Abstract
Purpose
This phase 1b study investigated the maximum tolerated dose (MTD; primary objective), safety, pharmacokinetics, and antitumor activity (secondary objectives) of eribulin combined with carboplatin in patients with solid tumors and, in particular, non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Methods
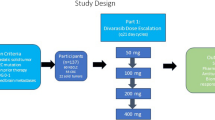
Two dose-escalation schemes were evaluated with carboplatin, at an area under the curve (AUC) of either 5 or 6 mg/mL·min. Eribulin, dose-escalated from 0.7 to 1.4 mg/m2 was administered 1 h before (Schedule A) or after (Schedule B) carboplatin as a 2–5-min bolus infusion on days 1 and 8 of a 21-day cycle. Following tolerability assessment, patients with NSCLC were recruited in an expansion cohort.
Results
The MTDs were eribulin 1.4 and 1.1 mg/m2 with carboplatin AUC 5 and AUC 6, respectively. The latter combination was used to treat NSCLC patients in the expansion cohort. Pharmacokinetics of eribulin and carboplatin were generally unaffected by administration sequence (i.e., administration of carboplatin did not significantly affect eribulin Cmax and AUC0–t and the converse was also observed). In the NSCLC cohort, the objective response rate was 27%. Median overall and progression-free survival durations were 12.1 and 4.2 months, respectively. No unexpected safety findings were observed.
Conclusions
The combination of eribulin and carboplatin demonstrated antitumor activity; however, recent therapeutic advances may be more promising approaches for first-line treatment of NSCLC.
Clinical trial registration NCT00268905.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dybdal-Hargreaves NF, Risinger AL, Mooberry SL (2015) Eribulin mesylate: mechanism of action of a unique microtubule-targeting agent. Clin Cancer Res 21:2445–2452
Smith JA, Wilson L, Azarenko O, Zhu X, Lewis BM, Littlefield BA, Jordan MA (2010) Eribulin binds at microtubule ends to a single site on tubulin to suppress dynamic instability. Biochemistry 49:1331–1337
SEER Cancer Statistics Factsheets: Lung and Bronchus Cancer. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute. http://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/lungb.html. Accessed 18 Apr 2019
National Comprehensive Cancer Network Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®) (2018) Non-small cell lung cancer. Version 2.2018. https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/sclc.pdf. Accessed 18 Apr 2019
Synold TW, Morgan RJ, Newman EM, Lenz HJ, Gandara DR, Colevas AD, Lewis MD, Doroshow J (2005) A phase I pharmacokinetic and target validation study of novel anti-tubulin agent E7389: a California Cancer Consoritum [abstract]. J Clin Oncol 23(16 suppl):3036
Mukohara T, Nagai S, Mukai H, Namiki M, Minami H (2012) Eribulin mesylate in patients with refractory cancers: a Phase I study. Invest New Drugs 30:1926–1933
Gitlitz BJ, Tsao-Wei DD, Groshen S, Davies A, Koczywas M, Belani CP, Argiris A, Ramalingam S, Vokes EE, Edelman M, Hoffman P, Ballas MS, Liu SV, Gandara DR (2012) A phase II study of halichondrin B analog eribulin mesylate (E7389) in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer previously treated with a taxane: a California Cancer Consortium trial. J Thorac Oncol 7:574–578
Spira AI, Iannotti NO, Savin MA, Neubauer M, Gabrail NY, Yanagihara RH, Zang EA, Cole PE, Shuster D, Das A (2012) A phase II study of eribulin mesylate (E7389) in patients with advanced, previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer 13:31–38
Katakami N, Felip E, Spigel DR, Kim JH, Olivo M, Guo M, Nokihara H, Yang JC, Iannotti N, Satouchi M, Barlesi F (2017) A randomized, open-label, multicenter, phase 3 study to compare the efficacy and safety of eribulin to treatment of physician’s choice in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Ann Oncol 28:2241–2247
de Castria TB, da Silva EM, Gois AF, Riera R (2013) Cisplatin versus carboplatin in combination with third-generation drugs for advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD009256.pub2
