Abstract
Purpose
Idelalisib is a novel, potent inhibitor of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase delta (PI3Kδ), which is prominently expressed in cells of hematopoietic origin. Renal excretion plays a minor role in elimination of idelalisib in humans (~15 % of the dose is excreted in urine). This study evaluated the pharmacokinetics (PK) and safety of idelalisib and GS-563117 (its inactive primary metabolite) in subjects with severe renal impairment and healthy subjects.
Methods
Subjects with severe renal impairment were matched in age, sex, and body mass index with healthy subjects who had normal renal function. Each subject received a single oral dose of idelalisib at 150 mg, and safety assessments and PK analyses were performed.
Results
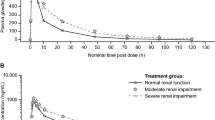
Compared with healthy subjects, the geometric least-squares mean ratio of area under the concentration–time curve from zero to last PK observation (AUClast), area under the concentration–time curve from zero to infinity (AUCinf), and maximum observed plasma concentration (C max) were 127, 127, and 105 % for idelalisib and 124, 124, and 96 % for GS-563117, respectively, in subjects with severe renal impairment.
Conclusions
There were no clinically relevant changes of idelalisib or GS-563117 PK in subjects with severe renal impairment versus matched healthy controls. No relevant relationships were identified between idelalisib or GS-563117 exposures and baseline creatinine clearance. Idelalisib dosing was generally well tolerated with most treatment-emergent adverse events and laboratory abnormalities assessed as grade 1 or 2 in severity. Accordingly, dose adjustments for idelalisib are not necessary in subjects with mild, moderate, or severe renal impairment.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Okkenhaug K, Vanhaesebroeck B (2003) PI3K in lymphocyte development, differentiation and activation. Nat Rev Immunol 3(4):317–330
Vanhaesebroeck B, Ali K, Bilancio A, Geering B, Foukas LC (2005) Signalling by PI3K isoforms: insights from gene-targeted mice. Trends Biochem Sci 30(4):194–204
Bernal A, Pastore RD, Asgary Z, Keller SA, Cesarman E, Liou HC, Schattner EJ (2001) Survival of leukemic B cells promoted by engagement of the antigen receptor. Blood 98(10):3050–3057
Lannutti BJ, Meadows SA, Herman SE, Kashishian A, Steiner B, Johnson AJ, Byrd JC, Tyner JW, Loriaux MM, Deininger M, Druker BJ, Puri KD, Ulrich RG, Giese NA (2011) CAL-101, a p110δ selective phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase inhibitor for the treatment of B-cell malignancies, inhibits PI3K signaling and cellular viability. Blood 117(2):591–594. doi:10.1182/blood-2010-03-275305
Herman SE, Lapalombella R, Gordon AL, Ramanunni A, Blum KA, Jones J, Zhang X, Lannutti BJ, Puri KD, Muthusamy N, Byrd JC, Johnson AJ (2011) The role of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-δ in the immunomodulatory effects of lenalidomide in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 117(16):4323–4327. doi:10.1182/blood-2010-11-315705
Hoellenriegel J, Meadows SA, Sivina M, Wierda WG, Kantarjian H, Keating MJ, Giese N, O’Brien S, Yu A, Miller LL, Lannutti BJ, Burger JA (2011) The phosphoinositide 3′-kinase delta inhibitor, CAL-101, inhibits B-cell receptor signaling and chemokine networks in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 118(13):3603–3612
Gopal AK, Kahl BS, de Vos S, Wagner-Johnston ND, Schuster SJ, Jurczak WJ, Flinn IW, Flowers CR, Martin P, Viardot A, Blum KA, Goy AH, Davies AJ, Zinzani PL, Dreyling M, Johnson D, Miller LL, Holes L, Li D, Dansey RD, Godfrey WR, Salles GA (2014) PI3Kδ inhibition by idelalisib in patients with relapsed indolent lymphoma. N Engl J Med 370(11):1008–1018. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1314583
Furman RR, Sharman JP, Coutre SE, Coutre SE, Cheson BD, Pagel JM, Hillmen P, Barrientos JC, Zelenetz AD, Kipps TJ, Flinn I, Ghia P, Eradat H, Ervin T, Lamanna N, Coiffier B, Pettitt AR, Ma S, Stilgenbauer S, Cramer P, Aiello M, Johnson DM, Miller LL, Li D, Jahn TM, Dansey RD, Hallek M, O’Brien SM (2014) Idelalisib and rituximab in relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med 370(11):997–1007. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1315226
Jin F, Robeson M, Zhou H, Kwan E, Ramananthan S (2013) Pharmacokinetics, metabolism and excretion of idelalisib [ASH abstract]. Blood 122(21):5570 (Online-only abstract published ahead of print December 6, 2013)
US Department of Health and Human Services/Food and Drug Administration/Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (2010) Guidance for industry: pharmacokinetics in patients with impaired hepatic function—study design, data analysis, and impact on dosing and labeling [draft]. www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/Guidances/UCM204959.pdf. Accessed 10 Dec 2014
Jin F, Zhou H, Holes L, Li X, Newcomb T, Dansey R, Ramanathan S (2104) Exposure-response of idelalisib, a novel Pi3kδ inhibitor, in the treatment of hematologic malignancies. Poster presented at: American Society of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 115th Annual Meeting. Atlanta, GA. Poster LBI-004
Acknowledgments
Editorial assistance was provided by Impact Communication Partners, Inc. Financial support for this study was provided by Gilead Sciences, Inc.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
This study was sponsored by Gilead Sciences, Inc. All authors are employees of Gilead Sciences, Inc., and may own stock or hold stock options in the company.
Ethical standard
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, F., Robeson, M., Zhou, H. et al. The pharmacokinetics and safety of idelalisib in subjects with severe renal impairment. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 76, 1133–1141 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-015-2898-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-015-2898-1