blood lipid by berberine in hyperlipidemic patients with chronic hepatitis or liver cirrhosis. Biomed Pharmacother 62(10):730–731. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2008.01.007
Cao C, Su M (2019) Effects of berberine on glucose-lipid metabolism, inflammatory factors and insulin resistance in patients with metabolic syndrome. Exp Ther Med 17(4):3009–3014. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2019.7295
Kalaiarasi A, Anusha C, Sankar R, Rajasekaran S, John Marshal J, Muthusamy K, Ravikumar V (2016) Plant isoquinoline alkaloid berberine exhibits chromatin remodeling by modulation of histone deacetylase to induce growth arrest and apoptosis in the A549 cell line. J Agric Food Chem 64(50):9542–9550. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.6b04453
Ortiz LM, Lombardi P, Tillhon M, Scovassi AI (2014) Berberine, an epiphany against cancer. Molecules 19(8):12349–12367. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules190812349
Ruan H, Zhan YY, Hou J, Xu B, Chen B, Tian Y, Wu D, Zhao Y, Zhang Y, Chen X, Mi P, Zhang L, Zhang S, Wang X, Cao H, Zhang W, Wang H, Li H, Su Y, Zhang XK, Hu T (2017) Berberine binds RXRalpha to suppress beta-catenin signaling in colon cancer cells. Oncogene 36(50):6906–6918. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2017.296
Hou D, Xu G, Zhang C, Li B, Qin J, Hao X, Liu Q, Zhang X, Liu J, Wei J, Gong Y, Liu Z, Shao C (2017) Berberine induces oxidative DNA damage and impairs homologous recombination repair in ovarian cancer cells to confer increased sensitivity to PARP inhibition. Cell Death Dis 8(10):e3070. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2017.471
Saxena S, Shukla S, Kakkar P (2018) Berberine induced modulation of PHLPP2-Akt-MST1 kinase signaling is coupled with mitochondrial impairment and hepatoma cell death. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 347:92–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2018.03.033
Ma W, Zhu M, Zhang D, Yang L, Yang T, Li X, Zhang Y (2017) Berberine inhibits the proliferation and migration of breast cancer ZR-75-30 cells by targeting Ephrin-B2. Phytomedicine 25:45–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2016.12.013
Xi S, Chuang K, Fang K, Lee Y, Chung J, Chuang Y (2014) Effect of berberine on activity and mRNA expression of N-acetyltransferase in human lung cancer cell line A549. J Tradit Chin Med 34(3):302–308
Li J, Liu F, Jiang S, Liu J, Chen X, Zhang S, Zhao H (2018) Berberine hydrochloride inhibits cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis of non-small cell lung cancer via the suppression of the MMP2 and Bcl-2/Bax signaling pathways. Oncol Lett 15(5):7409–7414. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2018.8249
Chen J, Huang X, Tao C, Xiao T, Li X, Zeng Q, Ma M, Wu Z (2019) Artemether attenuates the progression of non-small cell lung cancer by inducing apoptosis, cell cycle arrest and promoting cellular senescence. Biol Pharm Bull 42(10):1720–1725. https://doi.org/10.1248/bpb.b19-00391
Chen J, Li W, Cui K, Ji K, Xu S, Xu Y (2018) Artemisitene suppresses tumorigenesis by inducing DNA damage through deregulating c-Myc-topoisomerase pathway. Oncogene 37(37):5079–5087. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-018-0331-z
Nagasaka M, Zaki M, Kim H, Raza SN, Yoo G, Lin HS, Sukari A (2016) PD1/PD-L1 inhibition as a potential radiosensitizer in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: a case report. J Immunother Cancer 4:83. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40425-016-0187-0
Gurley KE, Moser R, Gu Y, Hasty P, Kemp CJ (2009) DNA-PK suppresses a p53-independent apoptotic response to DNA damage. EMBO Rep 10(1):87–93. https://doi.org/10.1038/embor.2008.214
Bohlman S, Manfredi JJ (2014) p53-independent effects of Mdm2. Subcell Biochem 85:235–246. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-017-9211-0_13
Roos WP, Kaina B (2013) DNA damage-induced cell death: from specific DNA lesions to the DNA damage response and apoptosis. Cancer Lett 332(2):237–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2012.01.007
Roos WP, Kaina B (2006) DNA damage-induced cell death by apoptosis. Trends Mol Med 12(9):440–450. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmed.2006.07.007
Li J, Gu L, Zhang H, Liu T, Tian D, Zhou M, Zhou S (2013) Berberine represses DAXX gene transcription and induces cancer cell apoptosis. Lab Invest 93(3):354–364. https://doi.org/10.1038/labinvest.2012.172
Gambi G, Di Simone E, Basso V, Ricci L, Wang R, Verma A, Elemento O, Ponzoni M, Inghirami G, Icardi L, Mondino A (2019) The transcriptional regulator Sin3A contributes to the oncogenic potential of STAT3. Cancer Res 79(12):3076–3087. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-0359
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Natural Science Foundation of China (nos. 81574038 and 81673979), Shenzhen Basic Discipline Layout Project (no. JCYJ20170412161254416), Shenzhen Sanming Project of Medical and Health (No. SZSM 201612049), the Science and Technology Project of Guangdong (no. 2014A020210001), Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (nos. 2018A030313393 and 2016A030313114), Scientific Research and Innovation Fund of Jinan University/the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (no. 21615464), and Science and Technology Program of Guangzhou (no. 201803010051).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, J., Huang, X., Tao, C. et al. Berberine chloride suppresses non-small cell lung cancer by deregulating Sin3A/TOP2B pathway in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 86, 151–161 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-020-04050-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-020-04050-y