Schiller JH, Harrington D, Belani CP, Langer C, Sandler A, Krook J, Zhu J, Johnson DH, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (2002) Comparison of four chemotherapy regimens for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 346:92–98
Kelly K, Crowley J, Bunn PA Jr, Presant CA, Grevstad PK, Moinpour CM, Ramsey SD, Wozniak AJ, Weiss GR, Moore DF, Israel VK, Livingston RB, Gandara DR (2001) Randomized phase III trial of paclitaxel plus carboplatin versus vinorelbine plus cisplatin in the treatment of patients with advanced non–small-cell lung cancer: a Southwest Oncology Group trial. J Clin Oncol 19:3210–3218
Ando M, Saka H, Ando Y, Minami H, Kuzuya T, Yamamoto M, Watanabe A, Sakai S, Shimokata K, Hasegawa Y (2005) Sequence effect of docetaxel and carboplatin on toxicity, tumor response and pharmacokinetics in non-small-cell lung cancer patients: a phase I study of two sequences. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 55:552–558
Rowinsky EK, Gilbert MR, McGuire WP, Noe DA, Grochow LB, Forastiere AA, Ettinger DS, Lubejko BG, Clark B, Sartorius SE (1991) Sequences of taxol and cisplatin: a phase I and pharmacologic study. J Clin Oncol 9:1692–1703
Goel S, Mita AC, Mita M, Rowinsky EK, Chu QS, Wong N, Desjardins C, Fang F, Jansen M, Shuster DE, Mani S, Takimoto CH (2009) A phase I study of eribulin mesylate (E7389), a mechanistically novel inhibitor of microtubule dynamics, in patients with advanced solid malignancies. Clin Cancer Res 15:4207–4212
Oguri S, Sakakibara T, Mase H, Shimizu T, Ishikawa K, Kimura K, Smyth RD (1988) Clinical pharmacokinetics of carboplatin. J Clin Pharmacol 28:208–215
de Bono JS, Molife LR, Sonpavde G, Maroto JP, Calvo E, Cartwright TH, Loesch DM, Feit K, Das A, Zang EA, Wanders J, Agoulnik S, Petrylak DP (2012) Phase II study of eribulin mesylate (E7389) in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer stratified by prior taxane therapy. Ann Oncol 23:1241–1249
Stein MN, Chen Y, Hudes GR, Carducci MA, Tan W, DiPaola RS (2010) ECOG 5805: a phase II study of eribulin mesylate (E7389) in patients (pts) with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) [abstract]. J Clin Oncol 28(Suppl 15):4556
Sella A, Yarom N, Zisman A, Kovel S (2009) Paclitaxel, estramustine and carboplatin combination chemotherapy after initial docetaxel-based chemotherapy in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Oncology 76:442–446
Sternberg CN, Petrylak DP, Sartor O, Witjes JA, Demkow T, Ferrero JM, Eymard JC, Falcon S, Calabro F, James N, Bodrogi I, Harper P, Wirth M, Berry W, Petrone ME, McKearn TJ, Noursalehi M, George M, Rozencweig M (2009) Multinational, double-blind, phase III study of prednisone and either satraplatin or placebo in patients with castrate-refractory prostate cancer progressing after prior chemotherapy: the SPARC trial. J Clin Oncol 27:5431–5438
Nakabayashi M, Sartor O, Jacobus S, Regan MM, McKearn D, Ross RW, Kantoff PW, Taplin ME, Oh WK (2008) Response to docetaxel/carboplatin-based chemotherapy as first- and second-line therapy in patients with metastatic hormone-refractory prostate cancer. BJU Int 101:308–312
Cabrespine A, Guy L, Khenifar E, Curé H, Fleury J, Penault-Llorca F, Kwiatkowski F, Barthomeuf C, Chollet P, Bay JO (2006) Randomized phase II study comparing paclitaxel and carboplatin versus mitoxantrone in patients with hormone-refractory prostate cancer. Urology 67:354–359
Ross RW, Beer TM, Jacobus S, Bubley GJ, Taplin ME, Ryan CW, Huang J, Oh WK, Prostate Cancer Clinical Trials Consortium (2008) A phase 2 study of carboplatin plus docetaxel in men with metastatic hormone-refractory prostate cancer who are refractory to docetaxel. Cancer 112:521–526
Cortes J, O’Shaughnessy J, Loesch D, Blum JL, Vahdat LT, Petrakova K, Chollet P, Manikas A, Diéras V, Delozier T, Vladimirov V, Cardoso F, Koh H, Bougnoux P, Dutcus CE, Seegobin S, Mir D, Meneses N, Wanders J, Twelves C, EMBRACE investigators (2011) Eribulin monotherapy versus treatment of physician’s choice in patients with metastatic breast cancer (EMBRACE): a phase 3 open-label randomised study. Lancet 377:914–923
Goel R, Lheureux S, Laurie SA, Halford RA, Jonker D, Chen EX, Keller D, Bourada V, Wang L, Doyle LA, Siu LL, Oza AM (2014) A phase I study of eribulin and gemcitabine in patients with advanced solid tumours. A study of the Princess Margaret Phase II Consortium. Ann Oncol 25(Suppl 4):IV156–IV157. Abstract 470P
Waller CF, Vynnychenko I, Bondarenko I, Shparyk Y, Hodge JP, Freeman A, Huber B, Lieberman R, Shelton MJ, Dave H (2015) An open-label, multicenter, randomized phase Ib/II study of eribulin mesylate administered in combination with pemetrexed versus pemetrexed alone as second-line therapy in patients with advanced nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer 16:92–99
Herbst RS, Baas P, Kim DW, Felip E, Perez-Gracia JL, Han JY, Molina J, Kim JH, Arvis CD, Ahn MJ, Majem M, Fidler MJ, de Castro G Jr, Garrido M, Lubiniecki GM, Shentu Y, Im E, Dolled-Filhart M, Garon EB (2016) Pembrolizumab versus docetaxel for previously treated, PD-L1-positive, advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (KEYNOTE-010): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 387:1540–1550
Borghaei H, Paz-Ares L, Horn L, Spigel DR, Steins M, Ready NE, Chow LQ, Vokes EE, Felip E, Holgado E, Barlesi F, Kohlhäufl M, Arrieta O, Burgio MA, Fayette J, Lena H, Poddubskaya E, Gerber DE, Gettinger SN, Rudin CM, Rizvi N, Crinò L, Blumenschein GR Jr, Antonia SJ, Dorange C, Harbison CT, Graf Finckenstein F, Brahmer JR (2015) Nivolumab versus docetaxel in advanced nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 373:1627–1639
Rittmeyer A, Barlesi F, Waterkamp D, Park K, Ciardiello F, von Pawel J, Gadgeel SM, Hida T, Kowalski DM, Dols MC, Cortinovis DL, Leach J, Polikoff J, Barrios C, Kabbinavar F, Frontera OA, De Marinis F, Turna H, Lee JS, Ballinger M, Kowanetz M, He P, Chen DS, Sandler A, Gandara DR, Group OAKS (2017) Atezolizumab versus docetaxel in patients with previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer (OAK): a phase 3, open-label, multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet 389:255–265
Acknowledgements
We thank all the patients and investigators who participated in this study. We would also like to thank Gresel Martinez of Eisai Inc., USA, Paloma Salazar of Eisai Ltd., UK. Editorial support, funded by Eisai Inc., was provided by Oxford PharmaGenesis Inc., Newtown, PA, USA. This study was funded by Eisai Inc.
Funding
Editorial support for this manuscript and styling for submission were provided by Oxford PharmaGenesis Inc, Newtown, PA, USA, and this support was funded by Eisai Inc., Woodcliff Lake, NJ, USA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Sanjay Goel: received funding for the study from Eisai Inc. Kirushna Kumar: received grant for conducting the study from Eisai. Christian Dittrich: received an unrestricted research grant from Eisai. Larisa Reyderman: employee of Eisai Inc. Joseph Aisner: received remuneration for DMC panels from Bristol-Myers Squibb and Merck-Serono. James Song: former employee of Eisai Inc. Daniel P. Petrylak: received consultant fees from AstraZeneca, Bayer, Bellicum, Dendreon, Exelixis, Ferring, Johnson and Johnson, Lilly, Medivation, Millennium, Pfizer, Roche Laboratories, and Sanofi Aventis (Tyme pharmaceuticals discontinued 1/31/17). Received grant support from Agensys, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Clovis, Dendreon, Eli Lilly, Endocyte, Genentech, Innocrin, Johnson and Johnson, Lilly, MedImmune, Medivation, Merck, Millennium, Novartis, Pfizer, Progenics, Roche Laboratories, Sanofi Aventis, and Sotio. Has ownership interest/investment in Bellicum, Tyme. Umang Swami and Minish Jain: no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goel, S., Swami, U., Kumar, K. et al. A phase 1b, multicenter, open-label, dose-finding study of eribulin in combination with carboplatin in advanced solid tumors and non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 84, 567–578 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-019-03877-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-019-03877-4